Abstract
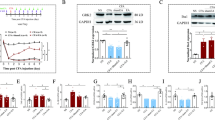
Electroacupuncture (EA) effectively improves arthritis-induced hyperalgesia and allodynia by repressing spinal microglial activation, which plays a crucial role in pain hypersensitivity following tissue inflammation. However, the mechanism by which EA suppresses spinal microglial activation in monoarthritis (MA) remains unclear. In the present study, a rat model of MA was established through unilateral ankle intra-articular injection of complete Freund’s adjuvant (CFA). The relationship among P2Y12 receptor (P2Y12R) expression, spinal microglial activation, and EA analgesia was investigated using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT‒PCR), western blotting, immunofluorescence (IF), and behavioral testing. The results found that EA treatment at the ipsilateral “Huantiao” (GB30) and “Yanglingquan” (GB34) acupoints markedly attenuated pain and spinal microglia M1 polarization in MA rats. In particular, P2Y12R expression was significantly increased at the mRNA and protein levels in the spinal dorsal horn in MA rats, whereas EA treatment effectively repressed the MA-induced upregulation of P2Y12R. IF analysis further revealed that most P2Y12R was expressed in microglia in the spinal dorsal horn. Pharmacological inhibition of P2Y12R by its antagonist (AR-C69931MX) decreased MA-induced spinal microglial activation and subsequent proinflammatory cytokine production. Consequently, AR-C69931MX significantly intensified the anti-pain hypersensitive function of EA in MA rats. Taken together, these results demonstrate that EA alleviates MA-induced pain by suppressing P2Y12R-dependent microglial activation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
He J, Su X, Xie W (2020) MiR-582-3p alleviates osteoarthritis progression by targeting YAP1. Mol Immunol 128:258–267
Creamer P (2000) Osteoarthritis pain and its treatment. Curr Opin Rheumatol 12:450–455
Shan S, Qi-Liang MY, Hong C, Tingting L, Mei H, Haili P, Yan-Qing W, Zhi-Qi Z, Yu-Qiu Z (2007) Is functional state of spinal microglia involved in the anti-allodynic and anti-hyperalgesic effects of electroacupuncture in rat model of Monoarthritis? Neurobiol Dis 26:558–568
Berman BM, Lao L, Langenberg P, Lee WL, Gilpin AM, Hochberg MC (2004) Effectiveness of acupuncture as adjunctive therapy in osteoarthritis of the knee: a randomized, controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 141:901–910
Schaible HG, Ebersberger A, Von Banchet GS (2002) Mechanisms of pain in arthritis. Ann N Y Acad Sci 966:343–354
Watkins LR, Milligan ED, Maier SF (2001) Glial activation: a driving force for pathological pain. Trends Neurosci 24:450–455
Fusco M, Skaper SD, Coaccioli S, Varrassi G, Paladini A (2017) Degenerative Joint diseases and Neuroinflammation. Pain Practice: The Official Journal of World Institute of Pain 17:522–532
Gensel JC, Kigerl KA, Mandrekar-Colucci SS, Gaudet AD, Popovich PG (2012) Achieving CNS axon regeneration by manipulating convergent neuro-immune signaling. Cell Tissue Res 349:201–213
Sun S, Cao H, Han M, Li TT, Zhao ZQ, Zhang YQ (2008) Evidence for suppression of electroacupuncture on spinal glial activation and behavioral hypersensitivity in a rat model of monoarthritis. Brain Res Bull 75:83–93
Sagar DR, Ashraf S, Xu L, Burston JJ, Menhinick MR, Poulter CL, Bennett AJ, Walsh DA, Chapman V (2014) Osteoprotegerin reduces the development of pain behaviour and joint pathology in a model of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73:1558–1565
Li J, Wei Y, Zhou J, Zou H, Ma L, Liu C, Xiao Z, Liu X, Tan X, Yu T, Cao S (2022) Activation of locus coeruleus-spinal cord noradrenergic neurons alleviates neuropathic pain in mice via reducing neuroinflammation from astrocytes and microglia in spinal dorsal horn. J Neuroinflamm 19:123
Fung KP, Lau SP (1984) Acupuncture. Lancet 2:45
Du SQ, Wang XR, Zhu W, Ye Y, Yang JW, Ma SM, Ji CS, Liu CZ (2018) Acupuncture inhibits TXNIP-associated oxidative stress and inflammation to attenuate cognitive impairment in vascular dementia rats. CNS Neurosci Ther 24:39–46
