Abstract
Background
Diabetes is a severe health burden for Bangladesh. Genetic polymorphism has been reported to be one of the major risk factors for diabetes in various studies. TCF7L2 (transcription factor 7 like 2) transcripts in the human β-cell have effects on β-cell survival, function, and Wnt signaling activation. This study aimed to evaluate the frequency and association of various polymorphisms namely TCF7L2 rs12255372 and rs7903146 among Bangladeshi patients with T2DM (Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus).
Methods
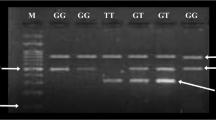
This case–control study included 300 patients with T2DM and 234 healthy individuals from two health facilities in the Chattogram Division of Bangladesh. Anthropometric measurements were assessed using a self-reported, structured, eight-item questionnaire. The polymorphisms were identified by PCR–RFLP and sequencing method.
Results
A strong association of T2DM with polymorphisms was observed, including rs12255372 (p = 0.0004) and rs7903146 (p = 0.005). It was observed that the risk genotype at rs12255372 was associated with age (p = 0.009), a family history of diabetes (p < 0.0001), and HbA1C (p < 0.0001). Furthermore, it was found that rs12255372 was substantially associated with hypertension (p = 0.03), eye problems (p = 0.01), and neurological abnormalities (p = 0.02).
Conclusion
This study postulates that TCF7L2 genetic polymorphism is associated with the risk of T2DM among the studied Bangladeshi population. The findings should be replicated through more studies with a large number of samples and in different populations.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tremblay J, Hamet P (2019) Environmental and genetic contributions to diabetes. Metabolism 100S:153952. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2019.153952
DeFronzo RA et al (2015) Type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Rev Dis Prim 1:15019. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2015.19
Itariu BK, Stulnig TM (2014) Autoimmune aspects of type 2 diabetes mellitus - a mini-review. Gerontology 60(3):189–196. https://doi.org/10.1159/000356747
Field SF, Howson JMM, Smyth DJ, Walker NM, Dunger DB, Todd JA (2007) Analysis of the type 2 diabetes gene, TCF7L2, in 13,795 type 1 diabetes cases and control subjects. Diabetologia 50(1):212–213. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0506-y
Galicia-Garcia U et al (2020) Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int JMol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21176275
Akter S, Rahman MM, Abe SK, Sultana P (2014) Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes and their risk factors among Bangladeshi adults: a nationwide survey. Bull World Health Organ 92(3):204–213. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.13.128371
Sladek R et al (2007) A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 445(7130):881–885. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05616
Xiong X, Shao W, Jin T (2012) New insight into the mechanisms underlying the function of the incretin hormone glucagon-like peptide-1 in pancreatic β-cells: the involvement of the Wnt signaling pathway effector β-catenin. Islets 4(6):359–365. https://doi.org/10.4161/isl.23345
Lyssenko V et al (2007) Mechanisms by which common variants in the TCF7L2 gene increase risk of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Invest 117(8):2155–2163. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI30706
Cauchi S et al (2007) TCF7L2 is reproducibly associated with type 2 diabetes in various ethnic groups: a global meta-analysis. J Mol Med (Berl) 85(7):777–782. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-007-0203-4
Chandak GR et al (2007) Common variants in the TCF7L2 gene are strongly associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Indian population. Diabetologia 50(1):63–67. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-006-0502-2
Chauhan G et al (2010) Impact of common variants of PPARG, KCNJ11, TCF7L2, SLC30A8, HHEX, CDKN2A, IGF2BP2, and CDKAL1 on the risk of type 2 diabetes in 5,164 Indians. Diabetes 59(8):2068–2074. https://doi.org/10.2337/db09-1386
Scott LJ et al (2006) Association of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) variants with type 2 diabetes in a Finnish sample. Diabetes 55(9):2649–2653. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0341
Zhang C et al (2006) Variant of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and the risk of type 2 diabetes in large cohorts of U.S. women and men. Diabetes 55(9):2645–2648. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-0643
Anjum N, Jehangir A, Liu Y (2018) Two TCF7L2 variants associated with type 2 diabetes in the Han nationality residents of China. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 28(10):794–797
Marquezine GF, Pereira AC, Sousa AGP, Mill JG, Hueb WA, Krieger JE (2008) TCF7L2 variant genotypes and type 2 diabetes risk in Brazil: significant association, but not a significant tool for risk stratification in the general population. BMC Med Genet 9:106. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-9-106
Hayashi T, Iwamoto Y, Kaku K, Hirose H, Maeda S (2007) Replication study for the association of TCF7L2 with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in a Japanese population. Diabetologia 50(5):980–984. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-007-0618-z
Mayans S et al (2007) TCF7L2 polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes in northern Sweden. Eur J Hum Genet 15(3):342–346. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ejhg.5201773
Lehrer S, Rheinstein PH (2021) Diabetes, cigarette smoking and transcription factor 7-like 2 (Tcf7L2) in the UK Biobank cohort. Bull Acad Natl Med 205(9):1146–1150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.banm.2021.09.001
Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes-2017 abridged for primary care providers. Clin Diabetes 35(1):5–26 (2017). https://doi.org/10.2337/cd16-0067.
