Abstract
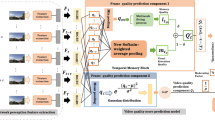
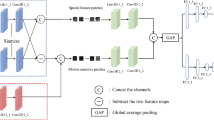
Quality assessment of real, user-generated content videos lacking reference videos is a challenging problem. For such scenarios, we propose an objective quality assessment method for no-reference video from the spatio-temporal perception characteristics of the video. First, a dual-branch network is constructed from distorted video frames and frame difference maps generated from a global perspective, considering the interaction between spatial and temporal information, incorporating a motion-guided attention module, and fusing spatio-temporal perceptual features from a multiscale perspective. Second, an InceptionTime network is introduced to further perform long-term sequence fusion to obtain the final perceptual quality score. Finally, the results were evaluated on the four user-generated content video databases of KoNViD-1k, CVD2014, LIVE_VQC and LIVE_Qualcomm, and the experimental results show that the network outperforms other partially recent no-reference VQA methods.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen S, Zheng B, Li J (2012) A method of image quality assessment for compressive sampling video transmission. J Electron 29(6):598–603
Chen J, Liu S, Chen Z (2017) Gender classification in live videos. In: 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp 1602–1606. IEEE
Mittal A, Moorthy AK, Bovik AC (2012) No-reference image quality assessment in the spatial domain. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(12):4695–4708
Mittal A, Saad MA, Bovik AC (2015) A completely blind video integrity oracle. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(1):289–300
Saad MA, Bovik AC, Charrier C (2014) Blind prediction of natural video quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(3):1352–1365. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2014.2299154
Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J (1997) Long short-term memory. Neural Comput 9(8):1735–1780. https://doi.org/10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735
Li D, Jiang T, Jiang M (2019) Quality assessment of in-the-wild videos. Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.1145/3343031.3351028
Otroshi Shahreza H, Amini A, Behroozi H (2019) No-reference video quality assessment using recurrent neural networks. In: 2019 5th Iranian Conference on Signal Processing and Intelligent Systems (ICSPIS), pp 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICSPIS48872.2019.9066015
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2015) Two-stream convolutional networks for action recognition. In: Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS)
Zhang Y, Gao X, He L, Lu W, He R (2018) Blind video quality assessment with weakly supervised learning and resampling strategy. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 29(8):2244–2255. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2018.2868063
Pan D, Wang X, Shi P, Yu S (2021) No-reference video quality assessment based on modeling temporal-memory effects. Displays 70:102075
Wu W, Liu Z, Chen Z, Liu S (2020) No-reference video quality assessment based on similarity map estimation. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP), pp 181–185. IEEE
Qian J, Wu D, Li L, Cheng D, Wang X (2014) Image quality assessment based on multi-scale representation of structure. Digital Signal Processing 33:125–133
Wang Z, Li Q (2007) Video quality assessment using a statistical model of human visual speed perception. JOSA A 24(12):61–69
Zhang L, Zhang L, Mou X, Zhang D (2011) Fsim: A feature similarity index for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 20(8):2378–2386
Xue W, Zhang L, Mou X, Bovik AC (2013) Gradient magnitude similarity deviation: A highly efficient perceptual image quality index. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(2):684–695
Kuang Z, Yu J, Li Z, Zhang B, Fan J (2018) Integrating multi-level deep learning and concept ontology for large-scale visual recognition. Pattern Recogn 78:198–214
Kuang Z, Guo Z, Fang J, Yu J, Babaguchi N, Fan J (2021) Unnoticeable synthetic face replacement for image privacy protection. Neurocomputing 457:322–333
Bosse S, Maniry D, Muller K-R, Wiegand T, Samek W (2018) Deep neural networks for no-reference and full-reference image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 27(1):206–219
Li S, Han X, Zubair M, Ma S (2019) Stereo image quality assessment based on sparse binocular fusion convolution neural network. In: 2019 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), pp 1–4. IEEE
Olshausen BA, Field DJ (1996) Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images. Nature 381(6583):607–609
Yu J, Rui Y, Tao D (2014) Click prediction for web image reranking using multimodal sparse coding. IEEE Trans Image Process 23(5):2019–2032
Su S, Yan Q, Zhu Y, Zhang C, Ge X, Sun J, Zhang Y (2020) Blindly assess image quality in the wild guided by a self-adaptive hyper network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 3667–3676
Zhang Y, Yang Q (2021) A survey on multi-task learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering
Seshadrinathan K, Bovik AC (2009) Motion tuned spatio-temporal quality assessment of natural videos. IEEE Trans Image Process 19(2):335–350