Ulett GA, Han S, Han JS (1998) Electroacupuncture: mechanisms and clinical application. Biol Psychiatry 44:129–138
Li X, He F, Tuo X, Qiu Y, Guo J, Wu Y, Meng X, Yang Z (2022) Electroacupuncture ameliorates peptic ulcer disease in association with gastroduodenal microbiota modulation in mice. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 12:935681
Mi WL, Mao-Ying QL, Wang XW, Li X, Yang CJ, Jiang JW, Yu J, Wang J, Liu Q, Wang YQ, Wu GC (2011) Involvement of spinal neurotrophin-3 in electroacupuncture analgesia and inhibition of spinal glial activation in rat model of monoarthritis. J Pain 12:974–984
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Tsuda M, Miyata H, Ueda K, Kohsaka S, Inoue K (2008) P2Y12 receptors in spinal microglia are required for neuropathic pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neuroscience: Official J Soc Neurosci 28:4949–4956
Burnstock G (2006) Purinergic P2 receptors as targets for novel analgesics. Pharmacol Ther 110:433–454
Inoue K, Tsuda M (2021) Nociceptive signaling mediated by P2X3, P2X4 and P2X7 receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 187:114309
Chen XM, Xu J, Song JG, Zheng BJ, Wang XR (2015) Electroacupuncture inhibits excessive interferon-gamma evoked up-regulation of P2X4 receptor in spinal microglia in a CCI rat model for neuropathic pain. Br J Anaesth 114:150–157
Xu J, Chen XM, Zheng BJ, Wang XR (2016) Electroacupuncture Relieves Nerve Injury-Induced Pain Hypersensitivity via the Inhibition of Spinal P2X7 Receptor-Positive Microglia. Anesth Analg 122:882–892
Wu Q, Yue J, Lin L, Yu X, Zhou Y, Ying X, Chen X, Tu W, Lou X, Yang G, Zhou K, Jiang S (2021) Electroacupuncture may alleviate neuropathic pain via suppressing P2X7R expression. Mol Pain 17:1744806921997654
Liu W, Rong Y, Wang J, Zhou Z, Ge X, Ji C, Jiang D, Gong F, Li L, Chen J, Zhao S, Kong F, Gu C, Fan J, Cai W (2020) Exosome-shuttled miR-216a-5p from hypoxic preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells repair traumatic spinal cord injury by shifting microglial M1/M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):47
Zhang B, Wei YZ, Wang GQ, Li DD, Shi JS, Zhang F (2018) Targeting MAPK pathways by Naringenin modulates Microglia M1/M2 polarization in Lipopolysaccharide-Stimulated cultures. Front Cell Neurosci 12:531
Lopes FSR, Giardini AC, Sant’Anna MB, Kimura LF, Bufalo MC, Vigerelli H, Zambelli VO, Picolo G (2022) Crotalphine modulates Microglia M1/M2 phenotypes and induces spinal Analgesia mediated by opioid-cannabinoid systems. Int J Mol Sci 23:11571
Jing F, Zhang Y, Long T, He W, Qin G, Zhang D, Chen L, Zhou J (2019) P2Y12 receptor mediates microglial activation via RhoA/ROCK pathway in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis in a mouse model of chronic migraine. J Neuroinflammation 16:217
Sipe GO, Lowery RL, Tremblay ME, Kelly EA, Lamantia CE, Majewska AK (2016) Microglial P2Y12 is necessary for synaptic plasticity in mouse visual cortex. Nat Commun 7:10905
Rivera A, Vanzulli I, Butt AM (2016) A central role for ATP signalling in glial interactions in the CNS. Curr Drug Targets 17:1829–1833
Gomez Morillas A, Besson VC, Lerouet D (2021) Microglia and Neuroinflammation: what place for P2RY12? Int J Mol Sci 22
(2015) Erratum: P2Y12 expression and function in alternatively activated human microglia. Neurology(R) Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2:e106
Mashima T, Iwasaki R, Kawata N, Kawakami R, Kumagai K, Migita T, Sano T, Yamaguchi K, Seimiya H (2019) In silico chemical screening identifies epidermal growth factor receptor as a therapeutic target of drug-tolerant CD44v9-positive gastric cancer cells. Br J Cancer 121:846–856
Zhang Y, Chen R, Hu Q, Wang J, Nie H, Yin C, Li Y, Wei H, Liu B, Tai Y, Fang J, Shao X, Jin X (2022) Electroacupuncture ameliorates mechanical Allodynia of a rat model of CRPS-I via suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation in spinal cord dorsal horn neurons. Front Cell Neurosci 16:826777
