Abstract
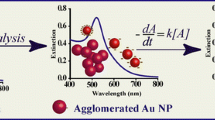
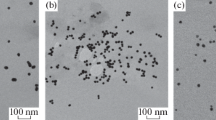
We have analyzed the titration process of gold nanoparticles with several amounts of protein A (0.3, 0.5, 1, 3, 6, and 9 μg/ml) in the presence of NaCl, which induces aggregation if the surface of particles is not fully covered with protein A. The colloidal solutions with different particle size (16, 18, 20, 33 nm) were synthesized by citrate reduction to be conjugated with protein A. UV–Visible spectroscopy was used to measure the absorption of the surface plasmon resonance of gold nanoparticles as a function of the concentration of protein A. Such dependence shows an aggregation region (0 < x<6 μg/ml), where the amount of protein A was insufficient to cover the surface of particles, obtaining aggregation caused by NaCl. The next part is the stability region (x ≥ 6 μg/ml), where the amount of protein used covers the surface of particles and protects it from the aggregation. In addition to that the ratio between the intensities of both: the aggregates and of the gold nanoparticle bands was plotted as a function of the concentration of protein A. It was determined that 6 μg/ml is a sufficient value of protein A to stabilize the gold nanoparticle–protein A system. This method provides a simple way to stabilize gold nanoparticles obtained by citrate reduction, with protein A.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alekseeva A, Bogatyrev V, Khlebtsov B, Melnikov A, Dykman L, Khlebtsov N (2006) Gold nanorods: synthesis and optical properties. Colloid J 68:661–678
Chen YM, Yu CJ, Cheng TL, Tseng WL (2008) Colorimetric detection of lysozyme based on electrostatic interaction with human serum albumin-modified gold nanoparticles. Langmuir 24(7):3654–3660
Dilan Q, Xiaoxiao H, Kemin W, Xiaojun JZ, Weihong T, Jiyun C (2007) Fluorescent nanoparticle-based indirect immunofluorescence microscopy for detection of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Biomed Biotechnol Article ID 89364: 9. doi:10.1155/2007/89364
Forsgren A (1970) Significance of protein A production by staphylococci. Infect Immun 2:672–673
Forsgren A, Sjöquist J (1966) Protein A from S. aureus. I. Pseudo-immune reaction with human 7-globulin. J Immunol 97:822–827
Goudswaard J, Van der Donk JA, Noordzij A, Van Dam RH, Vaerman JP (1978) Protein A reactivity of various mammalian immunoglobulins. Scand J Immunol 8:21–28
Haiss W, Thanh N, Aveyard J, Fernig D (2007) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from UV–Vis spectra. Anal Chem 79:4215–4221
Hayat MA (1989) Colloidal gold: principles, method and application, vol 1. Academic Press Inc, New York
Hermanson G (2008) Bioconjugate techniques. Academic Press Inc, San Diego
Horisberger M (1992) Colloidal gold and its application in cell biology. Int Rev Cytol Surv Cell Biol 136:227
Jennings T, Strouse G (2007) Past, present, and future of gold nanoparticles. bio-applications of nanoparticles: advances in experimental medicine and biology, vol. 620. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p 34
Khlebtsov N (2008) Determination of size and concentration of gold nanoparticles from extinction spectra. Anal Chem 80:6620–6625
Kimling J, Maier M, Okenve B, Kotaidis V, Ballot H, Plech A (2006) Turkevich method for gold nanoparticles synthesis revisited. J Phys Chem B 110:15700–15707
Langone JJ (1978) Protein A: a tracer for general use in immunoassay. J Immunol Methods 24:269–285
Langone JJ (1982) Protein A of Staphylococcus aureus and related immunoglobulin receptors produced by streptococci and pneumococci. Adv Immunol 32:157–252
Losin M, Toderas F, Baldeck PL, Astilean S (2009) Study of protein–gold nanoparticle conjugates by fluorescence and surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Mol Struct 924–926:196–200. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2009.02.004
Njoki P, Lim I, Mott D, Park H, Khan B, Mishra S, Sujakumar R, Luo J, Zhong C (2007) Size correlation of optical and spectroscopic properties for gold nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 111:14664–14669
Norde W (1986) Adsorption of proteins from solution at the solid–liquid interface. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 25:267
Patrick M, (2009) Microbiología Médica, 6 Ed (6a edición). Elsevier-Mosby, España p 209–223
Slot J, Geuze H (1984) Cold markers for single and double immunolabeling of ultrathin cryosections. In: Polak JM, Vardness IM (eds) Immunolabeling for electron microscopy. Elsevier, New York, p 139
Slouf M, Kuzel R, Matej Z (2006) Preparation and characterization of isomeric gold nanoparticles with precalculated size. Kristallogr Suppl 23:319–324
Smita T, Simon A, Robert B, Neelam K, James N, Mateusz S, Robert A, Porter (2010) Bioconjugation and characterisation of gold colloid-labelled proteins. J Immunol Methods 356:60–69. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2010.02.007
Sonvico F, Dubernet C, Colombo P, Couvreur P (2005) Metallic colloid nanotechnology, applications in diagnosis and therapeutics. Curr Pharm Des 11:2091
Wangoo N, Bhasin KK, Meht SK, Suri CR (2008). Synthesis and capping of water-dispersed gold nanoparticles by an amino acid: bioconjugation and binding studies. J Colloid Interface Sci. 323:247
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the financial support from Instituto Politecnico Nacional and Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ríos-Corripio, M.A., García-Pérez, B.E., Jaramillo-Flores, M.E. et al. UV–Visible intensity ratio (aggregates/single particles) as a measure to obtain stability of gold nanoparticles conjugated with protein A. J Nanopart Res 15, 1624 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1624-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1624-3