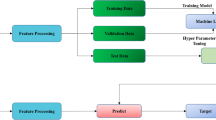
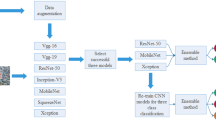
Abstract
The whole world is imposing efforts to combat the deadly COVID-19 virus that continues to have a disastrous effect on health, economy, education, transport & communication, and many other sectors. The crucial action taken to control its rapid spread is first to detect the infected person. Deep learning-based algorithms utilize mathematical models to detect Covid-19 cases. Deep learning approach is applied to track and diagnose Covid-19 and help radiologists and medical doctors enhance prognosis performance. X-ray images are popularly used deep learning methods for Covid-19 detection. However, the existing techniques suffer from several limitations that need to be addressed to detect Covid-19 cases more accurately: Firstly, there is a small number of Covid-19 images. Secondly, an unbalanced dataset. Thirdly, model overfitting, and fourthly, correct detection of Covid-19 and pneumonia cases sometimes does not provide accurate results because COVID-19 and pneumonia symptoms are similar. Therefore, this paper aimed to develop an automated solution to classify the detected Covid-19 into two classes to overcome the small and unbalanced dataset, and model overfitting problems. This study compared nine state-of-the-art CNN architectures through a transfer learning approach. Our approach achieved better results in comparison to the work done on this benchmark dataset yielding 99.86% accuracy with 99.9% recall using VGG-16 using deep learning model. The proposed framework presents a transfer learning technique to increase the performance of the deep learning-based Covid-19 detection method. Moreover, the Comparative evaluation presents that the proposed framework outperforms existing methods. Close results show that VGG-16 on a large dataset correctly identified COVID-19.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no publicly available datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study.
References
Alimadadi A, Aryal S, Manandhar I, Munroe PB, Joe B, Cheng X (2020) Artificial intelligence and machine learning to fight covid-19. Physiol Genomics 52(4):200–202. https://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00029.2020
Apostolopoulos ID, Mpesiana TA (2020) Covid-19: automatic detection from X-ray images utilizing transfer learning with convolutional neural networks. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 43(2):635–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13246-020-00865-4
Barstugan M, Ozkaya U, Ozturk S (2020) Coronavirus (COVID-19) classification using CT images by machine learning methods. arXiv 5:1–10
Brunese L, Mercaldo F, Reginelli A, Santone A (2020) Explainable deep learning for pulmonary disease and coronavirus COVID-19 detection from X-rays. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 196:105608. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2020.105608
Carbonneau M-A, Cheplygina V, Granger E, Gagnon G (2018) Multiple instance learning: a survey of problem characteristics and applications. Pattern Recognit 77:329–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2017.10.009
Cohen, JP (2020) Open database of covid-19 cases, https://github.com/ieee8023/covid-chestxray-dataset. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Farid AA, Selim GI, Khater HAA (2020) A novel approach of CT images feature analysis and prediction to screen for corona virus disease (COVID-19). Int J Sci Eng Res 11(03):1141–1149. https://doi.org/10.14299/ijser.2020.03.02
Ghoshal B, Tucker, A. (2020) Estimating uncertainty and interpretability in deep learning for coronavirus (COVID-19) detection. 1–14. http://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10769
Gozes O et al. (2020) Rapid AI development cycle for the coronavirus (COVID-19) Pandemic: Initial results for automated detection & patient monitoring using deep learning CT image analysis, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2003.05037. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Gunraj H, Wang L, Wong A (2020) COVIDNet-CT: A tailored deep convolutional neural network design for detection of COVID-19 Cases from Chest CT Images, pp. 1–12, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2009.05383. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Hall LO, Paul R, Goldgof DB, Goldgof GM (2020) Finding Covid-19 from chest x-rays using deep learning on a small dataset, pp. 1–8, [Online]. Available: http://arxiv.org/abs/2004.02060. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Han Z et al (2020) Accurate screening of COVID-19 using attention-based deep 3D multiple instance learning. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(8):2584–2594. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2020.2996256
