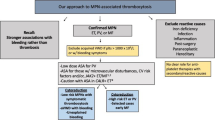
Abstract
Essential thrombocythemia (ET) is a classical myeloproliferative neoplasm that is susceptible to hypercoagulable state due to impaired hemostatic system, so that thrombotic complications are the leading cause of mortality in ET patients. The content used in this article has been obtained by the PubMed database and Google Scholar search engine from English-language articles (2000–2019) using the following keywords: "Essential thrombocythemia," "Thrombosis," "Risk factors" and "Hemostasis. In this neoplasm, the count and activity of cells such as platelets, leukocytes, endothelial cells, as well as erythrocytes are increased, which can increase the risk of thrombosis through rising intercellular interactions, expression of surface markers, and stimulation of platelet aggregation. In addition to these factors, genetic polymorphisms in hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), including mutations in JAK2, CALR, MPL, or genetic abnormalities in other genes associated with the hemostatic system may be associated with increased risk of thrombotic events. Moreover, disruption of coagulant factors can pave the way for thrombogeneration. Therefore, the identification of markers related to cell activation, genetic abnormalities, or alternation in the coagulant system can be used together as diagnostic and prognostic markers for the occurrence of thrombosis among ET patients. Thus, because thrombotic complications are the main factors of mortality in ET patients, a hemostatic viewpoint and risk assessment of cellular, genetic, and coagulation factors can have prognostic value and contribute to the choice of effective treatment and prevention of thrombosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- WBCs:
-
White blood cells
- RBCs:
-
Red blood cells
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- MPV:
-
Mean platelet volume
- TXA2:
-
Thromboxane-A2
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- sCD40L:
-
Soluble- CD40 ligand
- MPs:
-
Microparticles
- vWF:
-
Von Willebrand factor
- ECs:
-
Endothelial cells
- TM:
-
Thrombomodulin
- PAI-1:
-
Plasminogen- activator inhibitor
- TG:
-
Thrombin generation
- 4G:
-
4-Guanosine sequence
- 5G:
-
5-Guanosine sequence
- TF:
-
Tissue factor
- NOS3:
-
Nitric oxide synthase-3
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- MTHF:
-
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
- TFPI:
-
Tissue factor pathway inhibitor
- CAL:
-
Calreticulin
References
Małecki R, Gacka M, Kuliszkiewicz-Janus M, Jakobsche-Policht U, Kwiatkowski J, Adamiec R et al (2016) Altered plasma fibrin clot properties in essential thrombocythemia. Platelets 272:110–116
Pósfai É, Marton I, Borbényi Z, Nemes A (2016) Myocardial infarction as a thrombotic complication of essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Anatol J Cardiol 16(6):397–402
Alipanahzadeh H, Ghulamreza R, Shokouhian M, Bagheri M, Maleknia M (2019) Deep vein thrombosis: a less noticed complication in hematologic malignancies and immunologic disorders. J Thromb Thrombolysis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-02005-6
Vannucchi AM (2010) Insights into the pathogenesis and management of thrombosis in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Intern Emerg Med 5(3):177–184
Buxhofer-Ausch V, Steurer M, Sormann S, Schloegl E, Schimetta W, Gisslinger B et al (2016) Influence of platelet and white blood cell counts on major thrombosis—analysis from a patient registry in essential thrombocythemia. Eur J Haematol 97(6):511–516
Marchetti M, Tartari CJ, Russo L, Panova-Noeva M, Leuzzi A, Rambaldi A et al (2014) Phospholipid-dependent procoagulant activity is highly expressed by circulating microparticles in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Am J Hematol 89(1):68–73
