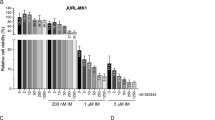
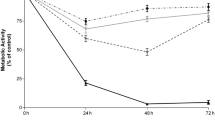
Abstract
Background
Due to its remarkable efficacy in producing hematologic, cytogenetic, and molecular remissions, the FDA approved Imatinib as the first-line treatment for newly diagnosed Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) patients. However, in some patients, failure to completely eradicate leukemic cells and the escape of these cells from death will lead to the development of resistance to Imatinib, and many are concerned about the prospects of this Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor (TKI). It has been documented that the compensatory overexpression of c-Myc is among the most critical mechanisms that promote drug efflux and resistance in CML stem cells.
Methods
In order to examine the potential of c-Myc inhibition through the use of 10058-F4 to enhance the anti-leukemic properties of Imatinib, we conducted trypan blue and MTT assays. Additionally, we employed flow cytometric analysis and qRT-PCR to assess the effects of this combination on cell cycle progression and apoptosis.
Results
The findings of our study indicate that the combination of 10058-F4 and Imatinib exhibited significantly stronger anti-survival and anti-proliferative effects on CML-derived-K562 cells in comparison to either agent administered alone. It is noteworthy that these results were also validated in the CML-derived NALM-1 cell line. Molecular analysis of this synergistic effect revealed that the inhibition of c-Myc augmented the efficacy of Imatinib by modulating the expression of genes related to cell cycle, apoptosis, autophagy, and proteasome.
Conclusions
Taken together, the findings of this investigation have demonstrated that the suppression of the c-Myc oncoprotein through the use of 10058-F4 has augmented the effectiveness of Imatinib, suggesting that this amalgamation could offer a fresh perspective on an adjunctive treatment for individuals with CML. Nevertheless, additional scrutiny, encompassing in-vivo examinations and clinical trials, is requisite.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goldman JM (ed) (2010) Editor chronic myeloid leukemia: a historical perspective. Seminars in hematology. Elsevier
Coppo P, Flamant S, Mas VD, Jarrier P, Guillier M, Bonnet ML, Lacout C, Guilhot F, Vainchenker W, Turhan AG (2006) BCR–ABL activates STAT3 via JAK and MEK pathways in human cells. Br J Haematol 134(2):171–179
Li Q, Wu Y, Fang S, Wang L, Qi H, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Li W (2015) BCR/ABL oncogene-induced PI3K signaling pathway leads to chronic myeloid leukemia pathogenesis by impairing the immuno-modulatory function of hemangioblasts. Cancer Gene Ther 22(5):227–237
Szeto M (2017) Mechanisms of RAS/MAPK signaling by BCR-ABL1 in chronic myeloid leukemia. UCSF
Mihailovic T, Marx M, Auer A, Van Lint J, Schmid M, Weber C, Seufferlein T (2004) Protein kinase D2 mediates activation of nuclear factor κB by bcr-abl in bcr-abl + human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res 64(24):8939–8944
Poudel G, Tolland MG, Hughes TP, Pagani IS (2022) Mechanisms of resistance and implications for treatment strategies in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Cancers 14(14):3300
Zehtabcheh S, Yousefi AM, Salari S, Safa M, Momeny M, Ghaffari SH, Bashash D (2021) Abrogation of histone deacetylases (HDACs) decreases survival of chronic myeloid leukemia cells: New insight into attenuating effects of the PI3K/c-Myc axis on panobinostat cytotoxicity. Cell Biol Int 45(5):1111–1121
Lin CY, Lovén J, Rahl PB, Paranal RM, Burge CB, Bradner JE, Lee TI, Young RA (2012) Transcriptional amplification in tumor cells with elevated c-Myc. Cell 151(1):56–67
García-Gutiérrez L, Delgado MD, León J (2019) MYC oncogene contributions to release of cell cycle brakes. Genes 10(3):244
Madden SK, de Araujo AD, Gerhardt M, Fairlie DP, Mason JM (2021) Taking the myc out of cancer: toward therapeutic strategies to directly inhibit c-Myc. Mol Cancer 20(1):1–18
Abraham SA, Hopcroft LE, Carrick E, Drotar ME, Dunn K, Williamson AJ, Korfi K, Baquero P, Park LE, Scott MT (2016) Dual targeting of p53 and c-MYC selectively eliminates leukaemic stem cells. Nature 534(7607):341–346
Levens D (2008) How the c-myc promoter works and why it sometimes does not. J Natl Cancer Inst Monogr 2008(39):41–43
Miller DM, Thomas SD, Islam A, Muench D, Sedoris K (2012) c-Myc and cancer metabolism. Clin Cancer Res 18(20):5546–5553
