Abstract
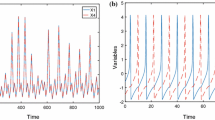
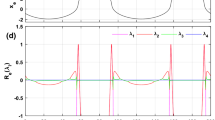
This paper addresses problem of synchronization of n-neurons which are electrically coupled to each other. Gap junction coupled chaotic FitzHugh–Nagumo (FHN) neurons and linearly coupled Hindmarsh–Rose (H–R) neurons are considered with each neuron subjected to external electrical stimulation. The neurons are assumed to be linked in a chain-like structure. It is shown that the suitable choice of coupling strength of gap junction is sufficient to meet out the synchronization condition. Simple stability analysis based on partial contraction approach is used to establish the exponential convergence of states of different neurons to each other. The conditions for complete synchronization are derived analytically for a general system having n-electrically coupled neurons. The advantage of the proposed approach lies in its simplicity and provides an alternative method of achieving synchronization. Further, in comparison with Lyapunov-based analysis, the formulation of error dynamics is avoided while establishing synchronizing conditions. Numerical simulations are shown for both FHN and Hindmarsh–Rose neurons separately to justify the effectiveness of the proposed approach to meet out synchronization requirements.










Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The system given in (12) represents auxiliary system for the actual system in (11) because replacement of \(\left( \xi _{i}, \eta _{i} \right) \) pair of states by \(\left( x_{i},y_{i} \right) \) pair results in actual system. In other words, actual system (11) represents one particular solution of auxiliary system in (12).
References
Ott, E., Grebogi, C., York, J.A.: Controlling chaos. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64(11), 1196–1199 (1990)
Jackson, E.A., Hubler, A.: Periodic entrainment of chaotic logistic map dynamics. Phys. D 44, 404–409 (1990)
Ogorzalek, M.J.: Taming chaos: Part II- control scheme via robust asymptotic feedback. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I 40(10), 700–706 (1993)
Femat, R., Alvarez, J., Castillo-Toledo, B., Gonzalez, J.: On robust chaos suppression in a class of no driven oscillators: application to the Chua’s circuit. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. 46, 1150–52 (1999)
Femat, R., Jauregui-Ortiz, R., Solys-Perales, G.: A chaos based communication scheme via robust asymptotic feedback. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. 48(10), 1161–1169 (2001)
Isidori, A.: Non-linear Control Systems. Springer, Berlin (1995)
Jayaram, A., Tadi, M.: Synchronization of chaotic systems based on SDRE method. Chaos Solitons Fractals 28(3), 707–715 (2006)
Sharma, B.B., Kar, I.N.: Parametric convergence and control of chaotic system using adaptive feedback linearization. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40, 1475–1483 (2009)
Yassen, M.T.: Controlling chaos and synchronization for new chaotic system using linear feedback control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 26, 913–920 (2005)
Pecora, L.M., Carroll, T.L.: Synchronization in chaotic systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 821–824 (1990)
Hu, J., Chen, S., Chen, L.: Adaptive control for anti-synchronization of Chua’s chaotic system. Phys. Lett. A 339, 455–460 (2005)
Li, D., Lu, J.A., Wu, X.: Linearly coupled synchronization of the unified chaotic systems and the Lorenz systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23, 79–85 (2005)
Grassi, G., Mascolo, S.: Nonlinear observer design to synchronize hyperchaotic systems via a scalar signal. IEEE Trans. Cric. Syst. I 44(10), 1011–1014 (1997)
Liao, T.L., Huang, N.S.: An observer based approach for chaotic synchronization and secure communication. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I 46(9), 1144–1149 (1999)
Boutayeb, M., Darouach, M., Rafaralahy, H.: Generalized state-space observers for chaotic synchronization with applications to secure communication. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. I 49(3), 345–349 (2002)
Park, J.H.: Stability criterion for synchronization of linearly coupled unified chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 23, 1319–1325 (2005)
Wang, Y., Guan, Z.H., Wang, H.O.: Feedback and adaptive control for the synchronization of Chen system via a single variable. Phys. Lett. A 312, 34–40 (2003)
Chen, M., Han, Z.: Controlling and synchronizing chaotic Genesio system via nonlinear feedback control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 17, 709–716 (2003)
Lu, J., Zhou, T., Zhang, S.: Chaos synchronization between linearly coupled chaotic systems. Chaos Solitons Fractals 14, 529–541 (2002)
Huang, X., Cao, J., Li, Y.: Takagi-Sugeno fuzzy-model-based control of hyperchaotic Chen system with norm-bounded uncertainties. J. Syst. Control Eng. 224(03), 223–234 (2010)
