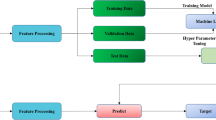
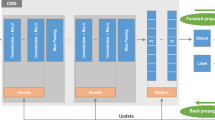
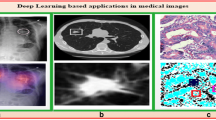
Abstract
Lung cancer is one of the deadliest cancers all over the world. One of the indications of lung cancers is the presence of the lung nodules which can appear individually or attached to the lung walls. The early detection of these nodules is crucial for saving the patient’s lives. Machine learning and image processing techniques, generally embedded in computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) systems, might help radiologists locate and assess the risk of these nodules. Accordingly, in this paper, we present a framework for identifying pulmonary nodules in lung CT images and a convolutional neural network (CNN) approach to automatically extract the features from lung images, followed by classifying the suspicious regions as either nodule or non-nodule objects. The proposed model is based on Le-Net architectural stylization and the light model is obtained after going through the innovative steps. A subset of LIDC public dataset including N = 7072 CT slices of varying nodule sizes (1 mm to 5 mm) is used to train and validate this approach. The proposed framework carries out all stages of lung segmentation as well as diagnosis and categorization of the existing nodules automatically. Training and validation steps of this network with configurations 2.4GHz Core i5 processor, 8GB memory, and Intel Graphics 520 are performed approximately in six hours and this system yields the performance with accuracy = 90.1%, sensitivity = 84.1%, specificity =91.7%, for identifying the nodules. Compared to other famous CNN architectures, the proposed model is agile (light and fast) and has appropriate performance, thereby is suitable for real-time medical image analysis.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affonso C, Sassi RJ, Barreiros RM (2015) Biological image classification using rough-fuzzy artificial neural network. Expert Syst Appl 42(24):9482–9488. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2015.07.075
Aghabalaei Khordehchi E, Ayatollahi A, Daliri MR (2017) Automatic lung nodule detection based on statistical region merging and support vector machines. Image Anal Stereol 36(2):65. https://doi.org/10.5566/ias.1679
Alakwaa W, Nassef M, Badr A (2017) Lung Cancer detection and classification with 3D convolutional neural network (3D-CNN). Int J Adv Comput Sci Appl 8(8). https://doi.org/10.14569/ijacsa.2017.080853
Alam M, Sankaranarayanan G, Devarajan V (2016) Lung Nodule Detection and Segmentation Using a Patch-Based Multi-Atlas Method. 2016 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI). https://doi.org/10.1109/csci.2016.0012.
Alilou M, Kovalev V, Snezhko E, Taimouri V (2014) A comprehensive framework for automatic detection of pulmonary nodules in lung ct images. Image Anal Stereol 33(1):13. https://doi.org/10.5566/ias.v33.p13-27
American Cancer Society, Cancer Facts and Figures (2015) https://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@editorial/documents/document/acspc-044552.pdf.
American Cancer Society, Key Statistics for Lung Cancer (2020) https://www.cancer.org/cancer/lung-cancer/about/key-statistics.html.
Amin SU, Alsulaiman M, Muhammad G, Mekhtiche MA, Shamim Hossain M (2019) Deep learning for EEG motor imagery classification based on multi-layer CNNs feature fusion. Futur Gener Comput Syst 101:542–554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2019.06.027
Armato SG, McLennan G, Bidaut L, McNitt-Gray MF, Meyer CR, Reeves AP, … Hoffman EA (2011) The lung image database consortium (LIDC) and image database resource initiative (IDRI): a completed reference database of lung nodules on CT scans. Med Phys 38(2):915–931. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.3528204
Bakator M, Radosav D (2018) Deep learning and medical diagnosis: a review of literature. Multimodal Technol Interact 2(3):47. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2030047
Bengio Y (2012) Deep learning of representations for unsupervised and transfer learning. In Proceedings of ICML workshop on unsupervised and transfer learning (pp. 17-36).
Cao J, Pang Y, Li X (2019) Triply Supervised Decoder Networks for Joint Detection and Segmentation. 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2019.00757.
De Carvalho Filho AO, Silva AC, de Paiva AC, Nunes RA, Gattass M (2018) Classification of patterns of benignity and malignancy based on CT using topology-based phylogenetic diversity index and convolutional neural network. Pattern Recogn 81:200–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.03.032
De Oliveira JEE (2011) Content-based image retrieval applied to BI-RADS tissue classification in screening mammography. World J Radiol 3(1):24–31. https://doi.org/10.4329/wjr.v3.i1.24
Dou Q, Chen H, Yu L, Qin J, Heng P-A (2017) Multilevel contextual 3-D CNNs for false positive reduction in pulmonary nodule detection. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 64(7):1558–1567. https://doi.org/10.1109/tbme.2016.2613502
Fragkiadaki K, Arbelaez P, Felsen P, Malik J (2015) Learning to segment moving objects in videos. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7299035.
