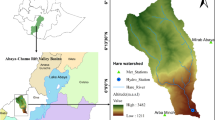
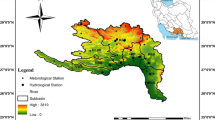
Abstract
Drought analysis is important for early warning of drought events in arid and semiarid regions. Reliance on a single variable or index is not adequate to conduct a comprehensive assessment of drought risk. Therefore, the use of multivariate drought indices can provide reliable information to assess drought characteristics. This study proposes a new multivariate drought index based on the combination of effective precipitation and runoff variables. The copula function was used to derive the joint distribution of effective precipitation and runoff. The new index, named effective precipitation runoff index (EPRI), is developed by using observed hydro-meteorological time series data collected from the Northeastern region of Iraq. This procedure can be considered as an approach that enables a comprehensive assessment of different types of drought, which can be seamlessly compared with the output of standardized precipitation index (SPI), standardized runoff index (SRI) and standardized effective precipitation index (SEPI). Based on the results of goodness-of-fit test, Clayton copula was selected as the best suitable copula for constructing the EPRI. It was found that the EPRI is approximately high correlated with SEPI and SRI indices, which indicates the reliability of the modeled EPRI index for monitoring drought.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Balasmeh O, Babbar R, Karmaker T (2020) A hybrid drought index for drought assessment in Wadi Shueib catchment area in Jordan. J Hydroinf 22(4):937–956. https://doi.org/10.2166/hydro.2020.038
Al-Timimi YK, Osamah AO (2016) Comparative study of four meteorological drought indices in Iraq. IOSR J Appl Phys 8(5):76–84. https://doi.org/10.9790/4861-0805037684
Awchi TA, Jasim AI (2017) Rainfall data analysis and study of meteorological draught in Iraq for the period 1970–2010. Tikrit J Eng Sci 24(1):110–121
Barker LJ, Hannaford J, Chiverton A, Svensson C (2016) From meteorological to hydrological drought using standardised indicators. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci Discuss 20:2483–2505. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-2483-2016
Bateni MM, Behmanesh J, Michele CD, Bazrafshan J, Rezaiem H (2018) Composite agrometeorological drought index accounting for seasonality and autocorrelation. J Hydrol Eng 23(6):04018020. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001654
Bayissa Y, Maskey S, Tadesse T, Andel SJ, Moges S, Griensven A, Solomatine D (2018) Comparison of the performance of six drought indices in characterizing historical drought for the upper Blue Nile Basin. Ethiop Geosci 8(3):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences8030081
Bazrafshan J, Hejabi S, Rahimi J (2014) Drought monitoring using the multivariate standardized precipitation index (MSPI). Water Resour Manag 28:1045–1060. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0533-2
Bazrafshan J, Nadi M, Ghorbani K (2015) Comparison of empirical copula-based joint deficit index (JDI) and multivariate standardized precipitation index (MSPI) for drought monitoring in Iran. Water Resour Manag 29:2027–2044. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-015-0926-x
Bos MG, Kselik RAL, Allen RG (2009) Water requirements for irrigation and the environment. Springer, Dordrecht
Bruce BW, Prairie JR, Maupin MA, Dodds JR, Eckhardt DW, Ivahnenko TI, Matuska PJ, Evenson EJ, Harrison AD (2019) Comparison of U.S. Geological survey and bureau of reclamation water-use reporting in the colorado river Basin. U.S. Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 5021, 41. https://doi.org/10.3133/sir20185021
Byun HR, Wilhite DA (1999) Daily quantification of drought severity and duration. J Clim 5:1181–1201
Cahoon JE, Yonts CD, Melvin SR (1992) G92-1099 Estimating Effective Rainfall. Historical Materials from University of Nebraska-Lincoln Extension. 1198. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/extensionhist/1198
Cheraghalizadeh M, Ghameshlou AN, Bazrafshan J, Bazrafshan O (2018) A copula-based joint meteorological–hydrological drought index in a humid region (Kasilian basin, North Iran). Arab J Geosci 11:300. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-018-3671-7
Dastane NG (1978) Effective rainfall in irrigated agriculture. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper, No.25, Rome, Italy
Dehghani M, Saghafian B, Zargar M (2019) Probabilistic hydrological drought index forecasting based on meteorological drought index using Archimedean copulas. Hydrol Res 50(5):1230–1250. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2019.051
