Abstract
The two- and three-dimensional incompressible backward stochastic convective Brinkman–Forchheimer (BSCBF) equations on a torus driven by Lévy noise are considered in this paper. A-priori estimates for adapted solutions of the finite-dimensional approximation of 2D and 3D BSCBF equations are obtained. For a given terminal data, the existence and uniqueness of pathwise adapted strong solutions is proved by using a standard Galerkin (or spectral) approximation technique and exploiting the monotonicity arguments. We also establish the continuity of the adapted solutions with respect to the terminal data. The above results are obtained for the absorption exponent \(r\in [1,\infty )\) for \(d=2\) and \(r\in [3,\infty )\) for \(d=3\), and any Brinkman coefficient \(\mu >0\), Forchheimer coefficient \(\beta >0\), and hence the 3D critical case (\(r=3\)) is also handled successfully. We deduce analogous results for 2D backward stochastic Navier–Stokes equations perturbed by Lévy noise also.
Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Notes
An \(\mathbb {H}\)-valued process X is optional if \(X:\Omega \times [0,T]\rightarrow \mathbb {H}\) is measurable with respect to the \(\sigma \)-algebra on \(\Omega \times [0,T]\) generated by the space of càdlàg
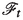 -adapted processes, and the Borel \(\sigma \)-algebra on \(\mathbb {H}\).
-adapted processes, and the Borel \(\sigma \)-algebra on \(\mathbb {H}\).
References
Antontsev, S.N., de Oliveira, H.B.: The Navier-Stokes problem modified by an absorption term. Appl. Anal. 89(12), 1805–1825 (2010)
Applebaum, D.: Lévy processes and stochastic calculus, Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics, Vol. 93, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (2004)
Al-Hussein, A.: Backward stochastic partial differential equations driven by infinite-dimensional martingales and applications. Stochastics 81(6), 601–626 (2009)
Bardos, C., Tartar, L.: Sur l’unicité retrograde des équations paraboliques et questions voisines. Arch. Ration. Mech. Anal. 50, 10–25 (1973)
Barbu, V., Röckner, M.: Backward uniqueness of stochastic parabolic like equations driven by Gaussian multiplicative noise. Stochastic Process. Appl. 126(7), 2163–2179 (2016)
Bessaih, H., Millet, A.: On stochastic modified 3D Navier-Stokes equations with anisotropic viscosity. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 462, 915–956 (2018)
Briand, P., Delyon, B., Hu, Y., Pardoux, E., Stoica, L.: \(L^p\) solutions of backward stochastic differential equations. Stochastic Process. Appl. 108, 109–129 (2003)
Brzeźniak, Z., Dhariwal, G.: Stochastic tamed Navier-Stokes equations on \(\mathbb{R}^3\): the existence and the uniqueness of solutions and the existence of an invariant measure, J. Math. Fluid Mech., 22, Ar. 23 (2020)
Brzeźniak, Z., Hausenblas, E., Razafimandimby, P.A.: Stochastic reaction-diffusion equations driven by jump processes. Potential Anal. 49, 131–201 (2018)
Brzeźniak, Z., Hausenblas, E., Zhu, J.: 2D stochastic Navier-Stokes equations driven by jump noise. Nonlinear Anal. 79, 122–139 (2013)
Burkholder, D.L.: The best constant in the Davis inequality for the expectation of the martingale square function. Trans. Am. Math. Soc. 354(1), 91–105 (2002)
Chen, S., Tang, S.: Semi-linear backward stochastic integral partial differential equations driven by a Brownian motion and a Poisson point process. Math. Control Relat. Fields 5(3), 401–434 (2015)
Da Prato, G., Zabczyk, J.: Stochastic Equations in Infinite Dimensions. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1992)
Davis, B.: On the integrability of the martingale square function. Israel J. Math. 8(2), 187–190 (1970)
Delbaen, F., Tang, S.: Harmonic analysis of stochastic equations and backward stochastic differential equations. Probab. Theory Related Fields 146, 291–336 (2010)
