Abstract
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is one of the most widely spread metabolic disordersand is also referred as a ‘lifestyle’ disorder. According toa study conducted by IDB, the number of individuals affected with diabetes is expected to increase from 463 to 700 million by the end of year 2045. Thus, there is a great need to developed targeted therapies that can maintain homeostasis of glucose levels and improving insulin sensitivity which can overcome hurdles associated with conventional medicine. Detailed analysis was conducted by analyzing various research and review papers which were searched using MEDLINE and EMBASE using various keywords. This search retrieved the most appropriate content on these molecules targeting Nrf-2 functions and Nrf-2 pathway associated with diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy. In this review article, we have highlighted the role of Nrf-2 in diabetic associated complications of neuropathy and nephropathy. Since hyperglycemia is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation, regulating Nrf-2 activity through various synthetic and natural activators whichmay provide therapeutic benefits for the treatment and mitigation of diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy as well. Based on the available literature on Nrf-2 activity and despite some controversies in the association of Nrf-2 activity and its therapeutic usage, it can be concluded that regulation of this pathway is a trigger in the development of diabetes-associated complications. Thus, targeting this pathway with various activators may emerge as a novel therapy in the treatment of diabetes and diabetes-associated complications.
Graphic abstract
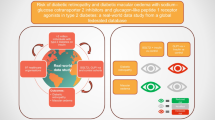
Nrf-2 activation leading to regulation of various downstream pathways responsible for managament of Diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy

Legend: Activities regulated by the activation of Nrf-2 pathway by Natural and Synthetic activators. Various downstream signalling pathway are involved in increase (+) and decrease (−) in levels of Nrf-2 levels. Subsequently controlling various mechanism involved in the pathogenies of Diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGE:
-
Advanced glycation end products
- AIDS:
-
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome
- AKT:
-
Progressive ankylosis protein
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response element
- ARE:
-
Anti-oxidant response element
- ATF:
-
Activating transcription factor
- bZIP:
-
Basic leucine zipper
- CAT:
-
Catalase
- CBP:
-
CREB-binding protein
- CNC-bZip:
-
Basic region leucine zipper factor family’
- COPD:
-
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- CREB:
-
CAMP response element binding protein
- DMF:
-
Dimethyl fumarate
- DN:
-
Diabetic nephropathy
- DPP-4:
-
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4
- FDA:
-
Food and drug administration
- G-6-PD:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GCL:
-
Glutamate cysteine ligase
- GCLC:
-
Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit
- GCLM:
-
Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSK-3:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3
- GSK-3β:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- HMOX1:
-
Heme oxygenase decycling-1
- O-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- Hrd1- 3:
-
Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl reductase degradation 1
- IDF:
-
International diabetes federation
- IRE-1:
-
Inositol requiring protein
- JNK:
-
C-Jun N-terminal kinases
- MDM2:
-
Murine double minue-2
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-kappa B
- NQO-1:
-
NADPH-quinone oxidoreductase-1
- Nrf-2:
-
Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2
- PERK:
-
Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- SRXN1:
-
Sulfiredoxin 1
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- TGF-B:
-
Transforming growth factor-beta
- UDP:
-
Uridine 5′-diphospho-glucuronosyltransferas
- UGT:
-
UDP-glucuronosyltransferase
- WHO:
-
World health organization
- β-TrCP:
-
Beta-transducin repeats-containing protein
References
IDF data https://diabetesatlas.org/data/en/world/. Accessed 22 Nov 2020
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (2020) National diabetes statistics report. Atlanta: centers for disease control and prevention, US Dept of Health and Human Services. 2020.