Dogan S, Berktay A, Singh VP (2012) Comparison of multi-monthly rainfall-based drought severity indices, with application to semi-arid Konya closed basin, Turkey. J Hydrol 470–471:255–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.09.003
Ebrahimpour M, Rahimi J, Nikkhah A, Bazrafshan J (2014) Monitoring agricultural drought using the standardized effective precipitation index. J Irrig Drain Eng. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0000771
Evkaya O, Yozgatligil C, Selcuk-Kestel AS (2019) Drought analysis using copula approach: a case study for Turkey. Commun Stat Case Stud Data Anal Appl 5(3):243–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/23737484.2019.1635923
Faridatul MI, Ahmed B (2020) Assessing agricultural vulnerability to drought in a heterogeneous environment: a remote sensing-based approach. Remote Sens 12:3363. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs12203363
Feng K, Su X, Zhang G, Javed T, Zhang Z (2020) Development of a new integrated hydrological drought index (SRGI) and its application in the Heihe River Basin, China. Theoret Appl Climatol 141:43–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-020-03184-6
Gupta V, Jain MK, Singh VP (2020) Multivariate modeling of projected drought frequency and hazard over India. J Hydrol Eng 25(4):04020003. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0001893
Hameed M, Ahmadalipour A, Moradkhani H (2018) Apprehensive drought characteristics over Iraq: results of a multidecadal spatiotemporal assessment. J Geosci 8(58):1–16
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A (2013) Multivariate standardized drought index: a parametric multi-index model. Adv Water Resour 57:12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advwatres.2013.03.009
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A (2014) A nonparametric multivariate multi-index drought monitoring framework. J Hydrometeorol 15:89–101. https://doi.org/10.1175/JHM-D-12-0160.1
Hao Z, Singh VP (2015) Drought characterization from a multivariate perspective: a review. J Hydrol 527:668–678. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2015.05.031
Hasan IF, Saeed YN (2020) Trend analysis of hydrological drought for selected rivers in Iraq. Tikrit J Eng Sci 27(1):51–57
Homdee T, Pongput K, Kanae S (2016) A comparative performance analysis of three standardized climatic drought indices in the Chi River basin, Thailand. Agric Nat Resour 50:211–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.anres.2016.02.002
Huang S, Huang Q, Leng G, Cuang J (2016) A hybrid index for characterizing drought based on a nonparametric kernel estimator. J Appl Meteorol Climatol 55:1377–1389. https://doi.org/10.1175/JAMC-D-15-0295.1
Jiménez-Donaire MP, Tarquis A, Giráldez JV (2020) Evaluation of a combined drought indicator and its potential for agricultural drought prediction in southern Spain. Nat Hazards Earth Syst Sci 20:21–33. https://doi.org/10.5194/nhess-20-21-2020
Kamruzzaman M, JaepilC M-W, Syewoon H (2019) Comparative evaluation of standardized precipitation index (SPI) and effective drought index (EDI) for meteorological drought detection over Bangladesh. J Korean Soc Agric Eng 61(1):145–159. https://doi.org/10.5389/KSAE.2019.61.1.145
Kao SC, Govindaraju RS (2010) A copula-based joint deficit index for droughts. J Hydrol 380:121–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.10.029
Khatiwada KR, Pandey VP (2019) Characterization of hydro-meteorological drought in Nepal Himalaya: a case of Karnali River Basin. Weather Clim Extremes 26:100239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wace.2019.100239
Kim S, Parhi P, Jun H, Lee J (2018) Evaluation of drought severity with a Bayesian network analysis of multiple drought indices. J Water Resour Plan Manag 144(1):05017016. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)WR.1943-5452.0000804
Liu Y, Zhu Y, Ren L, Yong B, Singh VP, Yuan F, Jiang S, Yang X (2019) On the mechanisms of two composite methods for construction of multivariate drought indices. Sci Total Environ 647:981–991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.07.273
Lloyd-Hughes B, Saunders MA (2002) A drought climatology for Europe. Int J Climatol 22(13):1571–1592. https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.846
Marek G, Gowda P, Marek T, Auvermann B, Evett S, Colaizzi P, Brauera D (2016) Estimating preseason irrigation losses by characterizing evaporation of effective precipitation under bare soil conditions using large weighing Lysimeters. Agric Water Manag 169:115–128
