Abstract
In this paper, we study the user association problem to minimize the total energy cost for a green heterogeneous network with hybrid energy supplies. The power consumption of a BS in both the access network and the backhaul links are modeled. We formulate a constrained total energy cost minimization problem, which is generally hard to tackle. We propose a centralized algorithm that exploits the available context-aware information of the network, including the network architecture knowledge, users’ data requirements, and available green energy, to find a feasible and near-optimal solution. Since it is difficult to collect all information in a heterogeneous network, we also propose a distributed algorithm based on the available context-aware information of each BS’s own. Simulations are used to compare our algorithms with the maximum channel gain (MCG) algorithm and the max-RSRP algorithm. Results demonstrate that the proposed context-aware user association algorithms can significantly reduce the total energy cost.








Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Without specifically stated, a BS can be either a macro BS or pico BS.
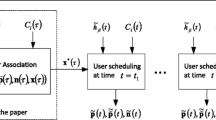
The initialization of the current decision epoch can be simply set as the association scheme in the last interval.
References
Fehske A, Fettweis G, Malmodin J, Biczok G (2011) The global footprint of mobile communications: the ecological and economic perspective. Commun Mag 49(8):55–62
XiaofeiWang A, Vasilakos V, Chen M, Liu Y, Kwon TT (2012) A survey of green mobile networks: opportunities and challenges. Mobile Netw Appl 17(1):4–20
Yang M, Li Y, Jin D, Zeng L, Wu X, Vasilakos AV (2015) Software-defined and virtualized future mobile and wireless networks: a survey. ACM/Springer Mobile Netw Appl 20(1):4–18
Lpez-Prez D, Chu X, Vasilakos AV, Claussen H (2013) On distributed and coordinated resource allocation for interference mitigation in self-organizing lte networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Netw 21(4):1145–1158
Andrews JG (2013) Seven ways that hetnets are a cellular paradigm shift. IEEE Commun Mag 51(3):136–144
Yao Y, Cao Q, Vasilakos AV (2013) Edal: an energy-efficient, delay-aware, and lifetime-balancing data collection protocol for wireless sensor networks. In: 2013 IEEE 10th international conference on mobile ad-hoc and sensor systems
Xiang L, Luo J, Vasilakos A (2011) Compressed data aggregation for energy efficient wireless sensor networks. In: 2011 8th annual IEEE communications society conference on sensor, mesh and ad hoc communications and networks
Zeng Y, Xiang K, Li D, Vasilakos AV (2013) Directional routing and scheduling for green vehicular delay tolerant networks. Wireless Netw 19(2):161–173
Damnjanovic A, Montojo J, Wei Y, Ji T, Luo T, Vajapeyam M, Yoo T, Song O, Malladi D (2011) A survey on 3gpp heterogeneous networks. IEEE Wireless Commun 18(3):10–21
Khan MA, Tembine H, Vasilakos AV (2012) Game dynamics and cost of learning in heterogeneous 4g networks. IEEE J Select Areas Commun 30(1):198–213
Demestichas PP, Stavroulaki V-AG, Papadopoulou L-MI, Vasilakos AV, Theologou ME (2004) Service configuration and traffic distribution in composite radio environments. IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybern Part C 34(1):69–81
Dhillon HS, Ganti RK, Baccelli F, Andrews JG (2012) Modeling and analysis of k-tier downlink heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE J Selected Areas Commun 30(3):550–560
Lpez-Prez D, Chu X, Vasilakos AV, Claussen H (2014) Power minimization based resource allocation for interference mitigation in ofdma femtocell networks. IEEE J Selected Areas Commun 32(2):333–344
Rao JB, Fapojuwo AO (2014) A survey of energy efficient resource management techniques for multicell cellular networks. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 16(1):154–180
Wang S, Ge M, Zhao W (2013) Energy-efficient resource allocation for ofdm-based cognitive radio networks. IEEE Trans Commun 61(8):3181–3191
Soh YS, Quek TQS, Kountouris M, Shin H (2013) Energy efficient heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE J Selected Area Commun 31(5):840–850
Tipmongkolsilp O, Zaghloul S, Jukan A (2011) The evolution of cellular backhaul technologies: current issues and future trends. IEEE Communi Surv Tutor 13(1):97–113
Li H, Attar A, Leung VCM (2012) Energy conservation via antenna scheduling in fiber-connected femto base stations. Mobile Netw Appl 17(5):685–694
Tombaz S, Monti P, Farias F, Fiorani M, Wosinska L, Zander J (2014) Is backhaul becoming a bottleneck for green wireless access networks? In: IEEE ICC
Han T, Ansari N (2013) On optimizing green energy utilization for cellular networks with hybrid energy supplies. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 12(8):3872–3882
Piro G, Miozzo M, Forte G, Baldo N, Grieco LA, Boggia G, Dini P (2013) Hetnets powered by renewable energy sources: sustainable next-generation cellular networks. IEEE Int Comput 17(1):32– 39
