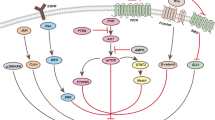
Abstract
We have previously demonstrated that bortezomib, a 26S proteasome inhibitor, effectively inhibits medulloblastoma growth in vivo in a genetically engineered Ptch1, p53 mouse model; however, bortezomib is also associated clinically with severe peripheral neuropathy, which would be disadvantageous for patients with central nervous system malignancy. The purpose of this study was to determine the mechanism of bortezomib efficacy in medulloblastoma in order to replicate more specifically the therapeutic advantage of targeting the ubiquitin-proteosome system. In our studies of upstream components of the ubiquitin–proteasome system, we identified the pro-apoptotic protein NOXA as a post-translationally modified target that is stabilized by bortezomib and induces caspase cleavage in the context of reactive oxidative stress induced cell death. These preclinical results may apply to the sizable fraction of Shh-driven human medulloblastoma and perhaps other medulloblastoma subtypes, independent of p53 status.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rutkowski S, Gerber NU, von Hoff K, Gnekow A, Bode U, Graf N, Berthold F, Henze G, Wolff JE, Warmuth-Metz M, Soerensen N, Emser A, Ottensmeier H, Deinlein F, Schlegel PG, Kortmann RD, Pietsch T, Kuehl J (2009) Treatment of early childhood medulloblastoma by postoperative chemotherapy and deferred radiotherapy. Neuro Oncol 11:201–210. doi:10.1215/15228517-2008-084
Packer RJ, Gajjar A, Vezina G, Rorke-Adams L, Burger PC, Robertson PL, Bayer L, LaFond D, Donahue BR, Marymont MH, Muraszko K, Langston J, Sposto R (2006) Phase III study of craniospinal radiation therapy followed by adjuvant chemotherapy for newly diagnosed average-risk medulloblastoma. J Clin Oncol 24:4202–4208. doi:10.1200/JCO.2006.06.4980
Gajjar A, Chintagumpala M, Ashley D, Kellie S, Kun LE, Merchant TE, Woo S, Wheeler G, Ahern V, Krasin MJ, Fouladi M, Broniscer A, Krance R, Hale GA, Stewart CF, Dauser R, Sanford RA, Fuller C, Lau C, Boyett JM, Wallace D, Gilbertson RJ (2006) Risk-adapted craniospinal radiotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy and stem-cell rescue in children with newly diagnosed medulloblastoma (St Jude Medulloblastoma-96): long-term results from a prospective, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol 7:813–820. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(06)70867-1
Lafay-Cousin L, Strother D (2009) Current treatment approaches for infants with malignant central nervous system tumors. Oncologist 14:433–444. doi:10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0193
Dahmane N, Ruiz i Altaba A (1999) Sonic hedgehog regulates the growth and patterning of the cerebellum. Development 126:3089–3100
Taniguchi E, Cho MJ, Arenkiel BR, Hansen MS, Rivera OJ, McCleish AT, Qualman SJ, Guttridge DC, Scott MP, Capecchi MR, Keller C (2009) Bortezomib reverses a post-translational mechanism of tumorigenesis for patched1 haploinsufficiency in medulloblastoma. Pediatr Blood Cancer 53:136–144. doi:10.1002/pbc.21968
Cavaletti G, Jakubowiak AJ (2010) Peripheral neuropathy during bortezomib treatment of multiple myeloma: a review of recent studies. Leuk Lymphoma 51:1178–1187. doi:10.3109/10428194.2010.483303
Uziel T, Zindy F, Xie S, Lee Y, Forget A, Magdaleno S, Rehg JE, Calabrese C, Solecki D, Eberhart CG, Sherr SE, Plimmer S, Clifford SC, Hatten ME, McKinnon PJ, Gilbertson RJ, Curran T, Sherr CJ, Roussel MF (2005) The tumor suppressors Ink4c and p53 collaborate independently with Patched to suppress medulloblastoma formation. Genes Dev 19:2656–2667. doi:10.1101/gad.1368605
Hosoyama T, Nishijo K, Garcia MM, Schaffer BS, Ohshima-Hosoyama S, Prajapati SI, Davis MD, Grant WF, Scheithauer BW, Marks DL, Rubin BP, Keller C (2010) A postnatal Pax7+ progenitor gives rise to pituitary. Adenomas Genes Cancer 1:388–402. doi:10.1177/1947601910370979
Prajapati SI, Kilcoyne A, Samano AK, Green DP, McCarthy SD, Blackman BA, Brady MM, Zarzabal LA, Tatiparthy AK, Sledz TJ, Duong T, Ohshima-Hosoyama S, Giles FJ, Michalek JE, Rubin BP, Keller C (2010) MicroCT-based virtual histology evaluation of preclinical medulloblastoma. Mol Imaging Biol doi:10.1007/s11307-010-0372-3