Stankowska K, Gadomska G, Boinska J, Michalska M, Bartoszewska-Kubiak A, Rość D (2016) Extrinsic blood coagulation pathway and risk factors for thrombotic events in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Pol Arch Med Wewn 126(5):340–346
De Stefano V, Za T, Rossi E, Vannucchi AM, Ruggeri M, Elli E et al (2010) Leukocytosis is a risk factor for recurrent arterial thrombosis in young patients with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Am J Hematol 85(2):97–100
Lussana F, Carobbio A, Salmoiraghi S, Guglielmelli P, Vannucchi AM, Bottazzi B et al (2017) Driver mutations (JAK2V617F, MPLW515L/K or CALR), pentraxin-3 and C-reactive protein in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. J Hematol Oncol 10(1):54
Duchemin J, Ugo V, Ianotto JC, Lecucq L, Mercier B, Abgrall JF (2010) Increased circulating procoagulant activity and thrombin generation in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. Thromb Res 126(3):238–242
Trifa AP, Cucuianu A, Popp RA, Coadă CA, Costache RM, Militaru MS et al (2014) The relationship between factor V Leiden, prothrombin G20210A, and MTHFR mutations and the first major thrombotic episode in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Ann Hematol 93(2):203–209
Finazzi G, Rambaldi A, Guerini V, Carobbo A, Barbui T (2007) Risk of thrombosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera according to JAK2 V617F mutation status. Haematologica 92(1):135–136
Lim Y, Lee JO, Kim SH, Kim JW, Kim YJ, Lee KW et al (2015) Prediction of thrombotic and hemorrhagic events during polycythemia vera or essential thrombocythemia based on leukocyte burden. Thromb Res 135(5):846–851
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Barbui T, Smith CW (2005) Pathogenesis of thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera: the role of neutrophils. Semin Hematol 42(4):239–247
Stief TW (2004) Regulation of hemostasis by singlet-oxygen (1DeltaO2*). Curr Vasc Pharmacol 2(4):357–362
Musolino C, Allegra A, Saija A, Alonci A, Russo S, Spatari G et al (2012) Changes in advanced oxidation protein products, advanced glycation end products, and s-nitrosylated proteins, in patients affected by polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Clin Biochem 45(16–17):1439–1443
Sambrano GR, Huang W, Faruqi T, Mahrus S, Craik C, Coughlin SR (2000) Cathepsin G activates protease-activated receptor-4 in human platelets. J Biol Chem 275(10):6819–6823
Lindquist Liljeqvist M, Silveira A, Hultgren R, Frebelius S, Lengquist M, Engström J et al (2018) Neutrophil elastase-derived fibrin degradation products indicate presence of abdominal aortic aneurysms and correlate with intraluminal thrombus volume. Thromb Haemost 118(2):329–339
David A, Kacher Y, Specks U, Aviram I (2003) Interaction of proteinase 3 with CD11b/CD18 (beta2 integrin) on the cell membrane of human neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 74(4):551–557
Savran Karadeniz M, Alp Enişte I, Şentürk Çiftçi H, Usta S, Tefik T, Şanlı Ö et al (2019) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin significantly correlates with ischemic damage in patients undergoing laparoscopic partial nephrectomy. Balkan Med J 36(2):121–128
Xu S, Venge P (2000) Lipocalins as biochemical markers of disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1482(1–2):298–307
Krzemień G, Pańczyk-Tomaszewska M, Adamczuk D, Kotuła I, Demkow U, Szmigielska A (2018) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin: a biomarker for early diagnosis of urinary tract infections in infants. Adv Exp Med Biol 1047:71–80
Lim R, Ahmed N, Borregaard N, Riley C, Wafai R, Thompson EW et al (2007) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) an early-screening biomarker for ovarian cancer: NGAL is associated with epidermal growth factor-induced epithelio-mesenchymal transition. Int J Cancer 120(11):2426–2434
