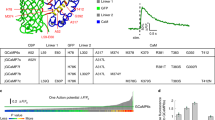
To date, intracellular calcium reporters are the most commonly used optical probes for detecting neuron activity. Synthetic low molecular weight and genetically encoded protein compounds provide an enormous variety of accessible methods for recording signals of different intensity at different levels of studying the nervous system, from detecting activity in synaptic boutons and dendritic spines to recording the activity of the central nervous system in free behavior in vivo. This paper presents a comparative description of methods for optical recording of changes in the intracellular calcium concentration and compares original experimental data obtained by each of the methods described. Advantages and drawbacks are described, and the potential areas of application of each of the commercially available and widely used types of calcium-sensitive reporters are outlined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams, P. J., Ben-Johny, M., Dick, I. E., et al., “Apocalmodulin itself promotes ion channel opening and Ca(2+) regulation,” Cell, 159, No. 3, 608–622 (2014).
Akerboom, J., Chen, T. W., Wardill, T. J., et al., “Optimization of a GCaMP calcium indicator for neural activity imaging,” J. Neurosci., 32, No. 40, 13,819–13,840 (2012).
Alexopoulou, A. N., Couchman, J. R., and Whiteford, J. R., “The CMV early enhancer/chicken beta actin (CAG) promoter can be used to drive transgene expression during the differentiation of murine embryonic stem cells into vascular progenitors,” BMC Cell Biol., 9, 2–2 (2008).
Barnett, L. M., Hughes, T. E., and Drobizhev, M., “Deciphering the molecular mechanism responsible for GCaMP6m’s Ca2+-dependent change in fluorescence,” PLoS One, 12, No. 2, e0170934 (2017).
Barykina, N. V., Subach, O. M., Doronin, D. A., et al., “A new design for a green calcium indicator with a smaller size and a reduced number of calcium-binding sites,” Sci. Rep., 6, No. 1, 34447 (2016).
Blockstein, L., Luk, C. C., Mudraboyina, A. K., et al., “A PVAc-based benzophenone-8 filter as an alternative to commercially available dichroic filters for monitoring calcium activity in live neurons via Fura-2 AM,” IEEE Photonics J., 4, No. 3, 1004–1012 (2012).
Canepari, M., Vogt, K., and Zecevic, D., “Combining voltage and calcium imaging from neuronal dendrites,” Cell. Mol. Neurobiol., 28, No. 8, 1079–1093 (2008).
Catterall, W. A., “Structure and regulation of voltage-gated Ca2+ channels,” Annu. Rev. Cell. Dev. Biol., 16, 521–555 (2000).
Chang, A., Abderemane-Ali, F., Hura, G. L., et al., “A calmodulin C-lobe Ca(2+)-dependent switch governs Kv7 channel function,” Neuron, 97, No. 4, 836–852 e6 (2018).
Chen, T.-W., Wardill, T. J., Sun, Y., et al., “Ultrasensitive fluorescent proteins for imaging neuronal activity,” Nature, 499, No. 7458, 295– 300 (2013).
Cong, L., Wang, Z., Chai, Y., et al., “Rapid whole brain imaging of neural activity in freely behaving larval zebrafish (Danio rerio),” eLife, 6, e28158 (2017).
Dana, H., Sun, Y., Mohar, B., et al., “High-performance calcium sensors for imaging activity in neuronal populations and microcompartments,” Nat. Methods, 16, No. 7, 649–657 (2019).
Dreosti, E., Odermatt, B., Dorostkar, M. M., and Lagnado, L., “A genetically encoded reporter of synaptic activity in vivo,” Nat. Methods, 6, No. 12, 883–889 (2009).
Fowler, C. J. and Tiger, G., “Calibration of Fura-2 signals introduces errors into measurement of thrombin-stimulated calcium mobilisation in human platelets,” Clin. Chim. Acta, 265, No. 2, 247–261 (1997).
Friedrich, R. W. and Korsching, S. I., “Combinatorial and chemotopic odorant coding in the zebrafish olfactory bulb visualized by optical imaging,” Neuron, 18, No. 5, 737–52 (1997).
