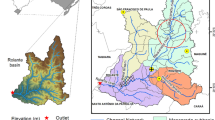
Abstract
Typhoon Aere swept over Taiwan with heavy rain, which induced huge discharge in the Danshuei River in August 2004. The flood in the Danshuei River intruded Sanchung through a culvert that was under construction. The deluge inundated thousands of premises and resulted in severe damage. This study reconstructs the event scenario using hydrologic and hydraulic methods to analyse the causes of the disaster. We integrated the radar rainfall estimations and rain gauge observations to recreate the temporal and spatial varied precipitation inputs; estimated the influent volume from the culvert using hydrologic equations; and simulated the flood dynamic within the study area during the event with a coupled overland and sewer flow model. The evidence showed that both the rainfall and the culvert flow contributed similar flood volume to the study area, but culvert discharge concentrated at single location within short time period such that the local drainage system could not cope with and notable damage was incurred.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CWB:
-
Central Weather Bureau, Taiwan
- EOC:
-
Emergency Operation Centre
- NCDR:
-
National Center for Disaster Reduction, Taiwan
- QPESUMS:
-
Quantitative Precipitation Estimation and Segregation Using Multiple Sensors
- SWMM:
-
Storm Water Management Model
- TACE:
-
Taiwan Association of Civil Engineer
- TAHE:
-
Taiwan Association of Hydraulic Engineer
- TIS:
-
Tongan Interception Station
- TPS:
-
Tongan Pumping Station
- UIM:
-
Urban Inundation Model
- WRA:
-
Water Resource Agency, Taiwan
- Z–R:
-
Reflectivity–Rainfall Relationship
References
Abbott MB (1998) Computational hydraulics. Ashgate Publishing Company, Burlington
Apirumanekul C, Mark O (2001) Modelling of urban flooding in Dhaka City. In: 4th DHI software conference, Helsingør, Denmark
Aryal RK, Jinadasa HKPK, Furumai H et al (2005) A long-term suspended solids runoff simulation in a highway drainage system. Water Sci Technol 52(5):159–167
Bouteligier R, Vaes G, Berlamont J et al (2005) Advection-dispersion modelling tools: what about numerical dispersion? Water Sci Technol 52(3):19–27
Carr RS, Smith GP (2006) Linking of 2D and Pipe hydraulic models at fine spatial scales. In: 7th International conference on urban drainage modelling and the 4th international conference on water sensitive urban design, Melbourne, Australia
Chen AS, Hsu MH, Chen TS et al (2005) An integrated inundation model for highly developed urban areas. Water Sci Technol 51(2):221–229
Chen AS, Hsu MH, Teng WH et al (2006) Establishing the database of inundation potential in Taiwan. Nat Hazards 37(1–2):107–132
Chu TK, Chen CJ, Cheng BL et al (2007) The services and applications of the extreme weather monitor system QPESUMS (in Chinese). Natl Geogr Inf Syst Commun (61):15–26. http://ngis.moi.gov.tw/TheFiles/journal/61/pdf/61-main1.pdf
Dey AK, Kamioka S (2006) An integrated modeling approach to predict flooding on urban basin. In: 7th International conference on urban drainage modelling and the 4th international conference on water sensitive urban design, Melbourne, Australia
Djordjevic S, Prodanovic D, Maksimovic C et al (2005) SIPSON—Simulation of interaction between pipe flow and surface overland flow in networks. Water Sci Technol 52(5):275–283
Ellis JH, Mcbean EA, Mulamoottil G (1982) Design of dual drainage systems using swmm. J Hydraul Div-Asce 108(10):1222–1227
Habib E, Krajewski WF (2002) Uncertainty analysis of the TRMM ground-validation radar-rainfall products: application to the TEFLUN-B field campaign. J Appl Meteorol 41(5):558–572
Heeringen K-Jv, Verwey A, Melger E (2002) Dutch approach to high speed urban drainage modeling with SOBEK. In: Urban drainage 2002, proceedings of the ninth international conference on urban drainage, Portland, Oregon, USA
Hernebring C, Jonsson LE, Thoren UB et al (2002) Dynamic online sewer modelling in Helsingborg. Water Sci Technol 45(4–5):429–436
Hsu MH, Chang TJ, Teng WH et al. (1999) The inundation potential analyses for Taipei City and Taipei County, National Science and Technology Program Hazards Mitigation Taipei, Taiwan
Huber WC, Dickinson RE (1988) Storm water management model. User’s Manual Ver. IV. U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, Athens Georgia, U.S.A.
Ji Z (1998) General hydrodynamic model for sewer/channel network systems. J Hydraul Eng-Asce 124(3):307–315
Linsley RK (1992) Water resources engineering. McGraw-Hill, New Jersey, p 841
Mays LW (2000) Water resources engineering. Wiley, New Jersey, p 780
Morin E, Krajewski WF, Goodrich DC et al (2003) Estimating rainfall intensities from weather radar data: the scale-dependency problem. J Hydrometeorol 4(5):782–797
Nasello C, Tucciarelli T (2005) Dual multilevel urban drainage model. J Hydraul Eng-Asce 131(9):748–754
Phillips BC, Yu S, Thompson GR et al. (2005) 1D and 2D modelling of urban drainage systems using XP-SWMM and Tuflow. In: 10th international conference on urban drainage, Copenhagen, Denmark
Rossman LA, Dickinson RE, Schade T et al. (2005) SWMM5: the USEPA’s newest tool for urban drainage analysis. In: 10th international conference on urban drainage, Copenhagen, Denmark
Schmitt TG, Thomas M, Ettrich N (2005) Assessment of urban flooding by dual drainage simulation model RisUrSim. Water Sci Technol 52(5):257–264
Smith D, Li J, Banting D (2005) A PCSWMM/GIS-based water balance model for the Reesor Creek watershed. Atmos Res 77(1–4):388–406
Spry RB and Zhang S (2006) Modelling of drainage systems and overland flowpaths at catchment scales In: 7th International conference on urban drainage modelling and the 4th international conference on water sensitive urban design, Melbourne, Australia
TACE, TAHE (2004) The investigation report for the flood event in the Sanchung area during Typhoon Aere (in Chinese), Taiwan Association of Civil Engineer, Taiwan Association of Hydraulic Engineer
WRA (2004) The report of Danshuei River flood event during Typhoon Aere (in Chinese), Water Resource Agency
Xin LY, Reuter G, Larochelle B (1997) Reflectivity-rain rate relationships for convective rainshowers in Edmonton—research note. Atmos-Ocean 35(4):513–521
Zhang J, Howard K, Gourley JJ (2005) Constructing three-dimensional multiple-radar reflectivity mosaics: examples of convective storms and stratiform rain echoes. J Atmos Oceanic Technol 22(1):30–42
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely appreciate Taipei City Government, Taipei County Government, Sanchung City Council, Central Weather Bureau and the Water Resource Agency, for providing the precious information and help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, A.S., Hsu, MH., Huang, CJ. et al. Analysis of the Sanchung inundation during Typhoon Aere, 2004. Nat Hazards 56, 59–79 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9549-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-010-9549-y