Abstract
Background
The Northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) is an economically important, and popular game bird in North America. Northern bobwhites have experiencing declines of > 3.5% annually in recent decades due to several factors. The eyeworm Oxyspirura petrowi is a nematode parasite frequently found in the eyes of bobwhites. Although reported frequently in wild bobwhites, there is no research to understand the host-parasite mechanism. Hence, it is important to investigate mechanisms of eyeworm invasion and immune modulation in bobwhite. Cytokine gene expression using RT-PCR is widely used to identify the innate immune response of a host to an infection.
Methodology
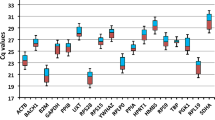
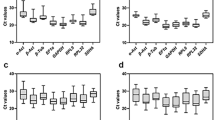
In this study, we evaluated ten reference genes (HMBS, RPL19, RPL32, RPS7, RPS8, TATA, SDHA, YWHAZ, GAPDH, and ACTB) for their stability across three tissues (liver, spleen, and caecal tonsils) of control and O. petrowi infected Northern bobwhites. Primer efficiency and reference genes stability were assessed using GeNorm, NormFinder, and BestKeeper.
Results
Expression of these reference genes with respect to O. petrowi infection in bobwhites showed RPL32 and HMBS were the most stable genes in the liver, HMBS and SDHA were the most stable genes in the spleen, and HMBS and YWHAZ were equally stable reference genes in the caecal tonsils.
Conclusion
Based on the geometric mean of all three analyses, our results indicate that the combination of RPL32 and HMBS for the liver, HMBS and SDHA for the spleen, and YWHAZ and HMBS for caecal tonsils might be used as reference genes for normalization in gene expression investigations on Northern bobwhites.

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the author upon reasonable request.
References
Johnson JL, Rollins D, Reyna KS (2012) What’s a quail worth? A longitudinal assessment of quail hunter demographics, attitudes, and spending habits in Texas. Proc. Natl. Quail Symposium 7:294–299. https://doi.org/10.7290/nqsp070m8p
Rollins D (2007) Quails on the rolling plains. In: Brennan L (ed) Texas quails: Ecology and Management, 1st edn. Texas A&M University, College Station, USA, pp 117–141
Hernández F, Brennan LA, DeMaso SJ, Sands JP, Wester DB (2013) On reversing the Northern bobwhite decline: 20 years later. Wildl Soc Bull 37:177–188. https://doi.org/10.1002/wsb.223
Bruno A (2014) Survey for Trichomonas Gallinae and Assessment of Helminth Parasites in Northern Bobwhites from the Rolling Plains Ecoregion. Thesis, Texas A&M University-Kingsville
Dunham N, Soliz LA, Fedynich AM, Rollins D, Kendall RJ (2014) Evidence of an Oxyspirura petrowi epizootic in northern bobwhites (Colinus virginianus), Texas, USA. J Wildl Dis 50:552–558. https://doi.org/10.7589/2013-10-275
Sauer J, Niven D, Hines J, Ziolkowski D Jr, Pardieck KL, Fallon JE, Link W (2017) The North American breeding bird survey, results and analysis 1966–2015. https://www.mbr-pwrc.usgs.gov/bbs/specl15.html. Accessed 11 October 2021
Dunham NR, Peper ST, Downing C, Brake E, Rollins D, Kendall RJ (2016) Infection levels of eyeworm Oxyspirura Petrowi and caecal worm Aulonocephalus pennula in the Northern bobwhite and scaled quail from the Rolling Plains of Texas. J Helminthol 91:569–577. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X16000663
Xiang L, Guo F, Yu Y, Parson LS, LaCoste L, Gibson A, Presley SM, Peterson M, Craig TM, Rollins D, Fedynich AM, Zhu G (2017) Multiyear survey of Coccidia, Cryptosporidia, Microsporidia, Histomona, and Hematozoa in Wild Quail in the Rolling Plains Ecoregion of Texas and Oklahoma, USA. J Eukaryot Microbiol 64:4–17. https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12330
Bruno A, Rollins D, Wester DB, Fedynich AM (2019) Helminth survey of the Northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) from the Rolling Plains of Texas, USA. Comp Parasitol 86:10–16. https://doi.org/10.1654/1525-2647-86.1.10
Herzog JL, Lukashow-Moore SP, Brym MZ, Kalyanasundaram A, Kendall RJ (2021) A Helminth Survey of Northern Bobwhite Quail (Colinus virginianus) and passerines in the Rolling Plains Ecoregion of Texas. J Parasitol 107:132–137. https://doi.org/10.1645/20-137
Dunham NR, Peper ST, Downing C, Brake E, Rollins D, Kendall R (2017) Infection levels of the eyeworm Oxyspirura Petrowi and caecal worm Aulonocephalus pennula in the northern bobwhite and scaled quail from the Rolling Plains of Texas. J Helminthol 91:569–577. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0022149X16000663
Dunham NR, Peper ST, Baxter CE, Kendall RJ (2014) The parasitic eyeworm Oxyspirura Petrowi as a possible cause of decline in the threatened lesser prairie-chicken (Tympanuchus pallidicinctus). PLoS ONE 9, e108244
Brym MZ, Henry C, Kendall RJ (2018) Elevated parasite burdens as a potential mechanism affecting northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) population dynamics in the Rolling Plains of West Texas. Parasitol Res 117:1683–1688. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-018-5836-4
Bruno A, Fedynich AM, Smith-Herron A, Rollins D (2015) Pathological response of northern bobwhites to Oxyspirura Petrowi infections. J Parasitol 101:364–368. https://doi.org/10.1645/14-526.1