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1993) The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, 179–183. Boston: American Meteorological Society, Anaheim, CA
McKee TB, Doesken NJ, Kleist J (1995) Drought Monitoring with Multiple Time Scales. In: 9th Conference on applied climatology. American Meteorological Society, Dallas, Texas
Mishra AK, Singh VP (2010) A review of drought concepts. J Hydrol 391(1):202–216
Nalbantis I, Tsakiris G (2009) Assessment of hydrological drought revisited. Water Resour Manage 23(5):881–897
Osuch M, Romanowicz RJ, Lawrence D, Wong WK (2016) Trends in projections of standardized precipitation indices in a future climate in Poland. Hydrol Earth Syst Sci 20:1947–1969. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-20-1947-2016
Ozkaya A, Zerberg YA (2019) 40-Year analysis of the hydrological drought index for the tigris Basin Turkey. J Water 11(4):657. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11040657
Palmer WC (1965) Meteorological droughts. U.S. Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau, Research Paper No.45, p 58
Páscoa P, Gouveia CM, Russo A, Trigo RM (2017) Drought trends in the Iberian Peninsula over the last 112 years. Adv Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4653126
Pathak AA, Channaveerappa DBM (2016) Comparison of two hydrological drought indices. Persp Sci 8:626–628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pisc.2016.06.039
Rahman MM, Islam MO, Hasanuzzaman M (2008) Study of effective rainfall for irrigated agriculture in South-Eastern Part of Bangladesh. World J Agric Sci 4(4):453–457
Rasheed AM (2010) Analysis of rainfall drought periods in the north of Iraq using standard precipitation index (SPI). Al-Rafidain Eng J 18(2):60
Saleh DK (2010) Stream gage descriptions and streamflow statistics for sites in the Tigris River and Euphrates River Basins, Iraq: U.S. Geological Survey Data Series 540, 146
Shiru MS, Shahid S, Alias N, Chung E-S (2018) Trend analysis of droughts during crop growing seasons of Nigeria. Sustainability 10:871. https://doi.org/10.3390/su10030871
Shukla S, Wood AW (2008) Use of a standardized runoff index for characterizing hydrologic drought. Geophys Res Lett 35:L02405
Sklar A (1959) Fonctions de Répartition à n Dimensions et Leurs Marges. Publications De L’ Institut Statistique De L’ Université De Paris 8:229–231
Smith M (1992) CROPWAT. A computer program for irrigation planning and management. FAO Irrigation and Drainage Paper 46. Rome, Italy
Svoboda M, Hayes M, Wood D (2012) Standardized Precipitation Index User Guide. World Meteorological Organization, (WMO-No. 1090), Geneva
Tigkas D, Vangelis H, Tsakiris G (2019) Drought characterisation based on an agriculture-oriented standardized precipitation index. Theoret Appl Climatol 135:1435–1447. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-018-2451-3
Tsakiris G, Vangelis H (2005) Establishing a drought index incorporating evapotranspiration. Eur Water 9(10):3–11
Vicente-Serrano SM, Beguería S, López-Moreno JI (2010) A multiscalar drought index sensitive to global warming: the standardized precipitation evapotranspiration index. J Clim 23(7):1696–1718
Wang F, Wang Z, Yang H, Di D, Zhao Y, Liang Q (2020) A new copula-based standardized precipitation evapotranspiration streamflow index for drought monitoring. J Hydrol 585:124793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2020.124793
Xu K, Qin G, Niu J, Wu C, Hu BX, Huang G, Wang P (2019) Comparative analysis of meteorological and hydrological drought over the Pearl River basin in southern China. Hydrol Res 50(1):301. https://doi.org/10.2166/nh.2018.178
Zhang T, Su X, Feng K (2021) The development of a novel nonstationary meteorological and hydrological drought index using the climatic and anthropogenic indices as covariates. Sci Total Environ 786:147385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.147385
Zhong F, Cheng Q, Wang P (2020) Meteorological drought, hydrological drought, and NDVI in the Heihe River Basin, Northwest China: evolution and propagation. Adv Meteorol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/2409068
Zuo D, Hou W, Wu H, Yan P, Zhang Q (2021) Feasibility of calculating standardized precipitation index with short-term precipitation data in china. Atmosphere 12:603. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos12050603
Funding
No funding was received to assist with the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, I.F., Abdullah, R. Multivariate index for monitoring drought (case study, Northeastern of Iraq). Nat Hazards 116, 3817–3837 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-023-05837-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-023-05837-x