Behl T, Kaur I, Kotwani A (2016) Implication of oxidative stress in progression of diabetic retinopathy. Surv Ophthalmol 61(2):187–196
Donath MY, Halban PA (2004) Decreased beta-cell mass in diabetes: significance, mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Diabetologia 47(3):581–589
Donath MY, Størling J, Maedler K, Mandrup-Poulsen T (2003) Inflammatory mediators and islet β-cell failure: a link between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. J Mol Med 81(8):455–470
Gupta A, Behl T, Sachdeva M (2020) Key milestones in the diabetes research: a comprehensive update. Obesity Med 17:100183
Kensler TW, Wakabayashi N, Biswal S (2007) Cell survival responses to environmental stresses via the Keap1-Nrf-2-ARE pathway. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 47:89–116
Itoh K, Chiba T, Takahashi S, Ishii T, Igarashi K, Katoh Y, Oyake T, Hayashi N, Satoh K, Hatayama I, Yamamoto M (1997) An Nrf-2/small Maf heterodimer mediates the induction of phase II detoxifying enzyme genes through antioxidant response elements. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 236(2):313–322
Wild AC, Moinova HR, Mulcahy RT (1999) Regulation of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase subunit gene expression by the transcription factor Nrf-2. J Biol Chem 274(47):33627–33636
Wu KC, McDonald PR, Liu JJ, Chaguturu R, Klaassen CD (2012) Implementation of a high-throughput screen for identifying small molecules to activate the Keap1-Nrf-2-ARE pathway. PLoS ONE 7(10):e44686
Ramkumar KM, Sekar TV, Foygel K, Elango B, Paulmurugan R (2013) Reporter protein complementation imaging assay to screen and study Nrf-2 activators in cells and living animals. Anal Chem 85(15):7542–7549
Zheng H, Whitman SA, Wu W, Wondrak GT, Wong PK, Fang D, Zhang DD (2011) Therapeutic potential of Nrf-2 activators in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 60(11):3055–3066
Staurengo-Ferrari L, Badaro-Garcia S, Hohmann MS, Manchope MF, Zaninelli TH, Casagrande R, Verri WA Jr (2019) Contribution of Nrf2 modulation to the mechanism of action of analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs in pre-clinical and clinical stages. Front Pharmacol 9:1536
Ma Q (2013) Role of Nrf-2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2014) The Nrf-2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 39(4):199–218
Gold R, Kappos L, Arnold DL, Bar-Or A, Giovannoni G, Selmaj K, Tornatore C, Sweetser MT, Yang M, Sheikh SI, Dawson KT (2012) Placebo-controlled phase 3 study of oral BG-12 for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 367(12):1098–1107
Motohashi H, Katsuoka F, Engel JD, Yamamoto M (2004) Small Maf proteins serve as transcriptional cofactors for keratinocyte differentiation in the Keap1–Nrf-2 regulatory pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101(17):6379–6384
Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2004) Nrf-2–Keap1 defines a physiologically important stress response mechanism. Trends Mol Med 10(11):549–557
Tocchetti GN, Rigalli JP, Arana MR, Villanueva SS, Mottino AD (2016) Modulation of expression and activity of intestinal multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 by xenobiotics. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 303:45–57
Katoh Y, Iida K, Kang MI, Kobayashi A, Mizukami M, Tong KI, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Itoh K, Yamamoto M (2005) Evolutionary conserved N-terminal domain of Nrf-2 is essential for the Keap1-mediated degradation of the protein by proteasome. Arch Biochem Biophys 433(2):342–350
Tong KI, Katoh Y, Kusunoki H, Itoh K, Tanaka T, Yamamoto M (2006) Keap1 recruits Neh2 through binding to ETGE and DLG motifs: characterization of the two-site molecular recognition model. Mol Cell Biol 26(8):2887–2900
