Abstract
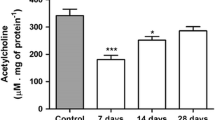
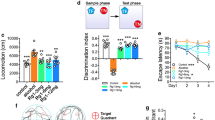
Based on the scientific evidence supporting the neuroinflammatory response contributes the cognitive impairment associated with chronic alcoholism and the neuroprotective actions of mefenamic acid with reversal of memory loss and brain inflammation in mice, this study was designed to evaluate the effect of mefenamic acid against chronic alcohol induced cognitive impairment in zebrafish model. Zebrafish were grouped and subjected to normal behavioral analysis in light–dark chamber for 10 days. The preference to dark compartment was noted in zebrafish. Zebrafish were grouped and exposed to escalating doses of alcohol for 28 days with and without mefenamic acid exposure (100 and 200 µg/L) and subjected to a fear conditioning passive avoidance task from day 13 of 28. The cognitive evaluation was performed for 10 days and the brain tissue was isolated to estimate acetylcholinesterase activity. In cognitive evaluation study, the normal zebrafish retained the memory of the learned task and avoided the dark. The alcohol exposed zebrafish showed impairment in retaining the memory of learned task. Mefenamic acid exposed zebrafish showed a significant protection against cognitive impairment caused by alcohol and retained the memory of learned task with a significant decrease in AChE activity in brain homogenate compared to alcohol exposed zebrafish. The results of this study suggest that the memory enhancing activity of mefenamic acid might be due to activation of cholinergic transmission that has protected neuroinflammatory and neurodegenerative conditions caused by alcohol.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gould TJ (2010) Addiction and cognition. Addict Sci Clin Pract 5(2):4–14
Rehm J, Mathers C, Popova S, Thavorncharoensap M. Teerawattananon Y, Patra J (2009) Global burden of disease and injury and economic cost attributable to alcohol use and alcohol-use disorders. Lancet 373:2223–2233
Hartman-Stein PE, La Rue A (2011) Enhancing cognitive fitness in adults—a guide to the use and development of community-based programs. Springer, New York, p 254
Stavro K, Pelletier J, Potvin S (2012) Widespread and sustained cognitive deficits in alcoholism: a meat-analysis. Addict Biol 18(2):203–213
Loeber S, Duka T, Marquez HW, Nakovics H, Heinz A, Mann K, Flor H (2010) Effects of repeated withdrawal from alcohol on recovery of cognitive impairment under abstinence and rate of relapse. Alcohol Alcohol 45(6):541–547
Beck A, Wüstenberg T, Genauck A, Wrase J, Schlagenhauf F, Smolka MN, Mann K, Heinz A (2012) Effect of brain structure, brain function, and brain connectivity on relapse in alcohol dependent patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69(8):842–852
Ryabinin AE (1998) Role of hippocampus in alcohol induced memory impairment: implications from behavioral and immediate early gene studies. Psychopharmacology 139(1–2):34–43
Agartz I, Momenam R, Rawlings RR, Kerich MJ, Hommer DN (1999) Hippocampal volume in patients with alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 56(4):356–363
Roberto M, Nelson TE, Ur CL, Gruol DL (2002) Long-term potentiation in the rat hippocampus is reversibly depressed by chronic intermittent ethanol exposure. J Neurophysiol 87:2385–2397
Ray S, Bates ME (2006) Acute alcohol effects on repetitive priming and word recognition memory with equivalent memory cues. Brain cogn 60(2):118–127
Walker DN, Freund G (1971) Impairment of shuttle box avoidance learning following prolonged alcohol consumption in rats. Pysiol Behav 7(5):773–778
Herrera MI, Kollifer-Frers R, Barreto G, Blanco E, Capani F (2016) Glial modulation by N-acylethanolamides in brain injury and neurodegeneration. Front Aging Neurosci 8:81
Valles SL, Blanco AM, Pascual M, Guerri C (2004) Chronic alcohol treatment enhances inflammatory mediators and cell death in the brain and in astrocytes. Brain Pathol 14(4):365–371
Tabet N (2006) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors for Alzheimer’s disease: anti-inflammatories in acetyl choline clothing. Age Aging 35(4):336–338
Wang T, Tan L, Wang HF, Tan CC, Meng XF, Wang C, Tang SW, Yu JT (2015) Anti-inflammatory drugs and risk of Alzheimer’s disease:an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 44(2):385–396
Cordle A, Koenigsknecht-Talboo J, Wilkinson B, Limpert A, Landreth G (2005) Mechanisms of statin-mediated inhibition of small G-protein function. J Biol Chem 280(4):34202–34209
Imbimbo BP, Solfrizzi V, Panza F (2010) Are NSAIDs useful to treat Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment? Front Aging Neurosci 2:19
Aisen PS, Schafer KA, Grundman M, Pfeiffer E, Sano M, Davis KL, Farlow MR, Jin S, Thomas RG, Thal LJ (2003) Effects of rofecoxib or naproxen vs placebo on Alzheimer disease progression: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 289(21):2819–2826
