Abstract
Background
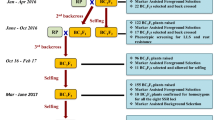
Groundnut is affected by a variety of abiotic and biotic stressors, including late leaf spot and rust, which cause significant economic loss. In this study, QTL for resistance to late leaf spot and rust from donor variety GPBD 4 were incorporated into a popular groundnut variety (ICGV 00350) through marker assisted backcross (MABC) breeding.
Methods
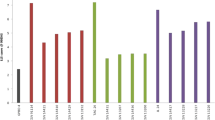
Eight foreground SSR markers [AhXII (GM1009, GM1573 and Seq8D09) and AhXV (GM1536, GM2009, GM2079, GM2301 and IPAHM103)] linked with disease resistant QTLs were utilized in this study. A set of 217 SSR markers spanning the whole groundnut genome were employed for background analysis. Three backcrosses with recurrent parent and selfing were followed in the cross ICGV 00350 × GPBD 4. Background analysis was carried out in BC3F2; while, phenotypic confirmation for resistance was carried out in BC3F3 generation.
Conclusion
Five advanced backcross lines in BC3F2 were found, with more than 90% recurrent parent genome. The phenotyping of the eight ILs recorded disease scores ranging from 2.0 to 3.0 for LLS and from 1.0 to 3.0 for rust disease scores. All these lines had superior characteristics compared to the recurrent parent ICGV 00350 in terms of late leaf spot and rust resistance. The enhanced ILs will be evaluated further for commercial release.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not provided.
Code availability
Not provided.
References
Bertioli DJ, Jenkins J, Clevenger J et al (2019) The genome sequence of segmental allotetraploid peanut Arachis hypogaea. Nat Genet 51:877–884. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41588-019-0405-z
Indiastat (2022) Directorate of Economics and Statistics, Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare, Govt. of India, New Delhi. In: https://www.indiastat.com/table/agriculture-data/2/groundnut-production/286906/17354/data.aspx (ON2282) & Past Issues
Pramanik A, Tiwari S, Tripathi MK et al (2022) Identification of groundnut germplasm lines for foliar disease resistance and high oleic traits using SNP and gene-based markers and their morphological characterization. Legume Res 45:305–310
Bhat RS, Jadhav MP, Patil P v, Shirasawa K (2022) Genomics-assisted breeding for resistance to leaf spots and rust diseases in peanut. In: Accelerated Plant Breeding, Volume 4. Springer, Berlin. pp 239–278. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81107-5_8
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genomics-assisted breeding for crop improvement. Trends Plant Sci 10:621–630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2005.10.004
Motagi BN, Bhat RS, Pujer S et al (2022) Genetic enhancement of groundnut: current status and future prospects. Accelerat Plant Breed 4:63–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-81107-5_3
Varshney RK, Bohra A, Yu J et al (2021) Designing future crops: genomics-assisted breeding comes of age. Trends Plant Sci 26:631–649. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2021.03.010
Varshney RK, Barmukh R, Roorkiwal M et al (2021) Breeding custom-designed crops for improved drought adaptation. Adv Genet 2:e202100017. https://doi.org/10.1002/ggn2.202100017
Hasan N, Choudhary S, Naaz N et al (2021) Recent advancements in molecular marker-assisted selection and applications in plant breeding programmes. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19:1–26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00231-1
Kulwal PL, Mir RR, Varshney RK (2022) Efficient breeding of crop plants. In: Fundamentals of Field Crop Breeding. Springer, Berlin. pp 745–777. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-16-9257-4
Varshney RK, Hoisington DA, Tyagi AK (2006) Advances in cereal genomics and applications in crop breeding. Trends Biotechnol 24:490–499. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibtech.2006.08.006
Bhawar PC, Tiwari S, Tripathi MK et al (2020) Screening of groundnut germplasm for foliar fungal diseases and population structure analysis using gene based SSR markers. Curr J Appl Sci Technol 39:75–84. https://doi.org/10.9734/cjast/2020/v39i230500
Daudi H, Shimelis H, Mathew I et al (2021) Genetic diversity and population structure of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) accessions using phenotypic traits and SSR markers: implications for rust resistance breeding. Genet Resour Crop Evol 68:581–604. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-020-01007-1
Tang Wang C, Dao Yang X, Xu Chen D et al (2007) Isolation of simple sequence repeats from groundnut. Electron J Biotechnol 10:473–480. https://doi.org/10.4067/S0717-34582007000300015
Janila P, Variath MT, Pandey MK et al (2016) Genomic tools in groundnut breeding program: status and perspectives. Front Plant Sci 7:289. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2016.00289
Bera SK, Kamdar JH, Kasundra S, v, et al (2018) Improving oil quality by altering levels of fatty acids through marker-assisted selection of ahfad2 alleles in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Euphytica 214:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-018-2241-0
Shasidhar Y, Variath MT, Vishwakarma MK et al (2020) Improvement of three popular Indian groundnut varieties for foliar disease resistance and high oleic acid using SSR markers and SNP array in marker-assisted backcrossing. Crop J 8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cj.2019.07.001
