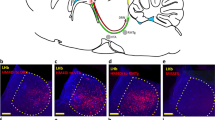
RNA interference studies using lentivirus transduction were performed to investigate the effects of decreased expression of dopamine receptors (D1R and D2R) in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala on the acquisition and extinction of conditioned defensive reflexes in rats. Immunohistochemical staining showed that transduction affected both neurons (mean 19%) and astrocytes (73%). As compared with controls, rats with decreased D1R expression showed degraded acquisition and facilitated extinction of a conditioned defensive reflex to sound, with acceleration of extinction of a passive avoidance reflex, and slowing of learning to seek a hidden platform in the Morris water maze by 1–2 days. In conditioned reflex fear, the behavior of rats with prolonged freezing changed more than that of rats with short periods of freezing when D1R expression in the amygdala was decreased. In rats with decreased D2R expression, extinction of the classical defensive reflex and the passive avoidance reflex was quicker. These results provide evidence of differences in the roles of D1R and D2R in the amygdala – functioning of D1R, in contrast to D2R, is important for acquisition of defensive refl exes and the manifestation of conditioned refl ex fear in the form of prolonged freezing. The activity of both D2R and D1R is significant for the resistance of reflexes to extinction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaguer, W., Capdevila, V., Ramirez, M., et al., “Post-training stimulation of the basolateral amygdale improves spatial learning in rats with lesion of the fimbria-fornix,” Restor. Neurol. Neurosci., 23, No. 1, 43–50 (2005).
Bananej, M., Karimi-Sori, A., Zarrindast, M. R., and Ahmadi, S., “D1 and D2 dopaminergic systems in the rat basolateral amygdale are involved in anxiogenic-like effects induced by histamine,” J. Psychopharmacol., 26, No. 4, 564–574 (2012).
Banerjee, A., Luong, J. A., Ho, A., et al., “Overexpression of Homer1a in the basal and lateral amygdala impairs fear conditioning and induces an autism-like social impairment,” Mol. Autism, 29, 7–16 (2016).
Cakir, T., Alsan S, Saybasili, H., et al., “Reconstruction and flux analysis of coupling between metabolic pathways of astrocytes and neurons: application to cerebral hypoxia,” Theor. Biol. Med. Model, 4, 48 (2007).
Chu, H. Y., Ito, W., Li, J., and Morozov, A., “Target-specifi c suppression of GABA release from parvalbumin interneurons in the basolateral amygdala by dopamine,” J. Neurosci., 32, No. 42, 14815–14820 (2012).
de la Mora, M. P., Gallegos-Cari, A., Arizmendi-García, Y., et al., “Role of dopamine receptor mechanisms in the amygdaloid modulation of fear and anxiety: Structural and functional analysis,” Prog. Neurobiol., 90, No. 2, 198–216 (2010).
de Solis, C. A., Holehonnur, R., Banerjee, A., et al., “Viral delivery of shRNA to amygdala neurons leads to neurotoxicity and defi cits in Pavlovian fear conditioning,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 124, 34–47 (2015).
de Souza Caetano, K. A., de Oliveira, A. R., and Brandão, M. L., “Dopamine D2 receptors modulate the expression of contextual conditioned fear: role of the ventral tegmental area and the basolateral amygdala,” Behav. Pharmacol., 24, No. 4, 264–274 (2013).
Dubrovina, N. I. and Zinov’eva, D. V., “Effects of activation and blockade of dopamine receptors on extinction of a passive avoidance reaction in mice with a depression-like state,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 58, No. 5, 605–610 (2008).
Dubrovina, N. I., “Effects of activation of D1 dopamine receptors on extinctionof a conditioned passive avoidance reaction and amnesia in aggressive and submissive mice,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 55, No. 4, 543–548 (2005).
Gafford, G. M., Guo, J. D., Flandreau, E. I., et al., “Cell-type specific deletion of GABA(A)α1 in corticotropin-releasing factor-containing neurons enhances anxiety and disrupts fear extinction,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 109, No. 40, 16330–16335 (2012).
Galliot, E., Levaillant, M., Beard, E., et al., “Enhancement of spatial learning by predator odor in mice: involvement of amygdale and hippocampus,” Neurobiol. Learn. Mem., 93, No. 2, 196–202 (2010).