Delbaen, F., Qiu, J., Tang, S.: Forward-backward stochastic differential systems associated to Navier-Stokes equations in the whole space. Stochastic Process. Appl. 125(7), 2516–2561 (2015)
Dong, Z., Zhang, R.: 3D tamed Navier-Stokes equations driven by multiplicative Lévy noise: Existence, uniqueness and large deviations. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 492(1), 124404 (2020)
Du, K., Qiu, J., Tang, S.: \(L^p\) theory for super-parabolic backward stochastic partial differential equations in the whole space. Appl. Math. Optim. 65(2), 175–219 (2012)
Du, K., Tang, S.: Strong solution of backward stochastic partial differential equations in \(C^2\) domains. Probab. Theory Related Fields 154(1–2), 255–285 (2012)
Du, K., Tang, S., Zhang, Q.: \(W^{m, p}\)-solution (\(p\ge 2\)) of linear degenerate backward stochastic partial differential equations in the whole space. J. Differential Equations 254(7), 2877–2904 (2013)
Duffie, D., Epstein, L.: Stochastic differential utility. Econometrica 60, 353–394 (1992)
El Karoui, N., Mazliak, L.: Backward Stochastic Differential Equations. Longman, Harlow, HK (1997)
Farwig, R., Kozono, H., Sohr, H.: An \(L^q\)-approach to Stokes and Navier-Stokes equations in general domains. Acta Math. 195, 21–53 (2005)
Fefferman, C.L., Hajduk, K.W., Robinson, J.C.: Simultaneous approximation in Lebesgue and Sobolev norms via eigenspaces. Proc. Lond. Math. Soc. (3)125(4), 759–777 (2022)
Fernando, B.P.W., Sritharan, S.S.: Nonlinear filtering of stochastic Navier-Stokes equation with Itô-Lévy noise. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 31(3), 381–426 (2013)
Galdi, G.P.: An introduction to the Navier–Stokes initial-boundary value problem. pp. 11–70 in Fundamental directions in mathematical fluid mechanics. Adv. Math. Fluid Mech. Birkhaüser, Basel (2000)
Ghidaglia, J.M.: Some backward uniqueness results. Nonlinear Anal. TMA 10(8), 777–790 (1986)
Hajduk, K.W., Robinson, J.C.: Energy equality for the 3D critical convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. J. Differential Equations 263, 7141–7161 (2017)
Hong, Y.: Stochastic analysis of backward tidal dynamics equation. Commun. Stoch. Anal. 5(4), 745–768 (2011)
Hu, Y., Ma, J., Yong, J.: On semi-linear degenerate backward stochastic partial differential equations. Probab. Theory Related Fields 123, 381–411 (2002)
Hu, Y., Peng, S.: Adapted solution of a backward semilinear stochastic evolution equations. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 9, 445–459 (1991)
Ichikawa, A.: Some inequalities for martingales and stochastic convolutions. Stoch. Anal. Appl. 4(3), 329–339 (1986)
Ikeda, N., Watanabe, S.: Stochastic Differential Equations and Diffusion Processes. North-Holland Publishing Company, Amsterdam (1981)
Kalantarov, V.K., Zelik, S.: Smooth attractors for the Brinkman-Forchheimer equations with fast growing nonlinearities, Commun. Pure. Appl. Anal. 11, 2037–2054 (2012)
Kruse, T., Popier, A.: Lp-solution for BSDEs with jumps in the case \(p<2\): corrections to the paper ‘BSDEs with monotone generator driven by Brownian and Poisson noises in a general filtration’. Stochastics 89(8), 1201–1227 (2017)
Kukavica, I.: Log-log convexity and backward uniqueness. Proc. Amer. Math. Soc. 135(8), 2415–2421 (2007)
Kumar, P., Mohan, M.T.: Well-posedness of an inverse problem for two and three dimensional convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations with the final overdetermination. Inverse Probl. Imaging 16(5), 1255–1298 (2022)
Kumar, P., Mohan, M.T.: Existence, uniqueness and stability of an inverse problem for two-dimensional convective Brinkman–Forchheimer equations with the integral overdetermination. Banach J. Math. Anal. 16(4), Paper No. 58, 32 pp (2022)
Kunita, H.: Stochastic flows and jump-diffusions, Probability Theory and Stochastic Modelling, 92. Springer, Singapore (2019)
