Abstract
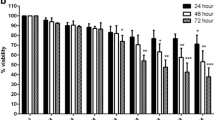
Sodium butyrate (NaBt), a histone deacetylase inhibitor, can cause apoptosis in a number of cancer cells. However, the mechanism of this action is poorly understood. Increased intracellular [Ca2+] level has been suggested as a likely mechanism, but there is little corroborating data. In this report we provide evidence that NaBt-treated MSN neuroblastoma cells undergo massive apoptosis in the presence of serum and regardless of external or internal [Ca2+] levels. Presented data suggest that apoptotic effect of NaBt is both time- and dose-dependent (LD50 1 mM); and that, presence of serum or cAMP, a second messenger molecule that modulates the apoptotic program in a wide variety of cells could not circumvent the apoptotic effect of NaBt. Our findings suggest that NaBt-induced apoptosis in MSN neuroblastoma cells occurs via a pathway that is independent of Ca2+flux, intracellular [Ca2+] or cAMP levels. Further, we also present data that exclude a role for PKC or histones acetylation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Lawrence F. Eng
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rozental, R., Faharani, R., Yu, Y. et al. Sodium Butyrate Induces Apoptosis in MSN Neuroblastoma Cells in a Calcium Independent Pathway. Neurochem Res 29, 2125–2134 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-004-6886-9
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-004-6886-9