Pandey MK, Khan AW, Singh VK et al (2017) QTL-seq approach identified genomic regions and diagnostic markers for rust and late leaf spot resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Biotechnol J 15:927–941. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12686
Kolekar RM, Sukruth M, Shirasawa K et al (2017) Marker-assisted backcrossing to develop foliar disease-resistant genotypes in TMV 2 variety of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Plant Breed 136:948–953. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbr.12549
Deshmukh DB, Marathi B, Sudini HK et al (2020) Combining high oleic acid trait and resistance to late leaf spot and rust diseases in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front Genet 11:514. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2020.00514
Ahmad S, Nawade B, Sangh C et al (2020) Identification of novel QTLs for late leaf spot resistance and validation of a major rust QTL in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). 3 Biotech 10:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13205-020-02446-4
Mandloi S, Tripathi MK, Tiwari S, Tripathi N (2022) Genetic diversity analysis among late leaf spot and rust resistant and susceptible germplasm in groundnut (Arachis hypogea L.). Isr J Plant Sci 1:1–9
Sujay V, Gowda MVC, Pandey MK et al (2012) Quantitative trait locus analysis and construction of consensus genetic map for foliar disease resistance based on two recombinant inbred line populations in cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Mol Breeding 30:773–788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-011-9661-z
Ramakrishnan P, Manivannan N, Mothilal A et al (2020) Marker assisted introgression of QTL region to improve late leaf spot and rust resistance in elite and popular variety of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cv TMV 2. Australas Plant Pathol 49:505–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-020-00721-9
Prabhu R, Manivannan N, Mothilal A, Ibrahim SM (2016) Artificial screening for foliar fungal diseases in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Adv Life Sci 5(14):5634–5638
Subrahmanyam P, McDonald D, Waliyar F et al (1995) Screening methods and sources of resistance to rust and late leaf spot of groundnut. Inf Bull 47:1
Pande S, Rao JN (2001) Resistance of wild Arachis species to late leaf spot and rust in greenhouse trials. Plant Dis 85:851–855. https://doi.org/10.1094/PDIS.2001.85.8.851
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Sundaram RM, Vishnupriya MR, Biradar SK et al (2008) Marker assisted introgression of bacterial blight resistance in Samba Mahsuri, an elite indica rice variety. Euphytica 160:411–422. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9564-6
Wageningen UR (2010) Graphical genotypes. Wageningen UR Plant Breeding. In: http://www.plantbreeding.wur.nl/UK/software_ggt.html
Prabhu R, Manivannan N, Mothilal A, Ibrahim SM (2016) Screening for parental polymorphism using molecular markers in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Adv Life Sci 5:5347–5352
Varshney RK, Thudi M, May GD, Jackson SA (2010) Legume genomics and breeding. Plant Breed Rev 33:257–304
Divya B, Robin S, Rabindran R et al (2014) Marker assisted backcross breeding approach to improve blast resistance in Indian rice (Oryza sativa) variety ADT43. Euphytica 200:61–77. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-014-1146-9
Varshney RK, Pandey MK, Janila P et al (2014) Marker-assisted introgression of a QTL region to improve rust resistance in three elite and popular varieties of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Theor Appl Genet 127:1771–1781. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-014-2338-3
Pandey MK, Gautami B, Jayakumar T et al (2012) Highly informative genic and genomic SSR markers to facilitate molecular breeding in cultivated groundnut (Arachis hypogaea). Plant Breed 131:139–147. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2011.01911.x
Tang R, Gao G, He L et al (2007) Genetic diversity in cultivated groundnut based on SSR markers. J Genet Genomics 34:449–459. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1673-8527(07)60049-6
Shirasawa K, Bhat RS, Khedikar YP et al (2018) Sequencing analysis of genetic loci for resistance for late leaf spot and rust in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Front Plant Sci 9:1727. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2018.01727
Gangurde AB, Patil TD, Thakare R, Chaudhari RD (2018) Effect of neem coated urea on nutrient availability, yield attributing characters and yield of pearl millet on vertisol. J Pharm Phytochem 7:2146–2149
Varshney RK, Mohan SM, Gaur PM et al (2014) Marker-assisted backcrossing to introgress resistance to Fusarium wilt race 1 and Ascochyta blight in C 214, an elite cultivar of chickpea. Plant Genome 7:2013–2110. https://doi.org/10.3835/plantgenome2013.10.0035
Funding
Authors are thankful to the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India, New Delhi for financial support to undertake this study (Grant No: BT/ PR6583/AGII /106/881/2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
The author declares that the study performed is true with novelty in the interpretations.
Consent to participate
All authors given consent to participate.
Consent for publication
All authors given consent for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajarathinam, P., Palanisamy, G., P, R. et al. Marker assisted backcross to introgress late leaf spot and rust resistance in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.). Mol Biol Rep 50, 2411–2419 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08234-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08234-y