Froz BR, de Carvalho Filho AO, Silva AC, de Paiva AC, Acatauassú Nunes R, Gattass M (2017) Lung nodule classification using artificial crawlers, directional texture and support vector machine. Expert Syst Appl 69:176–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2016.10.039
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology 278(2):563–577. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015151169
Glorot X, Bengio Y (2010) Understanding the difficulty of training deep feedforward neural networks. In Proceedings of the thirteenth international conference on artificial intelligence and statistics (pp. 249-256).
Greenspan H, van Ginneken B, Summers RM (2016) Guest editorial deep learning in medical imaging: overview and future promise of an exciting new technique. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1153–1159. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2016.2553401
Gruetzemacher R, Gupta A (2016) Using deep learning for pulmonary nodule detection & diagnosis.Twenty-second Americas Conference on Information Systems, San Diego.
Hassanpour H, Yousefian H, Zehtabi A (2011) Pixon-based image segmentation. Image Segmentation. https://doi.org/10.5772/15941.
Havaei M, Davy A, Warde-Farley D, Biard A, Courville A, Bengio Y, Pal C, Jodoin PM, Larochelle H (2017) Brain tumor segmentation with deep neural networks. Med Image Anal 35:18–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2016.05.004
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2015) Delving deep into rectifiers: surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 1026–1034. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2015.123.
He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J (2016) Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2016.90.
Heeneman T, Hoogendoorn M (2018) Lung nodule detection by using deep learning. University of Amsterdam, Research Paper.
Hossain MS, Muhammad G (2014) Cloud-based collaborative media service framework for HealthCare. Int J Distrib Sens Netw 10(3):858712. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/858712
Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S, Sun G, Wu E (2020) Squeeze-and-excitation networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 42(8):2011–2023. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2019.2913372
Ioffe S, Szegedy C (2015) Batch normalization: accelerating deep network training by reducing internal covariate shift. arXiv preprint arXiv:1502.03167.
Jacobs C, van Rikxoort EM, Murphy K, Prokop M, Schaefer-Prokop CM, van Ginneken B (2016) Computer-aided detection of pulmonary nodules: a comparative study using the public LIDC/IDRI database. Eur Radiol 26(7):2139–2147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-015-4030-7
Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton GE (2017) ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun ACM 60(6):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1145/3065386
Kumar D, Wong A, Clausi D A (2015) Lung nodule classification using deep features in CT images. 2015 12th conference on computer and robot vision, 133–138. https://doi.org/10.1109/crv.2015.25.
LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P (1998) Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proc IEEE 86(11):2278–2324. https://doi.org/10.1109/5.726791
Li S, Seybold B, Vorobyov A, Fathi A, Huang Q, Kuo C-CJ (2018) Instance Embedding Transfer to Unsupervised Video Object Segmentation. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2018.00683.
Li G, Xie Y, Wei T, Wang K, Lin L (2018) Flow Guided Recurrent Neural Encoder for Video Salient Object Detection. 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2018.00342.
Liang M, Tang W, Xu DM, Jirapatnakul AC, Reeves AP, Henschke CI, Yankelevitz D (2016) Low-dose CT screening for lung Cancer: computer-aided detection of missed lung cancers. Radiology 281(1):279–288. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016150063
Madero Orozco H, Vergara Villegas OO, Cruz Sánchez VG, Domínguez O, H. de J., & Nandayapa Alfaro, M. de J. (2015) Automated system for lung nodules classification based on wavelet feature descriptor and support vector machine. Biomed Eng Online 14(1):9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12938-015-0003-y
Monkam P, Qi S, Ma H, Gao W, Yao Y, Qian W (2019) Detection and classification of pulmonary nodules using convolutional neural networks: a survey. IEEE Access 7:78075–78091. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2019.2920980
Nithila EE, Kumar SS (2017) Automatic detection of solitary pulmonary nodules using swarm intelligence optimized neural networks on CT images. Eng Sci Technol, Int J 20(3):1192–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jestch.2016.12.006
Oudkerk M, Devaraj A, Vliegenthart R, Henzler T, Prosch H, Heussel CP, Bastarrika G, Sverzellati N, Mascalchi M, Delorme S, Baldwin DR, Callister ME, Becker N, Heuvelmans MA, Rzyman W, Infante MV, Pastorino U, Pedersen JH, Paci E, Duffy SW, de Koning H, Field JK (2017) European position statement on lung cancer screening. Lancet Oncol 18(12):e754–e766. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30861-6
Ozdemir O, Russell RL, Berlin AA (2020) A 3D probabilistic deep learning system for detection and diagnosis of lung Cancer using low-dose CT scans. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 39(5):1419–1429. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2019.2947595
Qian W, Song D, Lei M, Sankar R, Eikman E (2007) Computer-aided mass detection based on ipsilateral multiview mammograms. Acad Radiol 14(5):530–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2007.01.012
Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J (2017) Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 39(6):1137–1149. https://doi.org/10.1109/tpami.2016.2577031
Setio AAA, Ciompi F, Litjens G, Gerke P, Jacobs C, van Riel SJ, Wille MMW, Naqibullah M, Sanchez CI, van Ginneken B (2016) Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 35(5):1160–1169. https://doi.org/10.1109/tmi.2016.2536809
Severyn A, Moschitti A (2015) UNITN: training deep convolutional neural network for twitter sentiment classification. Proceedings of the 9th international workshop on semantic evaluation (SemEval 2015). https://doi.org/10.18653/v1/s15-2079.