Hu C, Gong J, Wang X, Zhou S, Niu Z (2014) Optimal green energy utilization in mimo systems with hybrid energy supplies. IEEE Trans Veh Technol
E-plus launches germanys first zero-co2, off-grid base station, Available: http://nsn.com/news-events/publications/unite-magazine-issue-10/e-plus-launches-germany-s-first-zero-co2-off-grid-base-station
Saraydar CU, Mandayam NB, Goodman DJ (2001) Pricing and power control in a multicell wireless data network. IEEE J Selected Area Commun 19(10):1883–1892
Koizumi T, Higuchi K (2013) Simple decentralized cell association method for heterogeneous networks in fading channel. In: IEEE vehicular technology conference
Oh J, Han Y (2012) Cell selection for range expansion with almost blank subframe in heterogeneous networks. In: IEEE 23rd international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications (PIMRC), pp 669–673
Jo H-S, Sang YJ, Xia P, Andrews JG (2012) Heterogeneous cellular networks with flexible cell association: a comprehensive downlink sinr analysis. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 11(10):3484–3495
Lee J-W, Mazumdar RR, Shroff NB (2006) Joint resource allocation and base-station assignment for the downlink in cdma networks. IEEE J Selected Area Commun 14(1):1–14
Corroy S, Falconetti L, Mathar R (2012) Dynamic cell association for downlink sum rate maximization in multi-cell heterogeneous networks. In: IEEE ICC
Pervaiz H, Musavian L, Ni Q (2013) Joint user association and energy-efficient resource allocation with minimum-rate constraints in two-tier hetnets. In: IEEE 24th international symposium on personal, indoor and mobile radio communications: MAC and cross-layer design track
Ye Q, Rong B, Chen Y, Al-Shalash M, Caramanis C, Andrews JG (2013) User association for load balancing in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 12(6):2706–2716
Sanjabi M, Razaviyayn M, Luo Z-Q (2014) Optimal joint base station assignment and beamforming for heterogeneous networks. IEEE Trans Signal Process 62(8):1950–1961
Jin Y, Qiu L (2013) Jonit user association and interference coordination in heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE Commun Lett 17(12):2296–2299
Shen K, Yu W (2014) Distributed pricing-based user association for downlink heterogeneous cellular networks. IEEE J Selected Area Commun 32(6):1100–1114
Son K, Kim H, Yi Y, Krishnamachari B (2011) Base station operation and user association mechanisms for energy-delay tradeoffs in green cellular networks. IEEE J Selected Area Commun 29(8):1525–1536
Mishra S, Rangineni S, Murthy CSR (2014) Exploiting an optimal user association strategy for interference management in hetnets. IEEE Commun Lett 18(10):1799–1802
Zhou J, Li M, Liu L, She X, Chen L (2010) Energy source aware target cell selection and coverage optimization for power saving in cellular networks. In: IEEE/ACM int. conf. green comput. commun., int. conf. cyber, physical social comput
Gong J, Thompson JS, Zhou S, Niu Z (2014) Base station sleeping and resource allocation in renewable energy powered cellular networks. IEEE Trans Commun 62(11):3801–3813
Shaddad R, Mohammad AB, Al-Gailani SA, Al-hetar AM, Elmagzoub MA (2014) A survey on access technologies for broadband optical and wireless networks. J Netw Comput Appl 41(1):459–472
Galeana-Zapin H, Ferrs R (2010) Design and evaluation of a backhaul-aware base station assignment algorithm for of dma-based cellular networks. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 9(10):3226–3237
Olmos JJ, Ferrús R, Galeana-Zapién H (2013) Analytical modeling and performance evaluation of cell selection algorithms for mobile networks with backhaul capacity constraints. IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 12(12):6011–6023
Mesodiakaki A, Adelantado F, Alonso L, Verikoukis C (2014) Energy-efficient context-aware user association for outdoor small cell heterogeneous networks. In: IEEE ICC
Auer G, Giannini V, Desset C, Godor I, Skillermark P, Olsson M, Imran MA, Sabella D, Gonzalez MJ, Blume O, Fehske A (2011) How much energy is needed to run a wireless network? IEEE Trans Wireless Commun 18(5):40–49
Huang K-C, Wang Z (2011) Millimeter wave communication systems. Wiley IEEE Press
Yen Y-S, Chao H-C, Chang R-S, Vasilako A (2011) Flooding-limited and multi-constrained qos multicast routing based on the genetic algorithm for manets. Math Comput Modell 53(11-12):2238–2250
3GPP TR36.814, Further advancements for E-UTRA physical layer aspects
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No: 61371141) and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. HUST2015QN081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Kong, Q. & Yang, L.T. Context-Aware User Association for Energy Cost Saving in a Green Heterogeneous Network with Hybrid Energy Supplies. Mobile Netw Appl 20, 802–816 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-015-0621-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11036-015-0621-4