Greba, Q. and Kokkinidis, L., “Peripheral and intraamygdalar administration of the dopamine D1 receptor antagonist SCH 23390 blocks fear-potentiated startle but not shock reactivity or the shock sensitization of acoustic startle,” Behav. Neurosci., 114, No. 2, 262–272 (2000).
Guarraci, F. A., Frohardt, R. J., and Kapp, B. S., “Amygdaloid D1 dopamine receptor involvement in Pavlovian fear conditioning,” Brain Res., 827, No. 1–2, 28–40 (1999).
Guarraci, F. A., Frohardt, R. J., Falls, W. A., and Kapp, B. S., “The effects of intra-amygdaloid infusions of a D2 dopamine receptor antagonist on Pavlovian fear conditioning,” Behav. Neurosci., 114, No. 3, 647–651 (2000).
Heldt, S. A., Zimmermann, K., Parker, K., et al., “BDNF deletion or TrkB impairment in amygdala inhibits both appetitive and aversive learning,” J. Neurosci., 34, No. 7, 2444–2450 (2014).
Inglis, F. M. and Moghaddam, B., “Dopaminergic innervation of the amygdala is highly responsive to stress,” J. Neurochem., 72, No. 3, 1088–1094 (1999).
Karasinska, J. M., George, S. R., El-Ghundi, M., et al., “Modifi cation of dopamine D(1) receptor knockout phenotype in mice lacking both dopamine D(1) and D(3) receptors,” Eur. J. Pharmacol., 399, No. 2–3, 171–181 (2000).
Kroner, S., Rosenkranz, J. A., Grace, A. A., and Barrionuevo, G., “Dopamine modulates excitability of basolateral amygdale neurons in vitro,” J. Neurophysiol., 93, No. 3, 1598–1610 (2005).
Lalumiere, R. T., Nguyen, L. T., and McGaugh, J. L., “Post-training intrabasolateral amygdale infusions of dopamine modulate consolidation of inhibitory avoidance memory: involvement of noradrenergic and cholinergic systems,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 20, No. 10, 2804–2810 (2004).
Lebedev, T. D., Spirin, P. V., and Prassolov, V. S., “Transfer and expression of small interfering RNAs in mammalian cells using lentiviral vectors,” Acta Naturae, 5, No. 2, 7–18 (2013).
LeDoux, J. E., “The amygdale,” Curr. Biol., 17, No. 20, 868–874 (2007).
Liu, Y. F., Chen, H. I., Wu, C. L., et al., “Differential effects of treadmill running and wheel running on spatial or aversive learning and memory: roles of amygdalar brain-derived neurotrophic factor and synaptotagmin I,” J. Physiol., 587, 3221–3231 (2009).
Mańko, M., Geracitano, R., and Capogna, M., “Functional connectivity of the main intercalated nucleus of the mouse amygdala,” J. Physiol., 589, No. Pt 8, 1911–1925 (2011).
Marowsky, A., Yanagawa, Y., Obata, K., Vogt, K. E., “A specialized subclass of interneurons mediates dopaminergic facilitation of amygdala function,” Neuron, 48, No. 6, 1025–1037 (2005).
Martina, M. and Bergeron, R., “D1 and D4 dopaminergic receptor interlay mediates coincident G protein-independent and dependent regulation of glutamate NMDA receptors in the lateral amygdale,” J. Neurochem., 106, No. 6, 2421–2435 (2008).
McNamara, R. K., Kirkby, R. D., dePape, G. E., and Corcoran, M. E., “Limbic seizures, but not kindling, reversibly impair place learning in the Morris water maze,” Behav. Brain Res., 50, No. 1–2, 167–175 (1992).
Nader, K. and LeDoux, J. E., “Inhibition of the mesoamygdala dopaminergic pathway impairs the retrieval of conditioned fear associations,” Behav. Neurosci., 113, No. 5, 891–901 (1999).
Nagatomo, K., Suga, S., Saitoh, M., et al., “Dopamine D1 receptor immunoreactivity on fine processes of GFAP-Positive astrocytes in the substantia nigra pars reticulata of adult mouse,” Front. Neuroanat., 11, No. 3, 1–11 (2017).