Pai, M.C.: Robust synchronization of chaotic systems using adaptive sliding mode output feedback control. J. Syst. Control Eng. 226(05), 598–605 (2012)
Mirollo, R.E., Strogatz, S.H.: Synchronization of pulse-coupled biological oscillators. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 50, 1645–1662 (1990)
Nischwitz, A., Glunder, H.: Local lateral inhibition-a key to spike synchronization. Biol. Cyber-net 73, 389–400 (1995)
Bennett, M.V.L., Verselis, V.K.: Biophysics of gap junction. Seminars Cell Biol. 3, 29–47 (1992)
Baigent, S., Stark, J., Warner, A.: Modeling the effect of gap junction nonlinearities in systems of coupled cells. J. Theor. Biol. 186, 223–239 (1997)
Baigent, S., Stark, J., Warner, A.: Convergent dynamics of two cells coupled by a nonlinear gap junction. Nonlinear Anal. 47, 257–268 (2001)
Baigent, S.: Cells coupled by voltage-dependent gap junctions: the asymptotic dynamical limit. Biosystems 68, 213–222 (2003)
Thompson, C.J., Bardos, D.C., Yang, Y.S., Joyner, K.H.: Nonlinear cable model for cells exposed to electric fields I. Chaos Solitons Fractals 10(11), 1825–1842 (1999)
Shuai, J.W., Durand, D.M.: Phase synchronization in two coupled chaotic neurons. Phys. Lett. A 264, 289–297 (1999)
Wang, J., Bin, D., Tsang, K.M.: Chaotic synchronization of neuron coupled with gap junction under external electrical stimulation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 22, 469–476 (2004)
Bin, D., Jiang, W., Xiangyang, F.: Synchronizing two coupled chaotic neurons in external electrical stimulation using backstepping control. Chaos Solitons Fractals 29, 182–189 (2006)
Che, Y.Q., Wang, J., Zhou, S.S., Bin, D.: Robust synchronization control of coupled chaotic neurons under external electrical stimulation. Chaos Solitons Fractals 40, 1333–1342 (2009)
Yu, H., Wang, J., Liu, C., Deng, B., Wei, X.: Vibrational resonance in excitable neuronal systems. Chaos (2011). doi:10.1063/1.3644390
Yu, H., Wang, J., Deng, B., Wei, X., Wong, Y.K., Chan, W.L., Tsang, K.M.: Chaotic phase synchronization in small-world networks of bursting neurons. Chaos 21, 013127 (2011). doi:10.1063/1.3565027
Yang, D.: Self-synchronization of coupled chaotic FitzHugh–Nagumo systems with unreliable communication links. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18(10), 2783–2789 (2013)
Ciszak, M., Euzzor, S., Gelrude, A., Tito, F., Meucci, R.: Noise and coupling induced synchronization in a network of chaotic neurons. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 18(4), 938–945 (2013)
Iqbal, M., Rehan, M., Khaliq, A., Rehman, S.U., Hong, K.S.: Synchronization of coupled different chaotic FitzHugh–Nagumo neurons with unknown parameters under communication-direction-dependent coupling. Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 2014, 1–12 (2014)
Sharma, B.B., Kar, I.N.: Observer-based synchronization scheme for a class of chaotic systems using contraction theory. Nonlinear Dyn. 63(3), 429–445 (2011)
Aminzarey, Z., Sontag, E.D.: Contraction methods for nonlinear systems: A brief introduction and some open problems. IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, pp. 3835–3847 (2014)
Aylward, E.M., Parrilo, P.A., Slotine, J.J.E.: Stability and robustness analysis of nonlinear systems via contraction metrics and sos programming. Automatica 44(8), 2163–2170 (2008)
Angeli, D.: A Lyapunov approach to incremental stability properties. IEEE Trans. Aut. Control 47(3), 410–421 (2002)
Fromian, V., Scorletti, G., Ferreres, G.: Nonlinear performance of a PI controlled missile: an explanation. Int. J. Robust Nonlinear Control 9(8), 485–518 (1999)
Pecora, L.M., Carroll, T.L.: Master stability functions for synchronized coupled systems. Phys. Rev. Lett. 80(10), 2109–2112 (1998)
Heagy, J.F., Carroll, T.L., Pecora, L.M.: Synchronous chaos in coupled oscillator systems. Phys. Rev. E 50(3), 1874–1885 (1994)
Wang, W., Slotine, J.J.E.: On partial contraction analysis for coupled nonlinear oscillators. Biol. Cybern. 92, 1 (2004)
Sanjaya, M., Mamat, M., Salleh, Z., Mohd, I.: Bidirectional chaotic synchronization of Hindmarsh–Rose neuron model. Appl. Math. Sci. 5(54), 2685–2695 (2011)
Linaro, D., Righero, M., Biey, M., Storace, M.: Synchronization properties in networks of Hindmarsh–Rose neurons and their PWL approximations with linear symmetric coupling, IEEE international symposium on circuits and systems, pp. 1685–1688 (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Handa, H., Sharma, B.B. Synchronization of a set of coupled chaotic FitzHugh–Nagumo and Hindmarsh–Rose neurons with external electrical stimulation. Nonlinear Dyn 85, 1517–1532 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2776-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11071-016-2776-3