Gleichmann, M. and Mattson, M. P., “Neuronal calcium homeostasis and dysregulation,” Antioxid. Redox. Signal., 14, No. 7, 1261–1273 (2011).
Grewe, B. F., Langer, D., Kasper, H., et al., “High-speed in vivo calcium imaging reveals neuronal network activity with near-millisecond precision,” Nat. Methods, 7, No. 5, 399–405 (2010).
Grienberger, C. and Konnerth, A., “Imaging calcium in neurons,” Neuron, 73, No. 5, 862–85 (2012).
Grynkiewicz, G., Poenie, M., and Tsien, R. Y., “A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties,” J. Biol. Chem., 260, No. 6, 3440–3450 (1985).
Heim, N. and Griesbeck, O., “Genetically encoded indicators of cellular calcium dynamics based on troponin C and green fluorescent protein,” J. Biol. Chem., 279, No. 14, 14,280–14,286 (2004).
Higley, M. J. and Sabatini, B. L., “Calcium signaling in dendritic spines,” Cold Spring Harb. Persp. Biol., 4, No. 4, a005686-a005686 (2012).
Hovis, K. R., Padmanabhan, K., and Urban, N. N., “A simple method of in vitro electroporation allows visualization, recording, and calcium imaging of local neuronal circuits,” J. Neurosci. Meth., 191, No. 1, 1–10 (2010).
Kemenes, I., Straub, V. A., Nikitin, E. S., et al., “Role of delayed nonsynaptic neuronal plasticity in long-term associative memory,” Curr. Biol., 16, No. 13, 1269–1279 (2006).
Koester, H. J. and Johnston, D., “Target cell-dependent normalization of transmitter release at neocortical synapses,” Science, 308, No. 5723, 863–866 (2005).
Kumada, T. and Komuro, H., “Completion of neuronal migration regulated by loss of Ca(2+) transients,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 101, No. 22, 8479–8484 (2004).
Lin, K., Sadée, W., and Quillan, J. M., “Rapid measurements of intracellular calcium using a fluorescence plate reader,” Biotechniques, 26, No. 2, 318–22, 324–6 (1999).
LoTurco, J., Manent, J.-B., and Sidiqi, F., “New and improved tools for in utero electroporation studies of developing cerebral cortex,” Cereb. Cortex, 19, Suppl. 1, i120–i125 (2009).
Mangialavori, I., Ferreira-Gomes, M., Pignataro, M. F., et al., “Determination of the dissociation constants for Ca2+ and calmodulin from the plasma membrane Ca2+ pump by a lipid probe that senses membrane domain changes,” J. Biol. Chem., 285, No. 1, 123–130 (2010).
Mao, T., O’Connor, D. H., Scheuss, V., et al., “Characterization and subcellular targeting of GCaMP-type genetically-encoded calcium indicators,” PLoS One, 3, No. 3, e1796 (2008).
Matlashov, M. E., Bogdanova, Y. A., Ermakova, G. V., et al., “Fluorescent ratiometric pH indicator SypHer2: Applications in neuroscience and regenerative biology,” Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1850, No. 11, 2318–2328 (2015).
Matthews, E. A. and Dietrich, D., “Buffer mobility and the regulation of neuronal calcium domains,” Front. Cell. Neurosci., 9, 48–48 (2015).
Mehta, P., Kreeger, L., Wylie, D. C., et al., “Functional access to neuron subclasses in rodent and primate forebrain,” Cell Rep., 26, No. 10, 2818–2832.e8 (2019).
Nakai, J., Ohkura, M., and Imoto, K., “A high signal-to-noise Ca(2+) probe composed of a single green fluorescent protein,” Nat. Biotechnol, 19, No. 2, 137–141 (2001).
Nikiti, E. S., Balaban, P. M., and Kemenes, G., “Nonsynaptic plasticity underlies a compartmentalized increase in synaptic efficacy after classical conditioning,” Curr. Biol., 23, No. 7, 614–619 (2013).