Dunham NR, Reed S, Rollins D, Kendall RJ (2016) Oxyspirura Petrowi infection leads to pathological consequences in Northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus). Int J or Parasitol: Parasites Wildl 5:273–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijppaw.2016.09.004
Deist MS, Lamont SJ (2018) What makes the harderian gland transcriptome different from other chicken immune tissues? A gene expression comparative analysis. Front Physiol 9:492. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00492
Giulietti A, Overbergh L, Valckx D, Decallonne B, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2001) An overview of real-time quantitative PCR: applications to quantify cytokine gene expression. Methods 4:386–401. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1261
Kalyanasundaram A, Blanchard KR, Henry BJ, Henry C, Brym MZ, Kendall RJ (2019) Quantitative analysis of Northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) cytokines and TLR expression to eyeworm (Oxyspirura Petrowi) and caecal worm (Aulonocephalus pennula) glycoproteins. Parasitol Res 118:2909–2918. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-019-06418-3
Overbergh L, Giulietti A, Valckx D, Decallonne R, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2003) The use of real-time reverse transcriptase PCR for the quantification of cytokine gene expression. J Biomol Tech 14:33–43
Guénin S, Mauriat M, Pelloux J, Van Wuytswinkel O, Bellini C, Gutierrez L (2009) Normalization of qRT-PCR data: the necessity of adopting a systematic, experimental conditions-specific, validation of references. J Exp Bot 60:487–493. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/ern305
Adeola F (2018) Normalization of Gene expression by quantitative RT-PCR in human cell line: comparison of 12 endogenous reference genes. Ethiop J Health Sci 28:741–748. https://doi.org/10.4314/ejhs.v28i6.9
Kozera B, Rapacz M (2013) Reference genes in real-time PCR. J Appl Genet 54:391–406. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13353-013-0173-x
Cabiati M, Raucci S, Caselli C, Guzzardi MA, D’Amico A, Prescimone T, Giannessi D, Del Ry S (2012) Tissue-specific selection of stable reference genes for real-time PCR normalization in an obese rat model. J Mol Endocrinol 48:251–260. https://doi.org/10.1530/jme-12-0024
Bär M, Bär D, Lehmann B (2009) Selection and validation of candidate housekeeping genes for studies of human keratinocytes–review and recommendations. J Invest Dermatol 129:535–537. https://doi.org/10.1038/jid.2008.428
Selvey S, Thompson EW, Matthaei K, Lea RA, Irving MG, Griffiths LR (2001) β-Actin—an unsuitable internal control for RT-PCR. Mol Cell Probes 15:307–311. https://doi.org/10.1006/mcpr.2001.0376
Glare EM, Divjak M, Bailey MJ, Walters EH (2002) β-Actin and GAPDH housekeeping gene expression in asthmatic airways is variable and not suitable for normalising mRNA levels. Thorax 57:765–570. https://doi.org/10.1136/thorax.57.9.765
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55:611–622. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2008.112797
Eisenberg E, Levanon EY (2013) Human housekeeping genes, revisited. Trends Genet 29:569–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tig.2013.05.010
Kalyanasundaram A, Henry BJ, Henry C, Kendall RJ (2021) Molecular phylogenetic and in silico analysis of glyceraldeyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene from northern bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus). Mol Biol Rep 48:1093–1101. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06186-3
Carvalho AV, Couroussé N, Crochet S, Coustham V (2019) Identification of reference genes for quantitative gene expression studies in three tissues of Japanese quail. Genes 10:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030197
de Sousa FCB, do Nascimento CS, Macário MS et al (2021) Selection of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR normalization in European quail tissues. Mol Biol Rep 48:67–76. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-06134-7
Commons KA, Blanchard KR, Brym MZ, Henry C, Kalyanasundaram A, Skinner K, Kendall RJ (2019) Monitoring Northern Bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) populations in the Rolling Plains of Texas: parasitic infection implications. Rangel Ecol Manag 72:796–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rama.2019.04.004
Kalyanasundaram A, Brym MZ, Blanchard KR, Henry C, Skinner K, Henry BJ, Herzog JL, Hay A, Kendall RJ (2019) Life-cycle of Oxyspirura Petrowi (Spirurida: Thelaziidae), an eyeworm of the northern bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus). Parasit Vectors 12:555–565. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13071-019-3802-3
Kistler WM, Parlos JA, Peper ST, Dunham NR, Kendall RJ (2016) A quantitative PCR protocol for detection of Oxyspirura Petrowi in Northern bobwhites (Colinus virginianus). PLoS ONE 11. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166309
Kalyanasundaram A, Blanchard KR, Henry C, Brym M, Kendall RJ (2018) Development of a multiplex quantitative PCR assay for eyeworm (Oxyspirura Petrowi) and caecal worm (Aulonocephalus pennula) detection in Northern Bobwhite quail (Colinus virginianus) of the Rolling Plains Ecoregion, Texas. Vet Parasit 253:65–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2018.02.031
