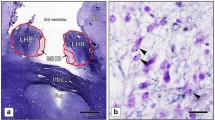
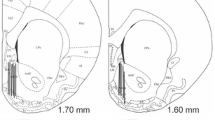
This is the first study reporting the locations of neurons expressing CART peptide (cocaine-amphetamineregulated transcript) throughout all the nuclear and paleocortical formations of the amygdaloid body (AB) and demonstrating the effects of sex steroids on immunoreactivity. The immunocytochemical reaction was performed on frontal brain sections from adult rats (seven females in estrus, seven females in metestrus, and seven males). The proportions of immunoreactive neurons to the total number of neurons in adjacent sections stained by the Nissl method were assessed in estrus and metestrus. In the dorsomedial and posterior cortical nuclei and the lateral capsular subnucleus of the central field, the relative numbers of immunoreactive neurons at estrus were significantly greater than at metestrus. These results provide evidence of the involvement of the olfactory and integrative centers of the AB in the pathogenesis of drug dependence and show that new and efficient methods of gene therapy might be developed using the intranasal route for drug administration.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
I. G. Akmaev and L. B. Kalimullina, The Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain: Functional Morphology and Neuroendocrinology [in Russian], Nauka, Moscow (1993).
I. G. Akmaev, L. B. Kalimullina, and L. A. Sharipov, “The central nucleus of the amygdaloid body of the brain: cytoarchitectonics, neuronal organization, connections,” Morfologiya, 123, No. 5, 515–523 (2003).
A. V. Akhmadeev, “Effects of the gender factor and neonatal androgenization on the dendroarchitectonics of neurons in the dorsomedial nucleus of the amygdaloid body of the brain,” Morfologiya, 129, No. 3, 30–33 (2006).
A. V. Akhmadeev and L. B. Kalimullina, “Dendroarchitectonics of neurons in the posterior cortical nucleus of the amygdaloid body of the rat brain in relation to the gender factor and neonatal androgenization,” Morfologiya, 125, No. 2, 22–25 (2004).
A. V. Akhmadeev and L. B. Kalimullina, “The ancient amygdala: cytoarchitectonics, organization and cytological characteristics of its neurons,” Morfologiya, 126, No. 5, 15–19 (2004).
A. V. Akhmadeev and L. B. Kalimullina, “Electron microscopic characteristics of neuroendrocrine neurons in the amygdaloid body of the brain in male and female rats at different stages of the estral cycle,” Morfologiya, 130, No. 6, 25–29 (2006).
E. D. Kholmskaya, Neuropsychology [in Russian], Pieter, Moscow (2006).
S. A. Chepurnov and N. E. Chepurnova, The Amygdaloid Complex of the Brain [in Russian], Moscow State University Press, Moscow (1981).
L. A. Sharipova, L. B. Kalimullina, and Z. R. Minibaeva, “The central nucleus of the amygdaloid complex of the brain: cytoarchitectonics, neuronal organization, and histophysiology,” Ross. Fiziol. Zh., 90, No. 2, 137–145 (2004).
J. C. Cavalcante, J. C. Brittencourt, and C. F. Elias, “Female odors stimulate CART neurons in the ventral premammillary nucleus of male rats,” Physiol. Behav., 88, No. 1–2, 160–166 (2006).
P. R. Coucevro, E. O. Koylu, and M. J. Kuhar, “Further studies on the anatomical distribution of CART by in situ hybridization,” J. Chem. Neuroanat., 12, No. 4, 229–241 (1997).
H. E. Covington, T. Kikusui, J. Goodhue, et al., “Brief social defeat stress: long-lasting effects of cocaine taking during a binge and zif268 mRNA expression in amygdala and prefrontal cortex,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 30, 310–321 (2005).
M. P. Danekar, P. S. Singru, D. M. Kokare, et al., “Importance of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide in central nucleus of amygdala in anxiogenic responses induced by ethanol withdrawal,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 32, No. 4, 546–556 (2007).
C. V. Dayas, T. M. McGranahan, R. Martin-Fardon, and F. Weiss, “Stimuli linked to ethanol availability activate hypothalamic CART and orexin neurons in a reinstatement model of relapse,” Biol. Psychiatry, 63, No. 2, 152–157 (2008).