Ladyzhenskaya, O.A.: The Mathematical Theory of Viscous Incompressible Flow. Gordon and Breach, New York (1969)
Lions, J.L.: Optimal Control of Systems Governed by Partial Differential Equations. Springer, New York (1978)
Liu, H., Gao, H.: Stochastic 3D Navier-Stokes equations with nonlinear damping: martingale solution, strong solution and small time LDP, Chapter 2 in Interdisciplinary Mathematical SciencesStochastic PDEs and Modelling of Multiscale Complex System, 9–36 (2019)
Liu, W., Röckner, M.: Local and global well-posedness of SPDE with generalized coercivity conditions. J. Differ. Equ. 254, 725–755 (2013)
Liu, W., Zhu, R.: Well-posedness of backward stochastic partial differential equations with Lyapunov condition. Forum Math. 32(3), 723–738 (2020)
Ma, J., Yong, J.: Adapted solution of a degenerate backward SPDE, with applications. Stochastic Process. Appl. 70, 59–84 (1997)
Ma, J., Yong, J.: On linear, degenerate backward stochastic partial differential equations. Probab. Theory Related Fields 113, 135–170 (1999)
Ma, J., Protter, P., Yong, J.: Solving forward-backward stochastic differential equations explicitly: a four step scheme. Probab. Theory Related Fields 98, 339–359 (1994)
Markowich, P.A., Titi, E.S., Trabelsi, S.: Continuous data assimilation for the three-dimensional Brinkman-Forchheimer-extended Darcy model. Nonlinearity 29(4), 1292–1328 (2016)
Manna, U., Mohan, M.T., Sritharan, S.S.: Stochastic non-resistive magnetohydrodynamic system with Lévy noise. Random Oper. Stoch. Equ. 25(3), 155–194 (2017)
Menaldi, J.-L., Sritharan, S.S.: Stochastic 2-D Navier-Stokes equation. Appl. Math. Optim. 46(1), 31–53 (2002)
Métivier, M.: Stochastic partial differential equations in infinite-dimensional spaces. Quaderni, Scuola Normale Superiore, Pisa (1988)
Mohan, M.T.: On convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations, Submitted
Mohan, M.T.: Stochastic convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. arXiv:2007.09376
Mohan, M.T.: Well-posedness and asymptotic behavior of stochastic convective Brinkman–Forchheimer equations perturbed by pure jump noise. Stoch. PDE: Anal. Comp. 10, 614–690 (2022)
Mohan, M.T.: \({\mathbb{L}}^p\)-solutions of deterministic and stochastic convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations. Anal. Math. Phys. 11, Ar. No.: 164 (2021)
Mohan, M.T.: Martingale solutions of two and three dimensional stochastic convective Brinkman-Forchheimer equations forced by Lévy noise, Submitted. arXiv:2109.05510
Motyl, E.: Stochastic Navier-Stokes equations driven by Lévy noise in unbounded 3D domains. Potential Anal. 38, 863–912 (2013)
Oksendal, B., Sulem, A.: Applied Stochastic Control of Jump Diffusions, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2019)
Oksendal, B., Proske, F., Zhang, T.: Backward stochastic partial differential equations with jumps and application to optimal control of random jump fields. Stochastics 77(5), 381–399 (2005)
Pardoux, E., Peng, S.: Adapted solution of a backward stochastic differential equation. Syst. Control Lett. 14, 55–61 (1990)
Peszat, S., Zabczyk, J.: Stochastic Partial Differential Equations with Lévy Noise. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK (2007)
Pardoux, E., Rascanu, A.: Stochastic Differential Equations. Backward SDEs, Partial Differential Equations, Springer, Cham (2014)
Qiu, J., Tang, S., You, Y.: 2D backward stochastic Navier-Stokes equations with nonlinear forcing. Stochastic Process. Appl. 122(1), 334–356 (2012)
Robinson, J.C.: Infinite-Dimensional Dynamical Systems, An Introduction to Dissipative Parabolic PDEs and the Theory of Global Attractors, Cambridge Texts in Applied Mathematics (2001)
Robinson, J.C., Rodrigo, J.L., Sadowski, W.: The Three-Dimensional Navier-Stokes Equations. Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics, Cambridge University Press, Classical Theory (2016)