Schliebs R (2005) Basal forebrain cholinergic dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: interrelationship with beta-amyloid, inflammation and neurotrophin signaling. Neurochem Res 30(6–7):895–908
Daniels MJD, Rivers-Auty J, Schilling T, Spencer NG, Watremez W, Fasolino V, Booth SJ, White CS, Baldwin AG, Freeman S, Wong R, Latta C, Yu S, Jackson J, Fischer N, Koziel V, Pillot T, Bagnall J, Allan SM, Paszek P, Galea J, Harte MK, Eder C, Lawrence CB, Brough D (2016) Fenamate NSAIDs inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome and protect against Alzheimer’s disease in rodent models. Nat Commun. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12504
Peretz A, Degani N, Nachman R, Uziyel Y, Gibor G, Shabat D, Attali B (2005) Meclofenamic acid and diclofenac, novel templates of KCNQ2/Q3 potassium channel openers, depress cortical neuron activity and exhibit anticonvulsant properties. Mol Pharmacol 67(4):1053–1066
Khansari PS, Halliwell RF (2009) Evidence for neuroprotection by the fenamate NSAID, mefenamic acid. Neurochem Int 55(2009):683–688
Coyne L, Su J, Patten D, Halliwell RF (2007) Characterization of the interaction between fenamates and hippocampal neurons GABA(A) receptors. Neurochem Int 51(6–7):440–446
Syapin PJ, Hickey WF, Kane CJM (2005) Alcohol brain damage and neuroinflammation: is there a connection? Alcoholism 29(6):1080–1089
Bilotta J, Saszik S (2001) The zebrafish as a model visual system. Int J Dev Neurosci 19(7):621–629
Guo S (2010) Using zebrafish to assess the impact of drugs on neural development and function. Expert Opin Drug Discov 4(7):715–726
Mueller T, Wullimann MF, Guo S (2008) Early teleostean basal ganglia development visualized by zebrafish Dlx2a, Lhx6, Lhx7, Tbr2 (eomesa), and GAD67 gene expression. J Comp Neurol 507:245–257
Boehmler W, Obrecht-Pflumio S, Canfield V, Thisse C, Thisse B, Levenson R (2004) Evolution and expression of D2 and D3 dopamine receptor genes in zebrafish. Dev Dyn 230:481–493
Norton WH, Folchert A, Bally-Cuif L (2008) Comparative analysis of serotonin receptor (HTR1A/HTR1B families) and transporter (slc6a4a/b) gene expression in the zebrafish brain. J Comp Neurol 511:521–542
Dlugos CA, Rabin RA (2003) Ethanol effects on three strains of zebrafish: model system for genetic investigations. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 74(2):471–480
Gerlai R, Lahav M, Guo S, Rosenthal A (2000) Drinks like a fish: zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a behavior genetic model to study alcohol effects. Pharm Biochem Behav 67:773–782
Gerlai R, Chatterjee D, Pereira T, Sawashima T, Krishnannair R (2009) Acute and chronic alcohol dose: population differences in behavior and neurochemistry of zebrafish. Genes Brain Behav 8(6):586–599
Ninkovic J, Folchert A, Makhankov YV, Neuhauss SC, Sillaber I, Straehle U, Bally-Cuif L (2006) Genetic identification of AChE as a positive modulator of addiction to the psychostimulant D-amphetamine in zebrafish. J Neurobiol 66(5):463–475
Rajesh V, Ilanthalir S (2016) Cognition enhancing activity of sulforaphane against scopolamine induced cognitive impairment in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Neurochem Res 41(10):2538–2548
Collard HR, Ji K, Lee S, Liu X, Kang S, Kho Y, Ahn B, Ryu J, Lee J, Choi K (2013) Toxicity and endocrine disruption in zebrafish (Danio rerio) and two freshwater invertebrates (Daphnia magna and Moina macrocopa) after chronic exposure to mefenamic acid. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 94:80–86
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr, Feath-erstone RM (1961) A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem Pharmacol 7:88–95
Cabe N, Laniepce A, Ritz L, Lannuzel C, Boudehent C, Vabret F, Eustache F, Beaunieux H, Pitel AL (2016) Cognitive impairments in alcohol dependence: from screening to treatment improvements. Encephale 42(1):74–81
Bernardin F, Maheut-Bosser A, Paille F (2014) Cognitive impairments in alcohol-dependent subjects. Front Psychiatry 5:78
Ridley NJ, Draper B, Withall A (2013) Alcohol-related dementia: an update of the evidence. Alzheimer’s Res Ther 5(1):3
Blednov YA, Benavidez JM, Geil C, Perra S, Morikawa H, Harris RA (2011) Activation of inflammatory signaling by lipopolysaccharide produces a prolonged increase in voluntary alcohol intake in mice. Brain Behav Immun 25(1):S92-S105
Anthony HC, Breitner JCS, Zandi PP (2000) Reduced prevalence of AD in users of NSAIDs and H2 receptor antagonists. Neurology 54:2066–2071
Broe GA, Grayson DA, Creasy HM, Waite LM, Casey BJ, Bennett HP, Brooks WS, Halliday GM (2000) Anti-inflammatory drugs protect against Alzheimer’s disease at low doses. Arch Neurol 27(11):1586–1591
Beard CM, Waring SC, O’Brien PC, Kurland LT, Kokmen E (1998) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and Alzheimer’s disease: a case control study in Rochester, Minnesota, 1980 through 1984. Myo Clin Proc 73(10):951–955
