Abstract
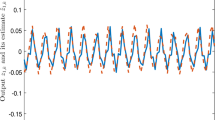
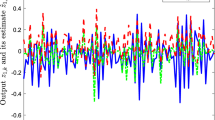
This paper studies the variance-constrained resilient \(H_{\infty }\) state estimation problem for discrete time-varying uncertain recurrent neural networks with random saturation observation under uncertain occurrence probability. In fact, the state estimation problem of stochastic recurrent neural networks with time-varying parameters has significant importance and wide applications. In order to characterize the realistic transmission process of neural signals, the phenomenon of random saturation observation is represented by introducing a random variable. In addition, the estimator gain is allowed to satisfy parameter perturbations to reflect the fragility of the estimator. The main objective is to present a finite-horizon resilient state estimation scheme without utilizing the augmentation method such that, in the presence of estimator parameter perturbations and random saturation observation, some sufficient criteria are obtained for the estimation error dynamical system satisfying both the pre-defined \(H_{\infty }\) performance constraint and the error variance boundedness. Finally, a numerical example demonstrates the feasibility of the presented resilient \(H_{\infty }\) SE method under variance constraint. From the engineering viewpoint, the proposed state estimation method under variance constraint has time-varying characteristics, which is suitable for online estimation applications. Moreover, both the state estimation and original neural state have the same order, which can reduce the computation burden.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sakthivel R, Aravinth N, Aouiti C, Arumugam K (2021) Finite-time synchronization of hierarchical hybrid coupled neural networks with mismatched quantization. Neural Comput Appl 33(24):16881–16897
Sakthivel R, Sakthivel R, Kwon OM, Selvaraj P (2021) Disturbance rejection for singular semi-Markov jump neural networks with input saturation. Appl Mathemat Comput 407:126301
Wang P, Li X, Wang N, Li Y, Shi K, Lu J (2022) Almost periodic synchronization of quaternion-valued fuzzy cellular neural networks with leakage delays. Fuzzy Sets Syst 426:46–65
Nagamani G, Karnan A, Soundararajan G (2021) Delay-dependent and independent state estimation for BAM cellular neural networks with multi-proportional delays. Circuits Syst Signal Proc 40(7):3179–3203
Shen H, Xing M, Huo S, Wu Z-G, Park JH (2019) Finite-time \(H_{\infty }\) asynchronous state estimation for discrete-time fuzzy Markov jump neural networks with uncertain measurements. Fuzzy Sets Syst 356:113–128
Yan X, Tong D, Chen Q, Zhou W, Xu Y (2019) Adaptive state estimation of stochastic delayed neural networks with fractional Brownian motion. Neural Process Lett 50(2):2007–2020
Tanaka G, Nakane R, Takeuchi T, Yamane T, Nakano D, Katayama Y, Hirose A (2020) Spatially arranged sparse recurrent neural networks for energy efficient associative memory. IEEE Trans Neural Net Learning Syst 31(1):24–38
Kasi SK, Das S, Biswas S (2021) Energy-efficient event pattern recognition in wireless sensor networks using multilayer spiking neural networks. Wireless Netw 27(3):2039–2054
Zou L, Wang Z, Zhou D (2020) Moving horizon estimation with non-uniform sampling under component-based dynamic event-triggered transmission. Automatica 120:109154
Mon Y-J, Lin C-M (2014) Image processing based obstacle avoidance control for mobile robot by recurrent fuzzy neural network. J Intell Fuzzy Syst 26(6):2747–2754
Ali MS, Gunasekaran N, Joo YH (2019) Sampled-data state estimation of neutral type neural networks with mixed time-varying delays. Neural Process Lett 50(1):357–378
Ali MS, Gunasekaran N, Zhu Q (2017) State estimation of T-S fuzzy delayed neural networks with Markovian jumping parameters using sampled-data control. Fuzzy Sets Syst 306:87–104
Shen H, Huang Z, Yang X, Wang Z (2018) Quantized energy-to-peak state estimation for persistent dwell-time switched neural networks with packet dropouts. Nonlinear Dyn 93(4):2249–2262