Halley YA, Dowd SE, Decker JE, Seabury PM, Bhattarai E, Johnson CD, Rollins D, Tizard IR, Brightsmith DJ, Peterson MJ, Taylor JF, Seabury CM (2014) A draft De Novo Genome Assembly for the Northern Bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) reveals evidence for a Rapid decline in Effective Population size beginning in the late pleistocene. PLoS ONE 9:e90240. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0090240
Oldeschulte DL, Halley YA, Wilson ML, Bhattarai EK, Brashear W, Hill J, Metz RP, Johnson CD, Rollins D, Peterson MJ, Bickhart DM, Decker JE, Sewell JF, Seabury CM (2017) Annotated draft genome assemblies for the Northern Bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) and the scaled quail (Callipepla squamata) reveal Disparate estimates of Modern Genome Diversity and historic effective Population size, G3 genes, genomes. Genetics 7:3047–3058. https://doi.org/10.1534/g3.117.043083
Olias P, Adam I, Meyer A, Scharff C, Gruber AD (2014) Reference genes for quantitative gene expression studies in multiple avian species. PLoS ONE 9:e99678. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0099678
Ginzinger DG (2002) Gene quantification using real-time quantitative PCR: an emerging technology hits the mainstream. Exp Hematol 30:503–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0301-472X(02)00806-8
Vandesompele J, Preter KD, Pattyn F, Poppe B, VanRoy N, De Paepe A, Speelman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome bio 3. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2002-3-7-research0034
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper–Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26:509–515. https://doi.org/10.1023/B:BILE.0000019559.84305.47
Andersen CL, Jensen JL, Orntoft TF (2004) Normalization of real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR data: a model-based variance estimation approach to identify genes suited for normalization, applied to bladder and colon cancer data sets. Cancer Res 64:5245–5250. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0496
Li YP, Bang DD, Handberg KJ, Jorgensen PH, Zhang MF (2005) Evaluation of the suitability of six host genes as internal control in real-time RT-PCR assays in chicken embryo cell cultures infected with infectious bursal disease virus. Vet Microbiolog 110(3–4):155–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetmic.2005.06.014
Zinzow-Kramer WM, Horton BM, Maney DL (2014) Evaluation of reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR in the brain, pituitary, and gonads of songbirds. Horm Behav 66(2):267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2014.04.011
Bagés S, Estany J, Tor M, Pena RN (2015) Investigating reference genes for quantitative real-time PCR analysis across four chicken tissues. Gene 561(1):82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2015.02.016
Nascimento CS, Barbosa LT, Brito C, Fernandes RPM, Mann RS, Pinto APG et al (2015) Identification of suitable reference genes for real time-quantitative polymerase chain reaction assays on Pectoralis major muscle in Chicken (Gallus gallus). PLoS ONE 10(5):e0127935. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0127935
Cooper D, Eleftherianos I (2016) Parasitic nematode immunomodulatory strategies: recent advances and perspectives. Pathog 5(3):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens5030058
Dung DT, Hop NT, Tho TH, Nawa Y, Doanh PN (2020) Pruritic cutaneous nematodiasis caused by avian eyeworm Oxyspirura larvae. Vietnam Emerg Infecti dis 26(4):786. https://doi.org/10.3201/eid2604.191592
Kalyanasundaram A, Bastille MO, Lukashow-Moore SP, Kendall RJ (2020) Avian and emerging human oxyspirura species compared by morphology, pathogenicity, Intermediate Host, and sequence homology. J Parasit 106(5):623–624. https://doi.org/10.1645/20-106
Funding
This research received funding and support from Park Cities Quail and the Rolling Plains Quail Research Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K., B.J.H., C.H., and R.J.K. contributed equally to experimental design. A.K and B.J.H. contributed equally to experimental work and analysis and J.Leach contributed to data analysis. A.K and J.L contributed equally to the first draft of the manuscript and all authors provided edits and comments on all versions. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical statement.
This experiment was approved by Texas Tech University Animal Care and Use Committee under protocols 18044-05 and 16071-08. All bobwhites were trapped and handled according to Texas Parks and Wildlife permit SRPT-0715-095.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
.
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kalyanasundaram, A., Henry, B.J., Henry, C. et al. Selection of suitable reference genes for normalization of RT-qPCR in three tissues of Northern bobwhite (Colinus virginianus) infected with eyeworm (Oxyspirura petrowi). Mol Biol Rep 51, 483 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09401-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-024-09401-z