Xie S, Lin H, Sun T, Arlinghaus RB (2002) Jak2 is involved in c-Myc induction by bcr-abl. Oncogene 21(47):7137–7146
Notari M, Neviani P, Santhanam R, Blaser BW, Chang J-S, Galietta A, Willis AE, Roy DC, Caligiuri MA, Marcucci G (2006) A MAPK/HNRPK pathway controls BCR/ABL oncogenic potential by regulating MYC mRNA translation. Blood 107(6):2507–2516
Oudat R, Khan Z, Glassman AB (2001) Detection of Trisomy 8 in Philadelphia chromosome–positive CML Patients using conventional cytogenetic and interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization techniques and its relation to c-myc involvement. Annals of Clinical & Laboratory Science 31(1):68–74
Fletcher S, Prochownik EV (2015) Small-molecule inhibitors of the myc oncoprotein. Biochimica Et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms. 1849(5):525–543
Wang J, Ma X, Jones HM, Chan LL-Y, Song F, Zhang W, Bae-Jump VL, Zhou C (2014) Evaluation of the antitumor effects of c-Myc-Max heterodimerization inhibitor 100258-F4 in ovarian cancer cells. J Translational Med 12:1–11
Ghaffarnia R, Nasrollahzadeh A, Bashash D, Nasrollahzadeh N, Mousavi SA, Ghaffari SH (2021) Inhibition of c-Myc using 10058-F4 induces anti-tumor effects in ovarian cancer cells via regulation of FOXO target genes. Eur J Pharmacol 908:174345
Zhang M, Fan H-Y, Li S-C (2015) Inhibition of c-Myc by 10058-F4 induces growth arrest and chemosensitivity in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Biomed Pharmacother 73:123–128
Lin C-P, Liu J-D, Chow J-M, Liu C-R, Liu HE (2007) Small-molecule c-Myc inhibitor, 10058-F4, inhibits proliferation, downregulates human telomerase reverse transcriptase and enhances chemosensitivity in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Anticancer Drugs 18(2):161–170
Guo J, Parise RA, Joseph E, Egorin MJ, Lazo JS, Prochownik EV, Eiseman JL (2009) Efficacy, pharmacokinetics, tisssue distribution, and metabolism of the Myc–Max disruptor, 10058-F4 [Z, E]-5-[4-ethylbenzylidine]-2-thioxothiazolidin-4-one, in mice. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63:615–625
Müller I, Larsson K, Frenzel A, Oliynyk G, Zirath H, Prochownik EV, Westwood NJ, Henriksson MA (2014) Targeting of the MYCN protein with small molecule c-MYC inhibitors. PLoS ONE 9(5):e97285
Holien T, Misund K, Olsen OE, Baranowska KA, Buene G, Børset M, Waage A, Sundan A (2015) MYC amplifications in myeloma cell lines: correlation with MYC-inhibitor efficacy. Oncotarget 6(26):22698
Cinar M, Rosenfelt F, Rokhsar S, Lopategui J, Pillai R, Cervania M, Pao A, Cinar B, Alkan S (2015) Concurrent inhibition of MYC and BCL2 is a potentially effective treatment strategy for double hit and triple hit B-cell lymphomas. Leuk Res 39(7):730–738
Albajar M, Gómez-Casares MT, Llorca J, Mauleon I, Vaqué JP, Acosta JC, Bermúdez A, Donato N, Delgado MD, León J (2011) MYC in chronic myeloid leukemia: induction of aberrant DNA synthesis and association with poor response to ImatinibMYC and Response to Imatinib in Chronic myeloid LeukemiaMYC and response to Imatinib in Chronic myeloid leukemia. Mol Cancer Res 9(5):564–576
Chen C, Gao H, Su X (2021) Autophagy-related signaling pathways are involved in cancer. Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine 22(1):1–13
Annunziata I, van de Vlekkert D, Wolf E, Finkelstein D, Neale G, Machado E, Mosca R, Campos Y, Tillman H, Roussel MF (2019) MYC competes with MiT/TFE in regulating lysosomal biogenesis and autophagy through an epigenetic rheostat. Nat Commun 10(1):3623
Toh PP, Luo S, Menzies FM, Rasko T, Wanker EE, Rubinsztein DC (2013) Myc inhibition impairs autophagosome formation. Hum Mol Genet 22(25):5237–5248
Ahmadi SE, Rahimi S, Zarandi B, Chegeni R, Safa M (2021) MYC: a multipurpose oncogene with prognostic and therapeutic implications in blood malignancies. J Hematol Oncol 14:1–49
Fu Z, Tindall D (2008) FOXOs, cancer and regulation of apoptosis. Oncogene 27(16):2312–2319
Zhang X, Tang N, Hadden TJ, Rishi AK, Akt (2011) FoxO and regulation of apoptosis. Biochim et Biophys Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Res 1813(11):1978–1986
Mani A, Gelmann EP (2005) The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway and its role in cancer. J Clin Oncol 23(21):4776–4789
Saavedra-García P, Martini F, Auner HW (2020) Proteasome inhibition in multiple myeloma: lessons for other cancers. Am J Physiology-Cell Physiol 318(3):C451–C62