Gong W, Liang J, Kan X, Nie X (2017) Robust state estimation for delayed complex-valued neural networks. Neural Process Lett 46(3):1009–1029
Zhang H, Qiu Z, Cao J, Abdel-Aty M, Xiong L (2020) Event-triggered synchronization for neutral-type semi-Markovian neural networks with partial mode-dependent time-varying delays. IEEE Trans Neural Net Learn Syst 31(11):4437–4450
Zhang H, Qiu Z, Xiong L (2019) Stochastic stability criterion of neutral-type neural networks with additive time-varying delay and uncertain semi-Markov jump. Neurocomputing 333:395–406
Zhang H, Qiu Z, Liu X, Xiong L (2020) Stochastic robust finite-time boundedness for semi-Markov jump uncertain neutral-type neural networks with mixed time-varying delays via a generalized reciprocally convex combination inequality. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 30(5):2001–2019
Hu J, Jia C, Yu H, Liu H (2022) Dynamic event-triggered state estimation for nonlinear coupled output complex networks subject to innovation constraints. IEEE/CAA J Automatica Sinica 9(5):941–944
Wang F, Wang Z, Liang J, Liu X (2019) Resilient state estimation for 2-D time-varying systems with redundant channels: a variance-constrained approach. IEEE Trans Cybernetics 49(7):2479–2489
Ding D, Wang Z, Han Q-L (2020) A set-membership approach to event-triggered filtering for general nonlinear systems over sensor networks. IEEE Trans Autom Control 65(4):1792–1799
Shen B, Wang Z, Wang D, Li Q (2020) State-saturated recursive filter design for stochastic time-varying nonlinear complex networks under deception attacks. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learning Syst 31(10):3788–3800
Rafaralahy H, Richard E, Boutayeb M, Zasadzinski M (2012) Sensor diagnosis and state estimation for a class of skew symmetric time-varying systems. Automatica 48(9):2284–2289
Tian E, Wang Z, Zou L, Yue D (2019) Chance-constrained \(H_{\infty }\) control for a class of time-varying systems with stochastic nonlinearities: the finite-horizon case. Automatica 107:296–305
Zou L, Wang Z, Han Q-L, Zhou D (2021) Moving horizon estimation of networked nonlinear systems with random access protocol. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernetics-Syst 51(5):2937–2948
Zou L, Wang Z, Zhou D (2020) Moving horizon estimation with non-uniform sampling under component-based dynamic event-triggered transmission. Automatica 120:109154
Liang J, Huang T, Hayat T, Alsaadi F (2015) \(H_{\infty }\) filtering for two-dimensional systems with mixed time delays, randomly occurring saturations and nonlinearities. Int J Gen Syst 44(2):226–239
Hu J, Li J, Kao Y, Chen D (2022) Optimal distributed filtering for nonlinear saturated systems with random access protocol and missing measurements: the uncertain probabilities case. Appl Mathematics Comput vol 418: Art No: 126844
Shen Z, Li C, Li Y (2021) Estimation of the domain of attraction of discrete-time impulsive Cohen-Grossberg neural networks model with impulse input saturation. Neural Process Lett 53(3):2029–2046
Liang J, Wang Z, Liu X (2014) Robust state estimation for two-dimensional stochastic time-delay systems with missing measurements and sensor saturation. Multidimension Syst Signal Process 25(1):157–177
Li Q, Shen B, Liu Y, Huang T (2017) Event-triggered \(H_{\infty }\) state estimation for discrete-time neural networks with mixed time delays and sensor saturations. Neural Comput Appl 28(12):3815–3825
Liu L, Ma L, Zhang J, Bo Y (2021) Distributed non-fragile set-membership filtering for nonlinear systems under fading channels and bias injection attacks. Int J Syst Sci 52(6):1192–1205
Xie L, Wang Y, Yang Y, Li L (2017) Non-fragile \(H_{\infty }\) state estimation for nonlinear networked system with probabilistic diverging disturbance and multiple missing measurements. Neurocomputing 230:270–278
Feng S, Yu H, Jia C, Gao P (2022) Joint state and fault estimation for nonlinear complex networks with mixed time-delays and uncertain inner coupling: non-fragile recursive method. Syst Sci Control Eng 10(1):603–615