Laurell H, Bouisson M, Berthelemy P, Rochaix P, Dejean S, Besse P et al (2006) Identification of biomarkers of human pancreatic adenocarcinomas by expression profiling and validation with gene expression analysis in endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration samples. World J Gastroenterol 12(21):3344–3351
Allegra A, Alonci A, Bellomo G, Campo S, Cannavò A, Penna G et al (2011) Increased serum levels of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Leuk Lymphoma 52(1):101–107
Gremmel T, Koppensteiner R, Kaider A, Eichelberger B, Mannhalter C, Panzer S (2015) Impact of variables of the P-selectin - P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1 axis on leukocyte-platelet interactions in cardiovascular disease. Thromb Haemost 113(4):806–812
Sanchez S, Ewton A (2006) Essential thrombocythemia: a review of diagnostic and pathologic features. Arch Pathol Lab Med 130(8):1144–1150
Vannucchi AM, Barbui T (2007) Thrombocytosis and thrombosis. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. https://doi.org/10.1182/asheducation-2007.1.363
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Vignoli A, Balducci D, Barbui T (2005) Leukocyte-platelet interaction in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Exp Hematol 33(5):523–530
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Evangelista V, Vignoli A, Licini M, Balicco M et al (2000) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation and hemostasis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood 96(13):4261–4266
Michiels JJ, Berneman Z, Schroyens W, Finazzi G, Budde U, van Vliet HH (2006) The paradox of platelet activation and impaired function: platelet-von Willebrand factor interactions, and the etiology of thrombotic and hemorrhagic manifestations in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Semin Thromb Hemost 32(6):589–604
Treliński J, Tybura M, Smolewski P, Robak T, Chojnowski K (2009) The influence of low-dose aspirin and hydroxyurea on platelet-leukocyte interactions in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 20(8):646–651
Abdulkarim K, Ridell B, Johansson P, Kutti J, Safai-Kutti S, Andréasson B (2011) The impact of peripheral blood values and bone marrow findings on prognosis for patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Eur J Haematol 86(2):148–155
Maleknia M, Valizadeh A, Pezeshki SMS, Saki N (2020) Immunomodulation in leukemia: cellular aspects of anti-leukemic properties. Clin Transl Oncol 22(1):1–10
Shahrabi S, Maleknia M, Tavakolifar Y, Zayeri DZ, Saki N (2019) Neutropenia and leukemia development: genetic risk factors and prognosis. Leuk Lymphoma 60(14):3363–3374
Panova-Noeva M, Marchetti M, Spronk HM, Russo L, Diani E, Finazzi G et al (2011) Platelet-induced thrombin generation by the calibrated automated thrombogram assay is increased in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Am J Hematol 86(4):337–342
Maleknia M, Ansari N, Haybar H, Maniati M, Saki N (2020) Inflammatory growth factors and in-stent restenosis: effect of cytokines and growth factors SN comprehensive. Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42399-020-00240-0
Ahnadi CE, Sabrinah Chapman E, Lépine M, Okrongly D, Pujol-Moix N, Hernández A et al (2003) Assessment of platelet activation in several different anticoagulants by the Advia 120 hematology system, fluorescence flow cytometry, and electron microscopy. Thromb Haemost 90(5):940–948
Milovanovic M, Lotfi K, Lindahl T, Hallert C, Järemo P (2010) Platelet density distribution in essential thrombocythemia. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 37(1):35–42
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Vignoli A, Balducci D, Russo L, Guerini V et al (2007) V617F JAK-2 mutation in patients with essential thrombocythemia: relation to platelet, granulocyte, and plasma hemostatic and inflammatory molecules. Exp Hematol 35(5):702–711