Oyaizu H, Adachi Y, Okumura T, Okigaki M, Oyaizu N, Taketani S, Ikebukuro K, Fukuhara S, Ikehara S (2001) Proteasome inhibitor 1 enhances paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cell line. Oncol Rep 8(4):825–829
Alves R, Gonçalves AC, Rutella S, Almeida AM, De Las Rivas J, Trougakos IP, Sarmento Ribeiro AB (2021) Resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukemia—from molecular mechanisms to clinical relevance. Cancers 13(19):4820
Soverini S, Bernardi S, Galimberti S (2020) Molecular testing in CML between old and new methods: are we at a turning point? J Clin Med 9(12):3865
Gabay M, Li Y, Felsher DW (2014) MYC activation is a hallmark of cancer initiation and maintenance. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine 4(6):a014241
Whitfield JR, Soucek L (2021) The long journey to bring a myc inhibitor to the clinic. J Cell Biol 220(8):e202103090
Wu S-X, Xiong R-G, Huang S-Y, Zhou D-D, Saimaiti A, Zhao C-N, Shang A, Zhang Y-J, Gan R-Y, Li H-B (2022) Effects and mechanisms of resveratrol for prevention and management of cancers: an updated review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. :1–19
Sheikh-Zeineddini N, Bashash D, Safaroghli‐Azar A, Riyahi N, Shabestari RM, Janzamin E, Safa M (2019) Suppression of c‐Myc using 10058‐F4 exerts caspase‐3‐dependent apoptosis and intensifies the antileukemic effect of vincristine in pre‐B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. J Cell Biochem 120(8):14004–14016
Ninomiya I, Yamazaki K, Oyama K, Hayashi H, Tajima H, Kitagawa H, Fushida S, Fujimura T, Ohta T (2014) Pioglitazone inhibits the proliferation and metastasis of human pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol Lett 8(6):2709–2714
Spender LC, Inman GJ (2012) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT/mTORC1/2 signaling determines sensitivity of Burkitt’s lymphoma cells to BH3 mimeticsPI3K/mTOR inhibition overcomes resistance of BL to ABT-737. Mol Cancer Res 10(3):347–359
Mosleh M, Safaroghli-Azar A, Bashash D (2020) Pan-HDAC inhibitor panobinostat, as a single agent or in combination with PI3K inhibitor, induces apoptosis in APL cells: an emerging approach to overcome MSC-induced resistance. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 122:105734
Wang H, Mannava S, Grachtchouk V, Zhuang D, Soengas M, Gudkov A, Prochownik E, Nikiforov M (2008) c-Myc depletion inhibits proliferation of human tumor cells at various stages of the cell cycle. Oncogene 27(13):1905–1915
Chang H, Zou Z (2020) Targeting autophagy to overcome drug resistance: further developments. J Hematol Oncol 13(1):159
Schmidt M, Fernandez de Mattos S, van der Horst A, Klompmaker R, Kops GJL, Lam EW-F, Burgering BM, Medema RH (2002) Cell cycle inhibition by FoxO forkhead transcription factors involves downregulation of cyclin D. Molecular and cellular biology. 22(22):7842–7852
Furukawa-Hibi Y, Kobayashi Y, Chen C, Motoyama N (2005) FOXO transcription factors in cell-cycle regulation and the response to oxidative stress. Antioxid Redox Signal 7(5–6):752–760
Tamura E, de Vasconcellos RF, Sarkar J, Libermann DA, Fisher TB (2012) F Zerbini L. GADD45 proteins: central players in tumorigenesis. Curr Mol Med 12(5):634–651
Sharpe JC, Arnoult D, Youle RJ (2004) Control of mitochondrial permeability by Bcl-2 family members. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research. 1644(2–3):107–113
Catic A, Maneix L, Iakova P, Mistry R, Stossi F, Yellapragada SV, Lulla PD (2021) Epigenetic silencing of MYC by Proteasome inhibitors. Blood 138:2212
Hu Z, Pan X-F, Wu F-Q, Ma L-Y, Liu D-P, Liu Y, Feng T-T, Meng F-Y, Liu X-L, Jiang Q-L (2009) Synergy between proteasome inhibitors and imatinib mesylate in chronic myeloid leukemia. PLoS ONE 4(7):e6257
Huang H, Ma L, Li J, Yu Y, Zhang D, Wei J, Jin H, Xu D, Gao J, Huang C (2014) NF-κB1 inhibits c-Myc protein degradation through suppression of FBW7 expression. Oncotarget 5(2):493
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences (Tehran, Iran) for supporting and funding this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.

Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zehtabcheh, S., Yousefi, AM., Momeny, M. et al. C-Myc inhibition intensified the anti-leukemic properties of Imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia cells. Mol Biol Rep 50, 10157–10167 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08832-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-023-08832-4