R. Graghia, C. Caillaud, R. Manicom, et al., “Gene delivery into the central nervous system by nasal instillation in rats,” Gene Ther., 2, No. 7, 418–423 (1995).
G. Dominguez, A. Lakatos, and M. I. Kuhar, “Characterization of the cocaine- and amphetamine-related transcript (CART) peptide gene promoter and its activation by a cyclic AMP-dependent signaling pathway in GH3 cells,” J. Neurochem., 80, No. 5, 885–893 (2002).
J. Douglass, A. A. McKinzie, and P. Coucevro, “PCR differential display identifies a rat brain mRNA that is transcriptionally regulated by cocaine and amphetamine,” J. Neurosci., 15, No. 3, 2471–2481 (1995).
P. Fagergren and Y. Hurd, “CART mRNA expression in rat monkey and human brain: relevance to cocaine abuse,” Physiol. Behav., 92, No. 1–2, 218–225 (2007).
S. B. Floresco and M. T. Tse, “Dopaminergic regulation of inhibitory and excitatory transmission in the basolateral amygdala-prefrontal cortex pathway,” J. Neurosci., 27, No. 8, 2045–2057 (2007).
R. A. Fuchs, M. W. Feltenstein, and R. E. See, “The role of the basolateral amygdala in stimulus-reward memory and extinction memory consolidation and subsequent conditioned cued reinstatement of cocaine seeking,” Eur. J. Neurosci., 23, No. 10, 2809–2813 (2006).
G. W. Hubert, D. C. Jones, M. C. Moffett, et al., “CART peptides as modulators of dopamine and psychostimulants and interactions with the mesolimbic dopaminergic system,” Biochem. Pharmacol., 75, No. 1, 57–62 (2008).
R. G. Hunter, M. M. Lim, K. B. Philpot, et al., “Species differences in brain distribution of CART mRNA and CART peptide between prairie and meadow voles,” Brain Res., 1048, No. 1–2, 12–23 (2005).
S. K. Itaya, “Anterograde transsynaptic transport of WGA-HRP in the rat olfactory pathways,” Brain Res., 409, No. 7, 205–214 (1987).
E. O. Koylu, B. Balkan, M. J. Kuhar, and S. Pogun, “Cocaine and amphetamine regulated transcript (CART) and the stress response,” Peptides, 27, No. 8, 1956–1969 (2006).
G. Lazar, M. Calle, E. W. Roubos, et al., “Immunohistochemical localization of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript peptide in the central nervous system of the frog Rana esculenta,” J. Comp. Neurol., 477, No. 3, 324–339 (2004).
C. C. Ledford, R. A. Fuchs, and R. E. See, “Potentiated reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior following D-amphetamine infusion into the basolateral amygdala,” Neuropsychopharmacology, 28, No. 10, 1721–1729 (2003).
A. Salinas, J. D. Wilde, and R. E. Maldve, “Ethanol enhancement of cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript mRNA and peptide expression in the nucleus accumbens,” J. Neurochem., 97, No. 2, 578–591 (2006).
N. Vrang, “Anatomy of hypothalamic CART neurons,” Peptides, 27, No. 8, 1970–1980 (2006).
M. A. Williams, J. Turchan,Y. Lu, et al., “Protection of human cerebral neurons from neurodegenerative insults by gene delivery of soluble tumor necrosis factor p75 receptor,” Exp. Brain Res., 165, No. 9, 383–391 (2005).
Y. Xu, W. Zhang, J. Klaus, et al., “Role of cocaine- and amphetamine- regulated transcript in estradiol-mediated neuroprotection,” Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 103, No. 39, 14489–14494 (2006).
S. C. Yang and K. R. Shich, “Gonadal hormone-mediated effects on the stimulation of dopamine turnover in mesolimbic and nigrostriatal systems by cocaine- and amphetamine-regulated transcript (CART) peptide in male rats,” Neuropharmacology, 53, No. 7, 801–809 (2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Translated from Morfologiya, Vol. 135, No. 2, pp. 12–16, March–April, 2009.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akhmadeev, A.V. Localization of CART-Positive Neurons in the Amygdaloid Body and the Relationship between Their Immunoreactivity and the Sex Steroid Level. Neurosci Behav Physi 40, 435–439 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9275-7
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-010-9275-7