Heemskerk JW, Bevers EM, Lindhout T (2002) Platelet activation and blood coagulation. Thromb Haemost 88(2):186–193
George FD (2008) Microparticles in vascular diseases. Thromb Res 122(Suppl 1):S55–S59
Panova-Noeva M, Marchetti M, Russo L, Tartari CJ, Leuzzi A, Finazzi G et al (2013) ADP-induced platelet aggregation and thrombin generation are increased in essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Thromb Res 132(1):88–93
Kim S, Kunapuli SP (2011) P2Y12 receptor in platelet activation. Platelets 22(1):56–60
Leon C, Alex M, Klocke A, Morgenstern E, Moosbauer C, Eckly A et al (2004) Platelet ADP receptors contribute to the initiation of intravascular coagulation. Blood 103(2):594–600
Maugeri N, Rovere-Querini P, Evangelista V, Covino C, Capobianco A, Bertilaccio MT et al (2009) Neutrophils phagocytose activated platelets in vivo: a phosphatidylserine, P-selectin, and {beta}2 integrin-dependent cell clearance program. Blood 113(21):5254–5265
Maugeri N, Malato S, Femia EA, Pugliano M, Campana L, Lunghi F et al (2011) Clearance of circulating activated platelets in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood 118(12):3359–3366
Viallard JF, Solanilla A, Gauthier B, Contin C, Déchanet J, Grosset C et al (2002) Increased soluble and platelet-associated CD40 ligand in essential thrombocythemia and reactive thrombocytosis. Blood 99(7):2612–2614
Bilgir F, Bilgir O, Kebapcilar L, Calan M, Ozdemirkiran F, Cinali T et al (2012) Soluble CD40 ligand, high sensitive C-reactive protein and fetuin-A levels in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Transfus Apher Sci 46(1):67–71
Treliński J, Chojnowski K, Cebula-Obrzut B, Smolewski P (2012) Impaired apoptosis of megakaryocytes and bone marrow mononuclear cells in essential thrombocythemia: correlation with JAK2V617F mutational status and cytoreductive therapy. Med Oncol 29(4):2388–2395
Reményi G, Szász R, Debreceni IB, Szarvas M, Batár P, Nagy B Jr et al (2013) Comparison of coated-platelet levels in patients with essential thrombocythemia with and without hydroxyurea treatment. Platelets 24(6):486–492
Trappenburg MC, van Schilfgaarde M, Marchetti M, Spronk HM, ten Cate H, Leyte A et al (2009) Elevated procoagulant microparticles expressing endothelial and platelet markers in essential thrombocythemia. Haematologica 94(7):911–918
Tesselaar ME, Romijn FP, Van Der Linden IK, Prins FA, Bertina RM, Osanto S (2007) Microparticle-associated tissue factor activity: a link between cancer and thrombosis? J Thromb Haemost 5(3):520–527
Roldán V, Marín F, Lip GY, Blann AD (2003) Soluble E-selectin in cardiovascular disease and its risk factors. A review of the literature. Thromb Haemost 90(6):1007–1020
Mezouar S, Mege D, Darbousset R, Farge D, Debourdeau P, Dignat-George F et al (2014) Involvement of platelet-derived microparticles in tumor progression and thrombosis. Semin Oncol 41(3):346–358
Pereira J, Alfaro G, Goycoolea M, Quiroga T, Ocqueteau M, Massardo L et al (2006) Circulating platelet-derived microparticles in systemic lupus erythematosus. Association with increased thrombin generation and procoagulant state. Thromb Haemost 95(1):94–99
Spronk HM, Dielis AW, De Smedt E, van Oerle R, Fens D, Prins MH et al (2008) Assessment of thrombin generation II: validation of the calibrated automated thrombogram in platelet-poor plasma in a clinical laboratory. Thromb Haemost 100(2):362–364
Tull SP, Bevins A, Kuravi SJ, Satchell SC, Al-Ani B, Young SP et al (2012) PR3 and elastase alter PAR1 signaling and trigger vWF release via a calcium-independent mechanism from glomerular endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 7(8):e43916