Samano AK, Ohshima-Hosoyama S, Whitney TG, Prajapati SI, Kilcoyne A, Taniguchi E, Morgan WW, Nelon LD, Lin AL, Togao O, Jung I, Rubin BP, Nowak BM, Duong TQ, Keller C (2010) Functional evaluation of therapeutic response for a mouse model of medulloblastoma. Transgenic Res 19:829–840. doi:10.1007/s11248-010-9361-1
Yauch RL, Dijkgraaf GJ, Alicke B, Januario T, Ahn CP, Holcomb T, Pujara K, Stinson J, Callahan CA, Tang T, Bazan JF, Kan Z, Seshagiri S, Hann CL, Gould SE, Low JA, Rudin CM, de Sauvage FJ (2009) Smoothened mutation confers resistance to a Hedgehog pathway inhibitor in medulloblastoma. Science 326:572–574. doi:10.1126/science.1179386
Sturla LM, Cowan CW, Guenther L, Castellino RC, Kim JY, Pomeroy SL (2005) A novel role for extracellular signal-regulated kinase 5 and myocyte enhancer factor 2 in medulloblastoma cell death. Cancer Res 65:5683–5689. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2283
Baou M, Kohlhaas SL, Butterworth M, Vogler M, Dinsdale D, Walewska R, Majid A, Eldering E, Dyer MJ, Cohen GM (2010) Role of NOXA and its ubiquitination in proteasome inhibitor-induced apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Haematologica 95:1510–1518. doi:10.3324/haematol.2010.022368
Aikawa T, Shinzawa K, Tanaka N, Tsujimoto Y (2010) Noxa is necessary for hydrogen peroxide-induced caspase-dependent cell death. FEBS Lett 584:681–688. doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2010.01.026
Argyriou AA, Iconomou G, Kalofonos HP (2008) Bortezomib-induced peripheral neuropathy in multiple myeloma: a comprehensive review of the literature. Blood 112:1593–1599. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-04-149385
Sun Y (2003) Targeting E3 ubiquitin ligases for cancer therapy. Cancer Biol Ther 2:623–629
Jia L, Yang J, Hao X, Zheng M, He H, Xiong X, Xu L, Sun Y (2010) Validation of SAG/RBX2/ROC2 E3 ubiquitin ligase as an anticancer and radiosensitizing target. Clin Cancer Res 16:814–824. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-1592
Pandit B, Gartel AL (2011) Proteasome inhibitors induce p53-independent apoptosis in human cancer cells. Am J Pathol 178:355–360. doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2010.11.010
Thompson MC, Fuller C, Hogg TL, Dalton J, Finkelstein D, Lau CC, Chintagumpala M, Adesina A, Ashley DM, Kellie SJ, Taylor MD, Curran T, Gajjar A, Gilbertson RJ (2006) Genomics identifies medulloblastoma subgroups that are enriched for specific genetic alterations. J Clin Oncol 24:1924–1931. doi:10.1200/JCO.2005.04.4974
Arastu-Kapur S, Anderl JL, Kraus M, Parlati F, Shenk KD, Lee SJ, Muchamuel T, Bennett MK, Driessen C, Ball AJ, Kirk CJ (2011) Non-proteasomal targets of the proteasome inhibitors bortezomib and carfilzomib: a link to clinical adverse events. Clin Cancer Res doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-1950
Parlati F, Lee SJ, Aujay M, Suzuki E, Levitsky K, Lorens JB, Micklem DR, Ruurs P, Sylvain C, Lu Y, Shenk KD, Bennett MK (2009) Carfilzomib can induce tumor cell death through selective inhibition of the chymotrypsin-like activity of the proteasome. Blood 114:3439–3447. doi:10.1182/blood-2009-05-223677
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by research grantsBrain Tumor from the National Brain Tumor Society and the Hyundai Motor Corporation Hope on Wheels Program. We thank Dr. Owen Lockerbie, Peter G. Smith and their colleagues at Millennium Pharmaceuticals for kindly providing MLN-4924. We are grateful to Drs. Richard Gilbertson and Martine Roussel for advice and guidance in the culture of primary medulloblastoma tumor cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Sachiko Ohshima-Hosoyama and Monika A. Davare contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima-Hosoyama, S., Davare, M.A., Hosoyama, T. et al. Bortezomib stabilizes NOXA and triggers ROS-associated apoptosis in medulloblastoma. J Neurooncol 105, 475–483 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0619-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0619-0