Abstract
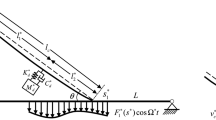
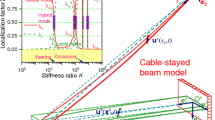
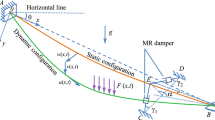
In this study, the large amplitude vibration of the cable-stayed beam subjected to external excitation is investigated. Emphasis is focused on the one-to-one resonant interaction between hybrid and hybrid/local modes, which may be activated in the veering and crossover regions. The Hamilton’s principle and multi-mode discretization are applied to obtain the discrete model governing the in-plane vibration of the cable-stayed beam. Then, the method of multiple scales is applied to solve the equation of motion, and the displacement of the cable-stayed beam and corresponding modulation equations are determined. In the following, the equilibrium solution of the modulation equations and the associated stability are examined to discuss the periodic motion of the cable-stayed beam. Whereas the shooting method is applied to investigate the dynamic solution to qualitatively illustrate the non-periodic motion. Numerical simulations are performed to verify the periodic solution and examine the nonlinear dynamics of the cable-stayed beam. Particular attention is placed on the chaotic dynamic of the cable-stayed beam in unstable region. It is shown that the equilibrium and dynamic solutions may undergo different bifurcations, i.e., Hopf, torus and cyclic-fold bifurcations.













Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
This assumption may conflict with the longitudinal deformability of the beam (Eq. (2)). However, it is limited to the tip of the beam, and the relevant effects on the displacement distribution of the beam should be very small.
References
Rega, G.: Nonlinear vibrations of suspended cables. Part I: modeling and analysis. Appl. Mech. Rev. 57, 443–478 (2004)
Geogakis, C.T., Taylor, C.A.: Nonlinear dynamics of cable stays. Part 1: sinusoidal cable support excitation. J. Sound Vib. 279, 619–639 (2005)
Warnitchai, P., Fujino, Y., Susumpow, T.: A non-linear dynamic model for cables and its application to a cable-structure system. J. Sound Vib. 187, 695–712 (1995)
Gattulli, V., Morandini, M., Paolone, A.: A parametric analytical model for non-linear dynamics in cable-stayed beam. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 31, 1281–1300 (2002)
Fujino, Y., Warnitchai, P., Pacheco, B.M.: An experimental and analytical study of autoparametric resonance in a 3DOF model of cable-stayed beam. Nonlinear Dyn. 4, 111–138 (1993)
Xia, Y., Fujino, Y.: Auto-parametric vibration of a cable-stayed-beam structure under random excitation. J. Eng. Mech. 132, 279–286 (2006)
Gattulli, V., Lepidi, M.: Nonlinear interactions in the planar dynamics of cable-stayed beam. Int. J. Solids Struct. 40, 4729–4748 (2003)
Gattulli, V., Lepidi, M., Macdonald, J.H.G., Taylor, A.C.: One-to-two global interaction in a cable-stayed beam observed through analytical, finite element and experimental models. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 40, 571–588 (2005)
Wei, M.H., Xiao, Y.Q., Liu, H.T.: Bifurcaton and chaos of a cable-beam coupled system under simultaneous internal and external resonances. Nonlinear Dyn. 67, 1969–1984 (2012)
Lenci, S., Ruzziconi, L.: Nonlinear phenomena in the single-mode dynamics of a cable-supported beam. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 19, 923–945 (2009)
Zhang, W., Cao, D.X.: Studies on bifurcation and chaos of a string-beam coupled system with two degress-of-freedom. Nonlinear Dyn. 45, 131–147 (2006)
Cong, Y., Kang, H., Guo, T.: Planar multimodal 1:2:2 internal resonance analysis of cable-stayed bridge. Mech. Syst. Signal Process. 120, 505–523 (2019)
Kang, H., Guo, T., Zhao, Y., Fu, W., Wang, L.: Dynamic modeling and in-plane 1:1:1 internal resonance analysis of cable-stayed bridge. Eur. J. Mech./A Solids 62, 94–109 (2017)
Lacarbonara, W., Rega, G., Nayfeh, A.H.: Resonant non-linear normal modes. Part I: analytical treatment for structural one-dimensional systems. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 38, 851–872 (2003)
Xu, Y.L., Yu, Z.: Vibration of inclined sag cables with oil dampers in cable-stayed bridges. J. Bridge Eng. 3, 194–203 (1998)
Rega, G., Srinil, N.: Nonlinear hybrid-mode resonant forced oscillations of sagged inclined cables at avoidances. J. Comput. Nonlinear Dyn. 2, 324–336 (2007)
Lacarbonara, W., Arafat, H.N., Nayfeh, A.H.: Non-linear interactions in imperfect beams at veering. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 40, 987–1003 (2005)
Srinil, N., Rega, G.: The effects of kinematic condensation on internally resonant forced vibrations of shallow horizontal cables. Int. J. Nonlinear Mech. 42, 180–195 (2007)
Gattulli, V., Lepidi, M.: Localization and veering in the dynamics of cable-stayed bridges. Comput. Struct. 85, 1661–1678 (2007)
Reddy, J.N.: Energy Principles and Variational Methods in Applied Mechanics, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York (2002)
Luongo, A., Zulli, D.: Mathematical Models of Beams and Cables. Wiley ISTE, New York (2013)
Wang, L., Zhang, X., Huang, S., Li, L.: Measured frequency for the estimation of cable force by vibration method. J. Eng. Mech. 141, 06014020-1-7 (2015)
Nayfeh, A.H., Balachandran, B.: Applied Nonlinear Dynamics. Wiley-Interscience, New York (1995)
Wang, L., Ma, J., Yang, M., Li, L., Zhao, Y.: Multimode dynamics of inextensional beams on the elastic foundation with two-to-one internal resonances. J. Appl. Mech. 80, 061016-1-11 (2013)
Rega, G., Lacarbonara, W., Nayfeh, A.H., Chin, C.M.: Multiple resonances in suspended cables: direct versus reduced-order models. Int. J. Non-linear Mech. 34, 901–924 (1999)
Wang, L., Zhao, Y.: Large amplitude motion mechanism and non-planar vibration character of stay cables subject to the support motions. J. Sound Vib. 327, 121–133 (2009)
Acknowledgements
The study was supported by Natural and Science Foundation of Hunan Province under Grant No. 2018JJ2029, Science and Technology Program of Ministry of Transport (2013318798320) and Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (Grant No. 19B192).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix
Appendix
The second-order nonlinear interaction coefficients of the modulation equations can be expressed as [14]:
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Peng, J., Zhang, X. et al. Nonlinear resonant response of the cable-stayed beam with one-to-one internal resonance in veering and crossover regions. Nonlinear Dyn 103, 115–135 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-06107-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-020-06107-2