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Ingall AH, Dixon J, Bailey A, Coombs ME, Cox D, McInally JI, Hunt SF, Kindon ND, Teobald BJ, Willis PA, Humphries RG, Leff P, Clegg JA, Smith JA, Tomlinson W (1999) Antagonists of the platelet P2T receptor: a novel approach to antithrombotic therapy. J Med Chem 42:213–220
Berman BM, Langevin HM, Witt CM, Dubner R (2010) Acupuncture for chronic low back pain. N Engl J Med 363:454–461
Goldman N, Chen M, Fujita T, Xu Q, Peng W, Liu W, Jensen TK, Pei Y, Wang F, Han X, Chen JF, Schnermann J, Takano T, Bekar L, Tieu K, Nedergaard M (2010) Adenosine A1 receptors mediate local anti-nociceptive effects of acupuncture. Nat Neurosci 13:883–888
Liu Q, Wu X, Guo J, Gao J, Liu B, Wang Y, Xia M, Pei L, Sun J (2021) Analgesic effect of Electroacupuncture on postherpetic neuralgia: a Trial Protocol for a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Pain and Therapy 10:1755–1771
Schweiger V, Secchettin E, Castellani C, Martini A, Mazzocchi E, Picelli A, Polati E, Donadello K, Valenti MT, Dalle Carbonare L (2020) Comparison between acupuncture and nutraceutical treatment with Migratens((R)) in patients with Fibromyalgia Syndrome: a prospective Randomized Clinical Trial. Nutrients 12
Patil S, Sen S, Bral M, Reddy S, Bradley KK, Cornett EM, Fox CJ, Kaye AD (2016) The role of acupuncture in Pain Management. Curr Pain Headache Rep 20:22
Luo X, Liu J, Li Q, Zhao J, Hao Q, Zhao L, Chen Y, Yin P, Li L, Liang F, Sun X (2023) Acupuncture for treatment of knee osteoarthritis: a clinical practice guideline. J Evid Based Med 16:237–245
Berman BM, Swyers JP, Ezzo J (2000) The evidence for acupuncture as a treatment for rheumatologic conditions. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 26:103–115 ix-x
Tozaki-Saitoh H, Takeda H, Inoue K (2022) The role of Microglial Purinergic receptors in Pain Signaling. Molecules 27
Koizumi S, Shigemoto-Mogami Y, Nasu-Tada K, Shinozaki Y, Ohsawa K, Tsuda M, Joshi BV, Jacobson KA, Kohsaka S, Inoue K (2007) UDP acting at P2Y6 receptors is a mediator of microglial phagocytosis. Nature 446:1091–1095
Garcia AE, Mada SR, Rico MC, Dela Cadena RA, Kunapuli SP (2011) Clopidogrel, a P2Y12 receptor antagonist, potentiates the inflammatory response in a rat model of peptidoglycan polysaccharide-induced arthritis. PLoS ONE 6:e26035
Horvath G, Goloncser F, Csolle C, Kiraly K, Ando RD, Baranyi M, Kovanyi B, Mate Z, Hoffmann K, Algaier I, Baqi Y, Muller CE, Von Kugelgen I, Sperlagh B (2014) Central P2Y12 receptor blockade alleviates inflammatory and neuropathic pain and cytokine production in rodents. Neurobiol Dis 70:162–178
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 81904283), Special Project for Clinical Research in the Health Industry of the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (No.20194Y0307), and Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine project (2021LK082).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 81904283), Special Project for Clinical Research in the Health Industry of the Shanghai Municipal Health Commission (No.20194Y0307), Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine project (2021LK082), and Shanghai Traditional Chinese Medicine "Three-year Action Plan" [ZY(2021-2023)-0211].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology: J.W., Y.Z. Resources, data curation and visualization: W.S., J.W., Y.W. Writing- original draft preparation: J.S. Supervision, writing- reviewing and editing: Y.Z.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical Approval
Animal experiments were performed with the approval of the Animal Ethics Committee of the Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine (201801080001), in line with the ARRIVE guidelines to minimize animal suffering.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Song, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Electroacupuncture Alleviates Pain by Suppressing P2Y12R-Dependent Microglial Activation in Monoarthritic Rats. Neurochem Res 49, 1268–1277 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-024-04114-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-024-04114-y