Qu F, Zhao X, Wang X, Tian E (2022) Probabilistic-constrained distributed fusion filtering for a class of time-varying systems over sensor networks: a torus-event-triggering mechanism. Int J Syst Sci 53(6):1288–1297
Hu J, Jia C, Liu H, Yi X, Liu Y (2021) A survey on state estimation of complex dynamical networks. Int J Syst Sci 52(16):3351–3367
Wen P, Li X, Hou N, Mu S (2022) Distributed recursive fault estimation with binary encoding schemes over sensor networks. Syst Sci Control Eng 10(1):417–427
Geng H, Liu H, Ma L, Yi X (2021) Multi-sensor filtering fusion meets censored measurements under a constrained network environment: advances, challenges and prospects. Int J Syst Sci 52(16):3410–3436
Zha L, Fang J-A, Liu J, Tian E (2018) Event-triggered non-fragile state estimation for delayed neural networks with randomly occurring sensor nonlinearity. Neurocomputing 273:1–8
Hou N, Dong H, Wang Z, Ren W, Alsaadi FE (2016) Non-fragile state estimation for discrete Markovian jumping neural networks. Neurocomputing 179:238–245
Gao Y, Hu J, Chen D, Du J (2019) Variance-constrained resilient \(H_{\infty }\) state estimation for time-varying neural networks with randomly varying nonlinearities and missing measurements. Adv Difference Equ vol 2019, no 1, Article No: 380
Dong H, Wang Z, Ho DWC, Gao H (2010) Variance-constrained \(H_{\infty }\) filtering for a class of nonlinear time-varying systems with multiple missing measurements: The finite-horizon case. IEEE Trans Signal Process 58(5):2534–2543
Shen B, Wang Z, Shu H, Wei G (2011) \(H_{\infty }\) filtering for uncertain time-varying systems with multiple randomly occurred nonlinearities and successive packet dropouts. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 21(14):1693–1709
Dong H, Hou N, Wang Z, Ren W (2018) Variance-constrained state estimation for complex networks with randomly varying topologies. IEEE Trans Neural Networks Learning Syst 29(7):2757–2768
Ding K, Zhu Q (2021) Extended dissipative anti-disturbance control for delayed switched singular semi-Markovian jump systems with multi-disturbance via disturbance observer, Automatica vol 128: Article No: 109556
Yang X, Wang H, Zhu Q (2022) Event-triggered predictive control of nonlinear stochastic systems with output delay. Automatica vol 140, Article No: 110230
Zhu Q (2019) Stabilization of stochastic nonlinear delay systems with exogenous disturbances and the event-triggered feedback control. IEEE Trans Autom Control 64(9):3764–3771
Zhu Q, Huang T (2021) \(H_{\infty }\) control of stochastic networked control systems with time-varying delays: the event-triggered sampling case. Int J Robust Nonlinear Control 31(18):9767–9781
Ma Y-S, Che W-W, Deng C, Wu Z-G (2021) Distributed model-free adaptive control for learning nonlinear MASs under DoS attacks. IEEE Trans Neural Net Learning Syst https://doi.org/10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3104978
Xu Y, Sun J, Wang G, Wu Z-G (2021) Dynamic triggering mechanisms for distributed adaptive synchronization control and its application to circuit systems. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst I-Regular Papers 68(5):2246–2256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant 12171124 and 72001059, the Natural Science Foundation of Heilongjiang Province of China under Grant ZD2022F003, the Heilongjiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Complex Intelligent System and Integration under Grant HPKL-CICS-202203, the Fundamental Research Funds in Heilongjiang Provincial Universities of China under Grant 135509121, the Educational Research Project of the Qiqihar University of China under Grant YB201904, and the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation of Germany.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Hu, J., Yu, H. et al. Variance-Constrained Resilient \(H_{\infty }\) State Estimation for Time-Varying Neural Networks with Random Saturation Observation Under Uncertain Occurrence Probability. Neural Process Lett 55, 5031–5054 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-11078-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-11078-z