Shen W, Zhou M, Yang F, Yang C, Tian J (2015) Multi-scale convolutional neural networks for lung nodule classification. Inform Process Med Imag 588–599. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-19992-4_46
Silveira M, Nascimento J, Marques, J (2007) Automatic segmentation of the lungs using robust level sets. 2007 29th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. https://doi.org/10.1109/iembs.2007.4353317.
Song Q, Zhao L, Luo X, Dou X (2017) Using deep learning for classification of lung nodules on computed tomography images. J Healthcare Eng 2017:8314740–8314747. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8314740
Song H, Wang W, Zhao S, Shen J, Lam K-M (2018) Pyramid dilated deeper ConvLSTM for video salient object detection. Lect Notes Comput Sci 744–760. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-01252-6_44.
Sun W, Tseng TL, Qian W, Zhang J, Saltzstein EC, Zheng B, Lure F, Yu H, Zhou S (2015) Using multiscale texture and density features for near-term breast cancer risk analysis. Med Phys 42(6):2853–2862. https://doi.org/10.1118/1.4919772
Sun W, Tseng TL, Zhang J, Qian W (2016) Computerized breast cancer analysis system using three stage semi-supervised learning method. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 135:77–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.07.017
Sun W, Huang X, Tseng T-L, Zhang J, Qian W (2016) Computerized lung cancer malignancy level analysis using 3D texture features. Medical Imaging 2016: Computer-Aided Diagnosis. https://doi.org/10.1117/12.2216329.
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, … Rabinovich A (2015) Going deeper with convolutions. 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). https://doi.org/10.1109/cvpr.2015.7298594.
Tajbakhsh N, Suzuki K (2017) Comparing two classes of end-to-end machine-learning models in lung nodule detection and classification: MTANNs vs. CNNs. Pattern Recogn 63:476–486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2016.09.029
Wang Y, Qiu Y, Thai T, Moore K, Liu H, Zheng B (2017) A two-step convolutional neural network based computer-aided detection scheme for automatically segmenting adipose tissue volume depicting on CT images. Comput Methods Prog Biomed 144:97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.03.017
Wang S, Zhou M, Liu Z, Liu Z, Gu D, Zang Y, Dong D, Gevaert O, Tian J (2017) Central focused convolutional neural networks: developing a data-driven model for lung nodule segmentation. Med Image Anal 40:172–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.media.2017.06.014
Wang B, Qi G, Tang S, Zhang L, Deng L, Zhang Y (2018) Automated pulmonary nodule detection: high sensitivity with few candidates. Lecture notes in computer science, 759–767. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-00934-2_84.
Wang W, Lu X, Shen J, Crandall DJ, Shao L (2019) Zero-shot video object segmentation via attentive graph neural networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision (pp. 9236-9245). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2019.00933.
Xie H, Yang D, Sun N, Chen Z, Zhang Y (2019) Automated pulmonary nodule detection in CT images using deep convolutional neural networks. Pattern Recogn 85:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.patcog.2018.07.031
Ypsilantis PP, Montana G (2016) Recurrent convolutional networks for pulmonary nodule detection in CT imaging. arXiv preprint arXiv:1609.09143.
Zhang J, Xia Y, Zeng H, Zhang Y (2018) Nodule: combining constrained multi-scale log filters with densely dilated 3D deep convolutional neural network for pulmonary nodule detection. Neurocomputing 317:159–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2018.08.022
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the potential reviewer’s for their constructive comments and suggestions that greatly contributed to improving this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Conflict of interest
Authors, Reza Majidpourkhoei, Mehdi Alilou, Kambiz Majidzadeh and Amin BabazadehSangar, declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majidpourkhoei, R., Alilou, M., Majidzadeh, K. et al. A novel deep learning framework for lung nodule detection in 3d CT images. Multimed Tools Appl 80, 30539–30555 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11066-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-021-11066-w