Amoli MM et al (2010) Replication of TCF7L2 rs7903146 association with type 2 diabetes in an Iranian population. Genet Mol Biol 33(3):449–451. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572010005000056
Alami FM et al (2012) Association of the TCF7L2 rs12255372 (G/T) variant with type 2 diabetes mellitus in an Iranian population. Genet Mol Biol 35(2):413–417. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572012005000029
McCarthy M, Menzel S (2001) The genetics of type 2 diabetes. Br J Clin Pharmacol 51(3):195–199. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2125.2001.00346.x
Rana H, Chavda P, Rathod C, Mavani M (2015) Socio-demographic and anthropometric profile of diabetic patients attending diabetes clinic in tertiary care hospital of central Gujarat.
Borah M, Goswami R (2017) Sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of a diabetic population at a tertiary care center in Assam, India. J Soc Heal Diabetes 05(01):37–42. https://doi.org/10.4103/2321-0656.193997
Hurst C, Thinkhamrop B, Tran HT (2015) The association between hypertension comorbidity and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes patients: a nationwide cross-sectional study in Thailand. Diabetes Metab J 39(5):395–404. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.5.395
Shokouhi S, Delpisheh A, Haghani K, Mahdizadeh M, Bakhtiyari S (2014) Association of rs7903146, rs12255372, and rs290487 polymorphisms in TCF7L2 gene with type 2 diabetes in an Iranian Kurdish ethnic group. Clin Lab 60(8):1269–1276. https://doi.org/10.7754/clin.lab.2013.130809
Bodhini D, Radha V, Dhar M, Narayani N, Mohan V (2007) The rs12255372(G/T) and rs7903146(C/T) polymorphisms of the TCF7L2 gene are associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Asian Indians. Metabolism 56(9):1174–1178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2007.04.012
El-Lebedy D, Ashmawy I (2016) Common variants in TCF7L2 and CDKAL1 genes and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Egyptians. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 14(2):247–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgeb.2016.10.004
Helgason A et al (2007) Refining the impact of TCF7L2 gene variants on type 2 diabetes and adaptive evolution. Nat Genet 39(2):218–225. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1960
Sale MM et al (2007) Variants of the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene are associated with type 2 diabetes in an African-American population enriched for nephropathy. Diabetes 56(10):2638–2642. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0012
Zhou K-C, Liu H-W, Wang C, Fu Y-J, Jin F (2019) Association of transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene polymorphism with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese Korean ethnicity population. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(5):e14288. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000014288
Alsmadi O et al (2008) Weak or no association of TCF7L2 variants with Type 2 diabetes risk in an Arab population. BMC Med Genet 9:72. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-9-72
Tong Y et al (2009) Association between TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus: a large human genome epidemiology (HuGE) review and meta-analysis. BMC Med Genet 10:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2350-10-15
Timpson NJ et al (2009) Adiposity-related heterogeneity in patterns of type 2 diabetes susceptibility observed in genome-wide association data. Diabetes 58(2):505–510. https://doi.org/10.2337/db08-0906
Salonen JT et al (2007) Type 2 diabetes whole-genome association study in four populations: the DiaGen consortium. Am J Hum Genet 81(2):338–345. https://doi.org/10.1086/520599
Steinthorsdottir V et al (2007) A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 39(6):770–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2043
Zeggini E et al (2007) Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 316(5829):1336–1341. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1142364
Guewo-Fokeng M et al (2015) Contribution of the TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) gene polymorphism to the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Cameroon. J Diabetes Metab Disord 14:26. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40200-015-0148-z
