Abstract
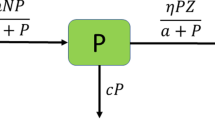
A plankton–herbivore state-dependent impulsive model with nonlinear impulsive functions and action threshold including population density and rate of change is proposed. Since the use of action threshold makes the model have complex phase set and pulse set, we adopt the Poincar\(\acute{\text{ e }}\) map as a tool to study its complex dynamics. The Poincar\(\acute{\text{ e }}\) map is defined on the phase set and its properties in different situations are analyzed. Furthermore, the periodic solution of model is discussed, including the existence and stability conditions of the order-1 periodic solution and the existence of the order-k (\(k\ge 2\)) periodic solutions. Compared with the fixed threshold in the existing literature, our results show that the use of action threshold is more practical, which is conducive to the sustainable development of population and makes people obtain more economic benefits. The analysis method used in this paper can study the complex dynamics of the model more comprehensively and deeply.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability statement
The author declares that the data supporting the results of this study are available in the article.
References
Mukhopadhyay, B., Bhattacharyya, R.: Role of gestation delay in a plankton-fish model under stochastic fluctuations. Math. Biosci. 215(1), 26–34 (2008)
Lv, Y., Pei, Y., Gao, S., Li, C.: Harvesting of a phytoplankton–zooplankton model. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 11(5), 3608–3619 (2010)
Zhang, T., Liu, X., Meng, X., Zhang, T.: Spatio-temporal dynamics near the steady state of a planktonic system. Comput. Math. Appl. 75(12), 4490–4504 (2018)
Yu, X., Yuan, S., Zhang, T.: Asymptotic properties of stochastic nutrient-plankton food chain models with nutrient recycling. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 34, 209–225 (2019)
Yu, X., Yuan, S., Zhang, T.: Survival and ergodicity of a stochastic phytoplankton–zooplankton model with toxin-producing phytoplankton in an impulsive polluted environment. Appl. Math. Comput. 347, 249–264 (2019)
Jia, D., Zhang, T., Yuan, S.: Pattern dynamics of a diffusive toxin producing phytoplankton–zooplankton model with three-dimensional patch. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 29, Article Number: 1930011 (2019)
Yan, S., Jia, D., Zhang, T., Yuan, S.: Pattern dynamics in a diffusive predator-prey model with hunting cooperations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 130, Article Number: 109428 (2020)
Peng, Y., Li, Y., Zhang, T.: Global bifurcation in a toxin producing phytoplankton–zooplankton system with prey-taxis. Nonlinear Anal. Real World Appl. 61 Article Number: 103326 (2021)
Fang, D., Pei, Y., Lv, Y., Chen, L.: Periodicity induced by state feedback controls and driven by disparate dynamics of a herbivore-plankton model with cannibalism. Nonlinear Dyn. 90(5), 1–16 (2017)
Tang, S., Tang, B., Wang, A., Xiao, Y.: Holling II predator-prey impulsive semi-dynamic model with complex poincaré map. Nonlinear Dyn. 81(3), 1575–1596 (2015)
Bainov, D.D., Simeonov, P.S.: Impulsive Differential Equation: Periodic Solutions and Applications. Pergamon Press Inc, Oxford (2015)
Li, D., Cheng, H., Liu, Y.: Dynamic analysis of beddington–deangelis predator-prey system with nonlinear impulse feedback control. Complexity (2019)
Wang, F., Zhang, X.: Adaptive finite time control of nonlinear systems under time-varying actuator failures. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Syst. 1–8 (2018)
Ciesielski, K.: On stability in impulsive dynamical systems. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Math. 52(84), 81–91 (2010)
Bonotto, E.M., Federson, M.: Limit sets and the Poincare–Bendixson theorem in impulsive semidynamical systems. J. Differ. Equ. 244(9), 2334–2349 (2008)
Baek, Hunki: The dynamics of a predator-prey system with state-dependent feedback control. Abstr. Appl. Anal. 2012, 1–17 (2012)
Yang, J., Tang, S.: Holling type II predator-prey model with nonlinear pulse as state-dependent feedback control. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 291, 225–241 (2016)
Liu, H., Cheng, H.: Dynamic analysis of a prey-predator model with state-dependent control strategy and square root response function. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2018(1), 63 (2018)
Li, T., Zhao, W.: Periodic solution of a neutral delay Leslie predator-prey model and the effect of random perturbation on the smith growth model. Complexity 2020, 15 (2020)
Li, Y., Li, Y., Liu, Y., Cheng, H.: Stability analysis and control optimization of a prey-predator model with linear feedback control. Discrete Dyn. Nat. Soc. 2018, 12 (2018)
Shi, Z., Cheng, H., Liu, Y., Li, Y.: A cydia pomonella integrated management predator-prey model with smith growth and linear feedback control. IEEE Access 7(1), 126066–126076 (2019)
Wang, Y., Cheng, H., Li, Q.: Dynamic analysis of wild and sterile mosquito release model with Poincaré map. Math. Biosci. Eng. 6(16), 7688–7706 (2019)
Shi, Z., Cheng, H., Wang, Y.: Optimization of an integrated feedback control for a pest management predator-prey model. Math. Biosci. Eng. 16(6), 7963–7981 (2019)
Xu, C., Yuan, S., Zhang, T.: Average break-even concentration in a simple chemostat model with telegraph noise. Nonlinear Anal. Hybrid Syst. 29, 373–382 (2018)
Qi, H., Leng, X., Meng, X., Zhang, T.: Periodic solution and ergodic stationary distribution of Seis dynamical systems with active and latent patients. Qual. Theory Dyn. Syst. 18(2), 347–369 (2019)
Zhang, T., Wang, J., Li, Y., Jiang, Z., Han, X.: Dynamics analysis of a delayed virus model with two different transmission methods and treatments. Adv. Differ. Equ. 2020(1), 1 (2020)
Wang, W., Lai, X.: Global stability analysis of a viral infection model in a critical case. Math. Biosci. Eng. 17, 1442–1449 (2020)
Li, D., Liu, Y., Cheng, H.: Dynamic complexity of a phytoplankton-fish model with the impulsive feedback control by means of Poincaré map. Complexity (2020)
Jiang, Z., Zhang, W., Zhang, J., Zhang, T.: Dynamical analysis of a Phytoplankton–Zooplankton system with harvesting term and Holling III functional response. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 28(13), 1850162 (2018)
Zhong, Z., Pang, L., Song, X.: Optimal control of phytoplankton-fish model with the impulsive feedback control. Nonlinear Dyn. 88(3), 2003–2011 (2017)
Yang, J., Tan, Y.: Effects of pesticide dose on Holling II predator-prey model with feedback control. J. Biol. Dyn. 12(1), 527–550 (2018)
Wang, Y., Cheng, H., Li, Q.: Dynamical properties of a herbivore-plankton impulsive semidynamic system with eating behavior. Complexity 2020, 1–15 (2020)
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (11371230), the SDUST Research Fund (2014TDJH102), Research on the basic theoretical framework and symmetry theory of soft robot dynamics(11872335).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, W., Zhang, T., Wang, Y. et al. Dynamic analysis of a plankton–herbivore state-dependent impulsive model with action threshold depending on the density and its changing rate. Nonlinear Dyn 107, 2951–2963 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-07022-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-021-07022-w