Tebay LE, Robertson H, Durant ST, Vitale SR, Penning TM, Dinkova-Kostova AT, Hayes JD (2015) Mechanisms of activation of the transcription factor Nrf-2 by redox stressors, nutrient cues, and energy status and the pathways through which it attenuates degenerative disease. Free Radical Biol Med 88:108–146
Hur EM, Zhou FQ (2010) GSK3 signalling in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 11(8):539–551
Hoeflich KP, Luo J, Rubie EA, Tsao MS, Jin OU, Woodgett JR (2000) Requirement for glycogen synthase kinase-3β in cell survival and NF-κB activation. Nature 406(6791):86–90
Martin D, Rojo AI, Salinas M, Diaz R, Gallardo G, Alam J, de Galarreta CM, Cuadrado A (2004) Regulation of heme oxygenase-1 expression through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt pathway and the Nrf-2 transcription factor in response to the antioxidant phytochemical carnosol. J Biol Chem 279(10):8919–8929
Salazar M, Rojo AI, Velasco D, de Sagarra RM, Cuadrado A (2006) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibits the xenobiotic and antioxidant cell response by direct phosphorylation and nuclear exclusion of the transcription factor Nrf-2. J Biol Chem 281(21):14841–14851
Wu T, Zhao F, Gao B, Tan C, Yagishita N, Nakajima T, Wong PK, Chapman E, Fang D, Zhang DD (2014) Hrd1 suppresses Nrf-2-mediated cellular protection during liver cirrhosis. Genes Dev 28(7):708–722
Kwak MK, Itoh K, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW (2002) Enhanced expression of the transcription factor Nrf-2 by cancer chemopreventive agents: role of antioxidant response element-like sequences in the Nrf-2 promoter. Mol Cell Biol 22(9):2883–2892
Lee OH, Jain AK, Papusha V, Jaiswal AK (2007) An auto-regulatory loop between stress sensors INrf-2 and Nrf-2 controls their cellular abundance. J Biol Chem 282(50):36412–36420
Sangokoya C, Telen MJ, Chi JT (2010) microRNA miR-144 modulates oxidative stress tolerance and associates with anemia severity in sickle cell disease. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 116(20):4338–4348
Gupta A, Shah K, Oza MJ, Behl T (2019) Reactivation of p53 gene by MDM2 inhibitors: a novel therapy for cancer treatment. Biomed Pharmacother 109:484–492
Sun Z, Chin YE, Zhang DD (2009) Acetylation of Nrf-2 by p300/CBP augments promoter-specific DNA binding of Nrf-2 during the antioxidant response. Mol Cell Biol 29(10):2658–2672
Rushworth SA, Zaitseva L, Murray MY, Shah NM, Bowles KM, MacEwan DJ (2012) The high Nrf-2 expression in human acute myeloid leukemia is driven by NF-κB and underlies its chemo-resistance. Blood J Am Soc Hematol 120(26):5188–5198
Cuadrado A, Martín-Moldes Z, Ye J, Lastres-Becker I (2014) Transcription factors NRF-2 and NF-κB are coordinated effectors of the Rho family, GTP-binding protein RAC1 during inflammation. J Biol Chem 289(22):15244–15258
Sun CC, Li SJ, Yang CL, Xue RL, Xi YY, Wang L, Zhao QL, Li DJ (2015) Sulforaphane attenuates muscle inflammation in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice via NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf-2)-mediated inhibition of NF-κB signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 290(29):17784–17795
Zwacka RM, Zhou W, Zhang Y, Darby CJ, Dudus L, Halldorson J, Oberley L, Engelhardt JF (1998) Redox gene therapy for ischemia/reperfusion injury of the liver reduces AP1 and NF-κB activation. Nat Med 4(6):698–704
Kim GY, Jeong H, Yoon HY, Yoo HM, Lee J, Park SH, Lee CE (2020) Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of suppressors of cytokine signaling target ROS via NRF-2/thioredoxin induction and inflammasome activation in macrophages. BMB Rep 53(12):640–645
Sun J, Wang HJ, Yu J, Li T, Han Y (2020) Protective effect of celastrol on type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in mice. Food Sci Nutr 8(11):6207–6216
Gupta A, Behl T, Panichayupakaranan P (2019) A review of phytochemistry and pharmacology profile of Juglans regia. Obesity Med 16:100142