Pourahmadi M, Erfanian S, Moradzadeh M, Jahromi AS (2015) Non-association between rs7903146 and rs12255372 polymorphisms in transcription factor 7-like 2 gene and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Jahrom City, Iran. Diabetes Metab J 39(6):512–517. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.512
Chang Y-C et al (2007) Association study of the genetic polymorphisms of the transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene and type 2 diabetes in the Chinese population. Diabetes 56(10):2631–2637. https://doi.org/10.2337/db07-0421
Zhang B-C, Li W-M, Zhu M-Y, Xu Y-W (2013) Association of TCF7L2 gene polymorphisms with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Han Chinese population: a meta-analysis. Gene 512(1):76–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.09.034
Neto ABL et al (2021) Prevalence of IGFBP3, NOS3 and TCF7L2 polymorphisms and their association with hypertension: a population-based study with Brazilian women of African descent. BMC Res Notes 14(1):186. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13104-021-05598-5
Yan Y et al (2010) The transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) polymorphism may be associated with focal arteriolar narrowing in Caucasians with hypertension or without diabetes: the ARIC study. BMC Endocr Disord 10:9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6823-10-9
Campbell RK (2009) Type 2 diabetes: where we are today: an overview of disease burden, current treatments, and treatment strategies. J Am Pharm Assoc 49(1):S3–S9. https://doi.org/10.1331/JAPhA.2009.09077
Egede LE, Ellis C (2010) Diabetes and depression: global perspectives. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 87(3):302–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diabres.2010.01.024
Mohan V, Seedat YK, Pradeepa R (2013) The rising burden of diabetes and hypertension in southeast asian and african regions: need for effective strategies for prevention and control in primary health care settings. Int J Hypertens 2013:409083. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/409083
Behl T, Kotwani A (2015) Exploring the various aspects of the pathological role of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in diabetic retinopathy. Pharmacol Res 99:137–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2015.05.013
Moreno A, Lozano M, Salinas P (2013) Diabetic retinopathy. Nutr Hosp 28(Suppl 2):53–56. https://doi.org/10.3305/nh.2013.28.sup2.6714
Suganthalakshmi B et al (2006) Association of VEGF and eNOS gene polymorphisms in type 2 diabetic retinopathy. Mol Vis 12:336–341
Sanghera DK et al (2008) TCF7L2 polymorphisms are associated with type 2 diabetes in Khatri Sikhs from North India: genetic variation affects lipid levels. Ann Hum Genet 72(Pt 4):499–509. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-1809.2008.00443.x
Bodhini D et al (2017) Interaction between TCF7L2 polymorphism and dietary fat intake on high density lipoprotein cholesterol. PLoS ONE 12(11):e0188382. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0188382
Assmann TS, Duarte GCK, Rheinheimer J, Cruz LA, Canani LH, Crispim D (2014) The TCF7L2 rs7903146 (C/T) polymorphism is associated with risk to type 2 diabetes mellitus in Southern-Brazil. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 58(9):918–925. https://doi.org/10.1590/0004-2730000003510
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank all the volunteers of Disease Biology and Molecular Epidemiology Research group (dBme), Chittagong for their support.
Funding
This work was funded Grant from Research and publication office, University of Chittagong.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization—AM; Method development – Writing—Original Draft Preparation, AS, KC and AM.; Writing—Review & Editing, MMH., FA., NAC., SRC and AM.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethical Review Committee of Chittagong Medical College Hospital (CMC/PG/2019/57).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Salauddin, A., Chakma, K., Hasan, M.M. et al. Association between TCF7L2 polymorphism and type 2 diabetes mellitus susceptibility: a case–control study among the Bangladeshi population. Mol Biol Rep 50, 609–619 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08081-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-08081-x