Kern S, Skoog I, Ostling S, Kern J, Borjesson-Hanson A (2012) Does low-dose acetylsalicylic acid prevent cognitive decline in women with high cardiovascular risk. A 5-year follow-up of a non-demented population-based cohort of Swedish elderly women. BMJ Open 2:(5)
Asanuma M, Nishibayashi-Asanuma S, Miyazaki I, Kohno M, Ogawa N (2001) Neuroprotective effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs by direct scavenging of nitric oxide radicals. J Neurochem 76(6):1895–1904
Ramos CM, Pou S, Rosen GM (1995) Effect of anti-inflammatory drugs on myrloperoxidase-dependent hydroxyl radical generation by human neutrophils. Biochem Pharmacol 49(8):1079–1084
Halliwell RF, Thomas P, Patten D, James CH, Martinez-Torres A, Miledi R, Smart TG (1999) Subunit-selective modulation of GABAA receptors by the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, mefenamic acid. Eur J Neurosci 11(8):2897–2905
Lerma J, Martín del Río R (1992) Chloride transport blockers prevent N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-channel complex activation. Mol Pharmacol 41(2):217–222
Partridge LD, Valenzuela CF (2000) Block of hippocampal CAN channels by flufenamate. Brain Res 867(1–2):143–148
White AM, Ghia AS, Levin ED, Swartzwelder HS (2000) Binge pattern ethanol exposure in adolescent and adult rats: differential impact on subsequent responsiveness to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24(8):1251–1256
Miller LC, Isa S, LoPreste G, Schaller JG, Dinarello CA (1990) Neonatal interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor: cord blood levels and cellular production. J Pediatr 117(6):961–965
Bilbo SD, Schwarz JM (2009) Early-life programming of later-life brain and behavior: a critical role for the immune system. Front Behav Neurosci 3:14
Pan Y, Kaiguo M, Razak Z, Westwood JT, Gerlai R (2011) Chronic alcohol exposure induced gene expression changes in zebrafish brain. Behave Brain Res 216(1):66–76
Ballard CG, Greig NH, Gullozet-Bongaarts AL, Enz A, Darvesh S (2005) Cholinesterases: roles in the brain during health and disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 2(3):307–318
Muraoka S, Miura T (2009) Inactivation of cholinesterase induced by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with horseradish peroxidase: implication for Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci 84:272–277
Wang H, Yu M, Ochani M, Amella CA, Tanovic M, Susarla S, Li JH, Wang H, Yang H, Ulloa L, Al-Abed Y, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2002) Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor alpha7 subunit is an essential regulator of inflammation. Nature 421(6921):384–388
George MS, Nahas Z, Bohning DE, Kozel FA, Anderson B, Chae JH, Lomarev M, Denslow S, Li X, Mu C (2002) Vagus nerve stimulation therapy: a research update. Neurology 59:S56-S61
George MS, Rush AJ, Sackeim HA, Marangell LB (2003) Vagus nerve stimulation (VNS): utility in neuropsychiatric disorders. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 6(1):73–83
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Nardi D, Zhang M, Yang H, Ombrellino M, Tracey KJ (2000) Role of vagus nerve signaling in CNI-1493-mediated suppression of acute inflammation. Auton Neurosci 85(1–3):141–147
Bernik TR, Friedman SG, Ochani M, Di Raimo R, Ulloa L, Yang H, Sudan S, Czura CJ, Ivanova SM, Tracey KJ (2002) Pharmacological stimulation of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J Exp Med 192(6):781–788
Tracy KJ (2002) The inflammatory reflex. Nature 420(6917):853–859
Baez-Pagan CA, Delgado-Velez M, Lasalde-Dominicci JA (2015) Activation of the macrophage α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor and control of inflammation. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 10(3):468–476
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to the management of The Erode College of Pharmacy and Research Institute, Erode, Tamil Nadu, INDIA for providing necessary facilities to carry out the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical Approval
This study did not involve endangered or protected species. No specific permissions were required for the activities involved in this study. All experimental manipulations (behavioral analysis, fear conditioning, cognitive evaluation) were conducted according to the principles of the Institutional Ethical Committee, The Erode College of Pharmacy, Erode, Tamilnadu, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajesh, V., Mridhulmohan, M., Jayaseelan, S. et al. Mefenamic Acid Attenuates Chronic Alcohol Induced Cognitive Impairment in Zebrafish: Possible Role of Cholinergic Pathway. Neurochem Res 43, 1392–1404 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2554-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-018-2554-3