Robinson, J.C., Sadowski, W.: A local smoothness criterion for solutions of the 3D Navier-Stokes equations. Rend. Semin. Mat. Univ. Padova 131, 159–178 (2014)
Robinson, J.C.: Attractors and finite-dimensional behaviour in the 2D Navier-Stokes equations. ISRN Math. Anal. 2013, Art. ID 291823, 29 pp
Röckner, M., Zhang, X.: Tamed 3D Navier-Stokes equation: existence, uniqueness and regularity, Infin. Dimens. Anal. Quantum Probab. Relat. Top. 12, 525–549 (2009)
Röckner, M., Zhang, X.: Stochastic tamed 3D Navier-Stokes equation: existence, uniqueness and ergodicity. Probab. Theory Related Fields 145, 211–267 (2009)
Rong, S.: On solutions of backward stochastic differential equations with jumps and applications. Stochas. Process. Appl. 66, 209–236 (1997)
Rong, S.: Theory of Stochastic Differential Equations with Jumps and Applications. Springer, New York (2005)
Sakthivel, K., Sritharan, S.S., Sivaguru, S.: Martingale solutions for stochastic Navier-Stokes equations driven by Lévy noise. Evol. Equ. Control Theory 1(2), 355–392 (2012)
Sritharan, S.S.: An Introduction to Deterministic and Stochastic Control of Viscous Flow, Chapter in Optimal Control of Viscous Flow, 1–42. SIAM, Philadelphia, PA (1998)
Sritharan, S.S.: Deterministic and stochastic control of Navier-Stokes equation with linear, monotone, and hyperviscosities. Appl. Math. Optim. 41(2), 255–308 (2000)
Sritharan, S.S., Sundar, P.: Large deviations for the two-dimensional Navier-Stokes equations with multiplicative noise. Stochastic Process. Appl. 116, 1636–1659 (2006)
Sundar, P., Yin, H.: Existence and uniqueness of solutions to the backward stochastic Lorenz system. Commun. Stoch. Anal. 1(3), 473–483 (2007)
Sundar, P., Yin, H.: Existence and uniqueness of solutions to the backward 2D stochastic Navier-Stokes equations. Stochastic Process. Appl. 119, 1216–1234 (2009)
Tang, S.: Semi-linear systems of backward stochastic partial differential equations in \({\mathbb{R} }^n\). Chin. Ann. Math. Ser. B 26, 437–456 (2005)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations. Theory and Numerical Analysis, North-Holland, Amsterdam (1984)
Temam, R.: Navier–Stokes Equations and Nonlinear Functional Analysis, 2nd Edition, CBMS-NSF Regional Conference Series in Applied Mathematics (1995)
Yao, S.: \({\mathbb{L} }^p\) solutions of backward stochastic differential equations with jumps. Stochastic Process. Appl. 127(11), 3465–3511 (2017)
Yong, J., Zhou, X.Y.: Stochastic Controls-Hamiltonian Systems and HJB Equations. Springer, New York (1999)
Zhang, J.: Backward Stochastic Differential Equations. Springer, New York (2017)
Zhou, Q., Ren, Y., Wu, W.: On solutions to backward stochastic partial differential equations for Lévy processes., J. Comput. Appl. Math.235(18), 5411–5421 (2011)
Acknowledgements
M. T. Mohan would like to thank the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Govt of India for Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE) Faculty Award (IFA17-MA110). The author is extremely thankful for the insightful comments and recommendations provided by the reviewers that have enabled them to enhance the quality of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author has no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mohan, M.T. Existence and Uniqueness of Solutions to Backward 2D and 3D Stochastic Convective Brinkman–Forchheimer Equations Forced by Lévy Noise. Math Phys Anal Geom 26, 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11040-023-09458-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11040-023-09458-5
Keywords
- Backward stochastic convective Brinkman–Forchheimer equations
- Strong solution
- Itô’s formula
- Galerkin approximation
- Monotonicity



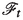 -adapted processes, and the Borel
-adapted processes, and the Borel