Stefanson AL, Bakovic M (2014) Dietary regulation of Keap1/Nrf-2/ARE pathway: focus on plant-derived compounds and trace minerals. Nutrients 6(9):3777–3801
Kumar A, Mittal R (2017) Nrf-2: a potential therapeutic target for diabetic neuropathy. Inflammopharmacology 25(4):393–402
Bhakkiyalakshmi E, Sireesh D, Rajaguru P, Paulmurugan R, Ramkumar KM (2015) The emerging role of redox-sensitive Nrf-2–Keap1 pathway in diabetes. Pharmacol Res 91:104–114
Zhang K, Xu Y (2020) Suppressing BRD4 exhibits protective effects against vincristine-induced peripheral neuropathy by alleviating inflammation and oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 532(2):271–279
Dos Santos GG, Oliveira AL, Santos DS, do Espirito Santo RF, Silva DN, Juiz PJ, Soares MB, Villarreal CF (2020) Mesenchymal stem cells reduce the oxaliplatin-induced sensory neuropathy through the reestablishment of redox homeostasis in the spinal cord. Life Sci 265:118755
Nioi P, Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB (2005) The carboxy-terminal Neh3 domain of Nrf-2 is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 25(24):10895–10906
Sun Z, Huang Z, Zhang DD (2009) Phosphorylation of Nrf-2 at multiple sites by MAP kinases has a limited contribution in modulating the Nrf-2-dependent antioxidant response. PLoS ONE 4(8):e6588
Petit-Paitel A (2010) GSK-3beta: a central kinase for neurodegenerative diseases. Med Sci 26(5):516–521
Rada P, Rojo AI, Evrard-Todeschi N, Innamorato NG, Cotte A, Jaworski T, Tobón-Velasco JC, Devijver H, García-Mayoral MF, Van Leuven F, Hayes JD (2012) Structural and functional characterization of Nrf-2 degradation by the glycogen synthase kinase 3/β-TrCP axis. Mol Cell Biol 32(17):3486–3499
Rojo AI, Sagarra MR, Cuadrado A (2008) GSK-3β down-regulates the transcription factor Nrf-2 after oxidant damage: relevance to exposure of neuronal cells to oxidative stress. J Neurochem 105(1):192–202
Culbreth M, Aschner M (2018) GSK-3β, a double-edged sword in Nrf2 regulation: implications for neurological dysfunction and disease. F1000Research 7:1042
Sun Z, Chin YE, Zhang DD (2009) Acetylation of Nrf2 by p300/CBP augments promoter-specific DNA binding of Nrf2 during the antioxidant response. Mol Cell Biol 29(10):2658–2672
Kawai Y, Garduño L, Theodore M, Yang J, Arinze IJ (2011) Acetylation-deacetylation of the transcription factor Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2) regulates its transcriptional activity and nucleocytoplasmic localization. J Biol Chem 286(9):7629–7640
Huang HC, Nguyen T, Pickett CB (2002) Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at Ser-40 by protein kinase C regulates antioxidant response element-mediated transcription. J Biol Chem 277(45):42769–42774
Steinberg SF (2015) Mechanisms for redox-regulation of protein kinase C. Front Pharmacol 6:128
Tonelli C, Chio II, Tuveson DA (2018) Transcriptional regulation by Nrf2. Antioxid Redox Signal 29(17):1727–1745
Wardyn JD, Ponsford AH, Sanderson CM (2015) Dissecting molecular cross-talk between Nrf2 and NF-κB response pathways. Biochem Soc Trans 43(4):621–626
Li W, Khor TO, Xu C, Shen G, Jeong WS, Yu S, Kong AN (2008) Activation of Nrf2-antioxidant signaling attenuates NFκB-inflammatory response and elicits apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 76(11):1485–1489
Stefanson AL, Bakovic M (2014) Dietary regulation of Keap1/Nrf2/ARE pathway: focus on plant-derived compounds and trace minerals. Nutrients 6(9):3777–3801
Nezu M, Suzuki N, Yamamoto M (2017) Targeting the KEAP1-NRF2 system to prevent kidney disease progression. Am J Nephrol 45(6):473–483
Zheng H, Whitman SA, Wu W, Wondrak GT, Wong PK, Fang D, Zhang DD (2011) Therapeutic potential of Nrf2 activators in streptozotocin-induced diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 60(11):3055–3066
Cui W, Bai Y, Miao X, Luo P, Chen Q, Tan Y, Rane MJ, Miao L, Cai L (2012) Prevention of diabetic nephropathy by sulforaphane: possible role of Nrf2 upregulation and activation. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012:1–12