van Rooy MJ, Pretorius E (2016) Platelet interaction with erythrocytes and propensity to aggregation in essential thrombocythaemia. Lancet 387(10024):1210
Vallés J, Santos MT, Aznar J, Martínez M, Moscardó A, Piñón M et al (2002) Platelet-erythrocyte interactions enhance alpha(IIb)beta(3) integrin receptor activation and P-selectin expression during platelet recruitment: down-regulation by aspirin ex vivo. Blood 99(11):3978–3984
De Stefano V, Rossi E, Za T, Ciminello A, Betti S, Luzzi C et al (2011) JAK2 V617F mutational frequency in essential thrombocythemia associated with splanchnic or cerebral vein thrombosis. Am J Hematol 86(6):526–528
Hobbs CM, Manning H, Bennett C, Vasquez L, Severin S, Brain L et al (2013) JAK2V617F leads to intrinsic changes in platelet formation and reactivity in a knock-in mouse model of essential thrombocythemia. Blood 122(23):3787–3797
James C, Ugo V, Casadevall N, Constantinescu SN, Vainchenker W (2005) A JAK2 mutation in myeloproliferative disorders: pathogenesis and therapeutic and scientific prospects. Trends Mol Med 11(12):546–554
Coucelo M, Caetano G, Sevivas T, Almeida Santos S, Fidalgo T, Bento C et al (2014) JAK2V617F allele burden is associated with thrombotic mechanisms activation in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia patients. Int J Hematol 99(1):32–40
Torregrosa JM, Ferrer-Marín F, Lozano ML, Moreno MJ, Martinez C, Anton AI et al (2016) Impaired leucocyte activation is underlining the lower thrombotic risk of essential thrombocythaemia patients with CALR mutations as compared with those with the JAK2 mutation. Br J Haematol 172(5):813–815
Vannucchi AM, Antonioli E, Guglielmelli P, Pancrazzi A, Guerini V, Barosi G et al (2008) Characteristics and clinical correlates of MPL 515W%3eL/K mutation in essential thrombocythemia. Blood 112(3):844–847
Ju MK, Fu RF, Li HY, Liu XF, Xue F, Chen YF et al (2018) Clinical Characteristic of "triple-negative" essential thrombocythaemia patients and mutation analysis by targeted Sequencing. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 26(4):1137–1145
Musallam KM, Aoun EG, Mahfouz RA, Khalife M, Taher AT (2010) JAK2V617F and prothrombin G20210A gene mutations in a patient with Budd-Chiari syndrome and essential thrombocythemia. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 16(4):472–474
Denninger MH, Chaït Y, Casadevall N, Hillaire S, Guillin MC, Bezeaud A et al (2000) Cause of portal or hepatic venous thrombosis in adults: the role of multiple concurrent factors. Hepatology 31(3):587–591
Mehtap O, Ateşoğlu EB, Tarkun P, Gönüllü E, Keski H, Topçu Y et al (2012) The association between gene polymorphisms and leukocytosis with thrombotic complications in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Turk J Haematol 29(2):162–169
Hoekstra T, Geleijnse JM, Kluft C, Giltay EJ, Kok FJ, Schouten EG (2003) 4G/4G genotype of PAI-1 gene is associated with reduced risk of stroke in elderly. Stroke 34(12):2822–2828
Robien K, Ulrich CM (2003) 5,10-Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase polymorphisms and leukemia risk: a HuGE minireview. Am J Epidemiol 157(7):571–582
Buxhofer-Ausch V, Olcaydu D, Gisslinger B, Schalling M, Frantal S, Thiele J et al (2014) Decanucleotide insertion polymorphism of F7 significantly influences the risk of thrombosis in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Eur J Haematol 93(2):103–111
Zhang X, Lynch AI, Davis BR, Ford CE, Boerwinkle E, Eckfeldt JH et al (2012) Pharmacogenetic association of NOS3 variants with cardiovascular disease in patients with hypertension: the GenHAT study. PLoS ONE 7(3):e34217
Mo X, Hao Y, Yang X, Chen S, Lu X, Gu D (2011) Association between polymorphisms in the coagulation factor VII gene and coronary heart disease risk in different ethnicities: a meta-analysis. BMC Med Genet 12:107