Korhonen J (2019) Two-level approach for no-reference consumer video quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(12):5923–5938
Tu Z, Wang Y, Birkbeck N, Adsumilli B, Bovik A (2021) Ugc-vqa: Benchmarking blind video quality assessment for user generated content. IEEE Trans Image Process 30:4449–4464. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2021.3072221
Tu Z, Yu X, Wang Y, Birkbeck N, Adsumilli B, Bovik AC (2021) Rapique: Rapid and accurate video quality prediction of user generated content. IEEE Open J Signal Process 2:425–440 arXiv:2101.10955
Li D, Jiang T, Jiang M (2021) Unified quality assessment of in-the-wild videos with mixed datasets training. Int J Comput Vision 129(4):1–20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11263-020-01408-w
Chen B, Zhu L, Li G, Lu F, Fan H, Wang S (2021) Learning generalized spatial-temporal deep feature representation for no-reference video quality assessment. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 32(4):1903–1916
Varga D, Szirányi T (2019) No-reference video quality assessment via pretrained cnn and lstm networks. SIViP 13(8):1569–1576. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11760-019-01510-8
Zhang J, Cao Y, Wu Q (2021) Vector of locally and adaptively aggregated descriptors for image feature representation. Pattern Recogn 116:107952
Sun W, Wang T, Min X, Yi F, Zhai G (2021) Deep learning based full-reference and no-reference quality assessment models for compressed ugc videos. In: 2021 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia & Expo Workshops (ICMEW), pp 1–6. IEEE Computer Society
Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2011) Rred indices: Reduced reference entropic differencing for image quality assessment. IEEE Trans Image Process 21(2):517–526
Zhou W, Chen Z (2020) Deep local and global spatiotemporal feature aggregation for blind video quality assessment. In: 2020 IEEE International Conference on Visual Communications and Image Processing (VCIP), pp 338–341. IEEE
Hosu V, Hahn F, Jenadeleh M, Lin H, Men H, Szirányi T, Li S, Saupe D (2017) The konstanz natural video database (konvid-1k). In: 2017 Ninth International Conference on Quality of Multimedia Experience (QoMEX), pp 1–6. https://doi.org/10.1109/QoMEX.2017.7965673
Simonyan K, Zisserman A (2014) Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint arXiv:1409.1556
Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L-J, Li K, Fei-Fei L (2009) Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 248–255. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2009.5206848
Li H, Chen G, Li G, Yu Y (2019) Motion guided attention for video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, pp 7274–7283
Gao F, Yu J, Zhu S, Huang Q, Tian Q (2018) Blind image quality prediction by exploiting multi-level deep representations. Pattern Recogn 81:432–442
Fawaz HI, Lucas B, Forestier G, Pelletier C, Schmidt DF, Weber J, Webb GI, Idoumghar L, Muller P-A, Petitjean F (2020) Inceptiontime: Finding alexnet for time series classification. Data Min Knowl Disc 34(6):1936–1962
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 1–9
Ying Z, Mandal M, Ghadiyaram D, Bovik A (2021) Patch-vq:’patching up’the video quality problem. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 14019–14029
Sinno Z, Bovik AC (2019) Large-scale study of perceptual video quality. IEEE Trans Image Process 28(2):612–627. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2018.2869673
Ghadiyaram D, Pan J, Bovik AC, Moorthy AK, Panda P, Yang K-C (2018) In-capture mobile video distortions: A study of subjective behavior and objective algorithms. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst Video Technol 28(9):2061–2077. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCSVT.2017.2707479
Nuutinen M, Virtanen T, Vaahteranoksa M, Vuori T, Oittinen P, Hökkinen J (2016) Cvd 2014 a database for evaluating no-reference video quality assessment algorithms. IEEE Trans Image Process 25(7):3073–3086. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2016.2562513
Seshadrinathan K, Soundararajan R, Bovik A, Cormack L (2010) Study of subjective and objective quality assessment of video. IEEE Trans Image Process 19:1427–1441. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIP.2010.2042111
Kingma DP, Ba JL (2015) Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. In: ICLR 2015 : International Conference on Learning Representations 2015
Mittal A, Soundararajan R, Bovik AC (2013) Making a “completely blind’’ image quality analyzer. IEEE Signal Process Lett 20(3):209–212. https://doi.org/10.1109/LSP.2012.2227726
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China [2018] under Grant No. 61741124 and in part by the Science Planning Project of Guizhou Province under Grant No. QKHPTRC[2018]5781.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
There is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tan, Y., Kong, G., Duan, X. et al. No-reference Video Quality Assessment Based on Spatio-temporal Perception Feature Fusion. Neural Process Lett 55, 1317–1335 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10939-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11063-022-10939-x