Hasan MJ, Alom MS, Ali MS (2021) Deep learning based detection and segmentation of COVID-19 & pneumonia on chest x-ray image. In: 2021 international conference on information and communication technology for sustainable development (ICICT4SD), Dhaka, Bangladesh, pp 210–214. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICICT4SD50815.2021.9396878
Islam MZ, Islam MM, Asraf A (2020) A combined deep CNN-LSTM network for the detection of novel coronavirus (COVID-19) using X-ray images. Inf Med Unlocked 20:100412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100412
Kassania SH, Kassasni PH, Wesolowski MJ, Schneider KA, Deters R (2020) Automatic detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in X-ray and CT images: A machine learning based approach, arXiv, vol. 2019, pp. 1–18
Liao L, Li H, Shang W, Ma L (2022) An empirical study of the impact of Hyperparameter tuning and model optimization on the performance properties of deep neural networks. ACM trans. Softw. Eng. Methodol. 31, 3, article 53 (July 2022), 40 pages. https://doi.org/10.1145/3506695
Mooney P (2018) Chest X-Ray Images (Pneumonia), https://www.kaggle.com/paultimothymooney/chest-xraypneumonia. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Narin, A, Kaya, C, Pamuk, Z (2020) Department of Biomedical Engineering, Zonguldak Bulent Ecevit University, 67100, Zonguldak, Turkey. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:2003.10849. https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.10849. Accessed 15 Oct 2021
Nour, M, Cömert, Z, Polat, K (2020) A novel medical diagnosis model for COVID-19 infection detection based on deep features and Bayesian optimization. Appl Soft Comput J xxxx, 106580. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106580
Oh Y, Park S, Ye JC (2020) Deep learning COVID-19 features on CXR using limited training data sets. arXiv 39(8):2688–2700
Ozturk, T, Talo, M, Azra, E, Baran, U, Yildirim, O (2020) Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource Centre with free information in English and mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID- 19 . The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect , the company ’ s public news and information. Computers in Biology and Medicine, January
Rahimzadeh M, Attar A (2020) A modified deep convolutional neural network for detecting COVID-19 and pneumonia from chest X-ray images based on the concatenation of Xception and ResNet50V2. Inf Med Unlocked 19:100360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100360
Saha P, Sadi MS, Islam MM (2021) EMCNet: automated COVID-19 diagnosis from X-ray images using convolutional neural network and ensemble of machine learning classifiers. Inf Med Unlocked 22:100505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imu.2020.100505
Sethy PK, Behera SK, Ratha PK, Biswas P (2020) Detection of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) based on deep features and support vector machine. Int J Math Eng Manag Sci 5(4):643–651. https://doi.org/10.33889/IJMEMS.2020.5.4.052
Singh D, Kumar V, Vaishali, Kaur M (2020) Classification of COVID-19 patients from chest CT images using multi-objective differential evolution–based convolutional neural networks. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 39(7):1379–1389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-020-03901-z
Ucara F, Korkmaz D (2020) Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID- 19 . The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect , the company ’ s public news and information , January
Wang X, Peng Y, Lu L, Lu Z, Bagheri M, Summers RM (2017) ChestX-Ray8: Hospital-scale chest x-ray database and benchmarks on weakly-supervised classification and localization of common thorax diseases. In: 2017 IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition (CVPR), Honolulu, HI, USA, pp 3462–3471. https://doi.org/10.1109/CVPR.2017.369
Wu J, Chen X-Y, Zhang H, Xiong L-D, Lei H, Deng S-H (2019) Hyperparameter optimization for machine learning models based on Bayesian Optimization. J Electron Sci Technol 17(1):26–40. https://doi.org/10.11989/JEST.1674-862X.80904120
Yang L, Shami A (2020) On hyperparameter optimization of machine learning algorithms: theory and practice. Neurocomputing 415:295–316, ISSN 0925-2312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.061
Zhong L, Gong P, Biging GS (2012) Correlation of Chest CT and RT-PCR Testing in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: A Report of 1014 Cases 78, no. May, pp. 1–15
Zhou T, Li L, Bredell G, Li J, Unkelbach J, Konukoglu E (2023) Volumetric memory network for interactive medical image segmentation, Medical Image Analysis, Volume 83, 102599, ISSN 1361-8415, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2022.102599
Funding
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Khero, K., Usman, M. & Fong, A. Deep learning framework for early detection of COVID-19 using X-ray images. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 6883–6908 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15995-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-15995-6