Naldini, L., Blomer, U., Gage, F. H., et al., “Effi cient transfer, integration, and sustained long-term expression of the transgene in adult rat brains injected with a lentiviral vector,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 93, No. 21, 11382–11388 (1996).
Pape, H. C., “GABAergic neurons: gate masters of the amygdale, mastered by dopamine,” Neuron, 48, No. 6, 1025–1037 (2005).
Pavlova, I. V., Rysakova, M. P., and Sergeeva, M. I., “Effects of blockade of D1 and D2 receptors in the basolateral amygdala on the behavior of rats with high and low levels of anxiety and fear,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 65, No. 4, 471–485 (2015).
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C., The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, Academic Press (1998).
Perez de la Mora, M., Gallegos-Cari, A., Crespo-Ramirez, M., et al., “Distribution of dopamine D(2)-like receptors in the rat amygdala and their role in the modulation of unconditioned fear and anxiety,” Neuroscience, 201, 252–66 (2012).
Peszely, L., Ollmann, T., Laszlo, K., et al., “Effects of ventral pallidal D1 dopamine receptor activation on memory consolidation in Morris water maze test,” Behav. Brain Res., 274, 211–218 (2014).
Pinto, A. and Sesack, S. R., “Ultrastructural analysis of prefrontal cortical inputs to the rat amygdale: spatial relationships to presumed dopamine axons and D1 and D2 receptors,” Brain Struct. Funct., 213, No. 1–2, 159–175 (2008).
Reuss, B., Lorenzen, A., and Unsicker, K., “Dopamine and epinephrine, but not serotonin, downregulate dopamine sensitivity in cultured cortical and striatal astroglial cells,” Recept. Chann., 7, No. 6, 441–451 (2001).
Salozhin, S. V. and Bol’shakov, A. P., “Transfection of nervous system cells,” Zh. Vyssh. Nerv. Deyat., 59, No. 1, 3–14 (2009).
Stuchlik, A., Rehakova, L., Telensky, P., and Vales, K., “Morris water maze learning in Long-Evans rats is differentially affected by blockade of D1-like and D2-like dopamine receptors,” Neurosci. Lett., 422, No. 3, 169–174 (2007).
Tukhbatova, G. R., Kuleshova, E. P., and Stepanichev, M. Yu., et al., “Optimization of a preparation of lentiviral particles for transduction of neurons in vivo,” Neurochem. J., 5, No. 4, 294–300 (2011).
Voller, J., Donek, A., Cendeln, J., et al., “The effect of D1-like receptor blockade on motor functions and spatial learning in B6CBA mice,” Prague Med. Rep., 109, No. 1, 32–39 (2008).
Vorhees, C. V. and Williams, M. T., “Assessing spatial learning and memory in rodents,” ILAR J., 55, No. 2, 310–333 (2014).
Wan, P., Wang, S., Zhang, Y., et al., “Involvement of dopamine D1 receptors of the hippocampal dentate gyrus in spatial learning and memory deficits in a rat model of vascular dementia,” Pharmazie, 69, No. 9, 709–710 (2014).
Xing, B., Kong, H., Meng, X., et al., “Dopamine D1 but not D3 receptor is critical for spatial learning and related signaling in the hippocampus,” Neuroscience, 169, No. 4, 1511–1519 (2010).
Yokoyama, M., Suzuki, E., Sato, T., et al., “Amygdalic levels of dopamine and serotonin rise upon exposure to conditioned fear stress without elevation of glutamate,” Neurosci. Lett., 379, No. 1, 37–41 (2005).
Zanassi, P., Paolillo, M., Montecucco, A., et al., “Pharmacological and molecular evidence for dopamine D(1) receptor expression by striatal astrocytes in culture,” J. Neurosci. Res., 58, No. 4, 544–552 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Translated from Zhurnal Vysshei Nervnoi Deyatel’nosti imeni I. P. Pavlova, Vol. 69, No. 2, pp. 194–210, March–April, 2019.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavlova, I.V., Rysakova, M.P., Spivak, J.S. et al. Effects of Decreases in Dopamine (D1 and D2) Receptor Expression in the Basolateral Amygdala of Rats on Conditioned Defensive Reflexes. Neurosci Behav Physi 50, 315–326 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-020-00903-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-020-00903-4