Shin S, Wakabayashi J, Yates MS, Wakabayashi N, Dolan PM, Aja S, Liby KT, Sporn MB, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW (2009) Role of Nrf2 in prevention of high-fat diet-induced obesity by synthetic triterpenoid CDDO-imidazolide. Eur J Pharmacol 620(1–3):138–144
Chang TT, Chen YA, Li SY, Chen JW (2020) Nrf-2 mediated heme oxygenase-1 activation contributes to the anti-inflammatory and renal protective effects of Ginkgo biloba extract in diabetic nephropathy. J Ethnopharmacol 14(266):113474
Jiang B, Guo L, Li BY, Zhen JH, Song J, Peng T, Yang XD, Hu Z, Gao HQ (2013) Resveratrol attenuates early diabetic nephropathy by down-regulating glutathione s-transferases Mu in diabetic rats. J Med Food 16(6):481–486
Pergola PE, Raskin P, Toto RD, Meyer CJ, Huff JW, Grossman EB, Krauth M, Ruiz S, Audhya P, Christ-Schmidt H, Wittes J (2011) Bardoxolone methyl and kidney function in CKD with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 365(4):327–336
De Zeeuw D, Akizawa T, Audhya P, Bakris GL, Chin M, Christ-Schmidt H, Goldsberry A, Houser M, Krauth M, Lambers Heerspink HJ, McMurray JJ (2013) Bardoxolone methyl in type 2 diabetes and stage 4 chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 369(26):2492–2503
Abdo S, Zhang SL, Chan JS (2015) Reactive oxygen species and nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 activation in diabetic nephropathy: a hidden target. J Diabetes Metab. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6156.1000547
Alaofi AL (2020) Sinapic acid ameliorates the progression of streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic nephropathy in rats via NRF2/HO-1 mediated pathways. Front Pharmacol 11:1119
Ma F, Wu J, Jiang Z, Huang W, Jia Y, Sun W (1866) P53/NRF2 mediates SIRT1’s protective effect on diabetic nephropathy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Mol Cell Res 8:1272–1281
Wang X, Liu Q, Kong D, Long Z, Guo Y, Wang S, Liu R, Hai C (2020) Down-regulation of SETD6 protects podocyte against high glucose and palmitic acid-induced apoptosis, and mitochondrial dysfunction via activating Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in diabetic nephropathy. J Mol Histol 51(5):549–558
Chen YJ, Kong L, Tang ZZ, Zhang YM, Liu Y, Wang TY, Liu YW (2019) Hesperetin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in rats by activating Nrf2/ARE/glyoxalase 1 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 111:1166–1175
Du L, Wang J, Chen Y, Li X, Wang L, Li Y, Jin X, Gu X, Hao M, Zhu X, Yin X (2020) Novel biphenyl diester derivative AB-38b inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome through Nrf2 activation in diabetic nephropathy. Cell Biol Toxicol 36(3):243–260
Ma B, Zhu Z, Zhang J, Ren C, Zhang Q (2020) Aucubin alleviates diabetic nephropathy by inhibiting NF-κB activation and inducing SIRT1/SIRT3-FOXO3a signaling pathway in high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. J Funct Foods 64:103702
Wu J, Sun X, Jiang Z, Jiang J, Xu L, Tian A, Sun X, Meng H, Li Y, Huang W, Jia Y (2020) Protective role of NRF2 in macrovascular complications of diabetes. J Cell Mol Med 24(16):8903–8917
Funding
The present study did not receive any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AG and TB: Conceived the idea and wrote the paper; AS: Figure Work; SBH and DG: Literature Survey; SB: Proof Read.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to publish
All the authors gave the consent to publish the present manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Behl, T., Sehgal, A. et al. Therapeutic potential of Nrf-2 pathway in the treatment of diabetic neuropathy and nephropathy. Mol Biol Rep 48, 2761–2774 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06257-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-021-06257-5