Nikitin, E. S., Zakharov, I. S., Samarova, E. I., et al., “Fine tuning of olfactory orientation behaviour by the interaction of oscillatory and single neuronal activity,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 22, No. 11, 2833–2844 (2005).
Osakada, F., Mori, T., Cetin, A. H., et al., “New rabies virus variants for monitoring and manipulating activity and gene expression in defined neural circuits,” Neuron, 71, No. 4, 617– (2011).
Roshchin, M. V., Matlashov, M. E., Ierusalimsky, V. N., et al., “A BK channel-mediated feedback pathway links single-synapse activity with action potential sharpening in repetitive firing,” Sci. Adv., 4, No. 7, eaat1357 (2018).
Ross, W. N., “Understanding calcium waves and sparks in central neurons,” Nat. Rev. Neurosci., 13, No. 3, 157–168 (2012).
Sah, P. and Clements, J. D., “Photolytic manipulation of [Ca2+]i reveals slow kinetics of potassium channels underlying the afterhyperpolarization in hippocampal pyramidal neurons,” J. Neurosci., 19, No. 10, 3657–3664 (1999).
Steinmetz, N. A., Buetfering, C., Lecoq, J., et al., “Aberrant cortical activity in multiple GCaMP6-expressing transgenic mouse lines,” eNeuro, 4, No. 5) (2017).
Storace, D. A., Braubach, O. R., Jin, L., et al., “monitoring brain activity with protein voltage and calcium sensors,” Sci. Rep., 5, No. 1, 10212 (2015).
Tervo, D. G., Hwang, B. Y., Viswanathan, S., et al., “A designer AAV variant permits efficient retrograde access to projection neurons,” Neuron, 92, No. 2, 372–382 (2016), https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.09.021 .
Tian, L., Hires, S. A., Mao, T., et al., “Imaging neural activity in worms, flies and mice with improved GCaMP calcium indicators,” Nat. Methods, 6, No. 12, 875–881 (2009).
van Den Pol, A. N., Mocarski, E., Saederup, N., et al., “Cytomegalovirus cell tropism, replication, and gene transfer in brain,” J. Neurosci., 19, No. 24, 10948–10965 (1999).
Wachowiak, M. and Cohen, L. B., “Representation of odorants by receptor neuron input to the mouse olfactory bulb,” Neuron, 32, No. 4, 723– 735 (2001).
Wang, S. S. and Augustine, G. J., “Confocal imaging and local photolysis of caged compounds: dual probes of synaptic function,” Neuron, 15, No. 4, 755–760 (1995).
Wang, T., Kumada, T., Morishima, T., et al., “Accumulation of GABAergic neurons, causing a focal ambient GABA gradient, and downregulation of KCC2 are induced during microgyrus formation in a mouse model of polymicrogyria,” Cereb. Cortex, 24, No. 4, 1088–1101 (2014).
Watakabe, A., Ohtsuka, M., Kinoshita, M., et al., “Comparative analyses of adeno-associated viral vector serotypes 1, 2, 5, 8 and 9 in marmoset, mouse and macaque cerebral cortex,” Neurosci. Res., 93, 144–157 (2015).
Wilson, J. M., Dombeck, D. A., Díaz-Ríos, M., et al., “Two-photon calcium imaging of network activity in XFP-expressing neurons in the mouse,” J. Neurophysiol., 97, No. 4, 3118–3125 (2007).
Yang, Y., Liu, N., He, Y., et al., “Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP,” Nat. Commun., 9, No. 1, 1504 (2018).
Zheng, K., Bard, L., Reynolds, J. P., et al., “Time-resolved imaging reveals heterogeneous landscapes of nanomolar Ca(2+) in neurons and astroglia,” Neuron, 88, No. 2, 277–288 (2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 72, No. 2, pp. 149–158, March–April, 2022.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nikitin, E.S., Roshchin, M.V., Borodinova, A.A. et al. Use of Optical Probes for Visualizing Intracellular Calcium and Recording Action Potentials in Neurons. Neurosci Behav Physi 52, 1212–1217 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01350-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-023-01350-7