Girelli D, Russo C, Ferraresi P, Olivieri O, Pinotti M, Friso S et al (2000) Polymorphisms in the factor VII gene and the risk of myocardial infarction in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 343(11):774–780
Cacciola RR, Cipolla A, Di Francesco E, Giustolisi R, Cacciola E (2005) Treatment of symptomatic patients with essential thrombocythemia: effectiveness of anagrelide. Am J Hematol 80(1):81–83
Szumowska A, Galar M, Bolkun L, Kloczko J (2016) Plasma concentrations of protein Z and protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 22(7):679–684
Tabatabai A, Fiehler R, Broze GJ Jr (2001) Protein Z circulates in plasma in a complex with protein Z-dependent protease inhibitor. Thromb Haemost 85(4):655–660
Brogren H, Wallmark K, Deinum J, Karlsson L, Jern S (2011) Platelets retain high levels of active plasminogen activator inhibitor 1. PLoS ONE 6(11):e26762
Briere J, Guilmin F (2001) Management of patients with essential thrombocythemia: current concepts and perspectives. Pathol Biol (Paris) 49(2):178–183
Undas A (2014) Fibrin clot properties and their modulation in thrombotic disorders. Thromb Haemost 112(1):32–42
Tefferi A, Barbui T (2019) Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am J Hematol 94(1):133–143
Moulard O, Mehta J, Fryzek J, Olivares R, Iqbal U, Mesa RA (2014) Epidemiology of myelofibrosis, essential thrombocythemia, and polycythemia vera in the European Union. Eur J Haematol 92(4):289–297
Tefferi A, Elliott M (2007) Thrombosis in myeloproliferative disorders: prevalence, prognostic factors, and the role of leukocytes and JAK2V617F. Semin Thromb Hemost 33(4):313–320
Finazzi G, Carobbio A, Guglielmelli P, Cavalloni C, Salmoiraghi S, Vannucchi AM et al (2014) Calreticulin mutation does not modify the IPSET score for predicting the risk of thrombosis among 1150 patients with essential thrombocythemia. Blood 124(16):2611–2612
Barbui T, Barosi G, Birgegard G, Cervantes F, Finazzi G, Griesshammer M et al (2011) Philadelphia-negative classical myeloproliferative neoplasms: critical concepts and management recommendations from European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol 29(6):761–770
Barbui T, Finazzi G, Carobbio A, Thiele J, Passamonti F, Rumi E et al (2012) Development and validation of an international prognostic score of thrombosis in World Health Organization-essential thrombocythemia (IPSET-thrombosis). Blood 120(26):5128–5133 quiz 252
Haider M, Gangat N, Lasho T, Abou Hussein AK, Elala YC, Hanson C et al (2016) Validation of the revised international prognostic score of thrombosis for essential thrombocythemia (IPSET-thrombosis) in 585 mayo clinic patients. Am J Hematol 91(4):390–394
Hashimoto Y, Nakamae H, Tanaka T, Omura H, Horiuchi M, Yoshimura T et al (2018) Validation of previous prognostic models for thrombosis and exploration of modified models in patients with essential thrombocythemia. Eur J Haematol 101(4):508–513
Tefferi A, Barbui T (2017) Polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia: 2017 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification, and management. Am J Hematol 92(1):94–108
Grinfeld J, Nangalia J, Baxter EJ, Wedge DC, Angelopoulos N, Cantrill R et al (2018) Classification and personalized prognosis in myeloproliferative neoplasms. N Engl J Med 379(15):1416–1430
Pikman Y, Lee BH, Mercher T, McDowell E, Ebert BL, Gozo M et al (2006) MPLW515L is a novel somatic activating mutation in myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. PLoS Med 3(7):e270
Malcovati L, Rumi E, Cazzola M (2014) Somatic mutations of calreticulin in myeloproliferative neoplasms and myelodysplastic/myeloproliferative neoplasms. Haematologica 99(11):1650–1652
Wolanskyj AP, Schwager SM, McClure RF, Larson DR, Tefferi A (2006) Essential thrombocythemia beyond the first decade: life expectancy, long-term complication rates, and prognostic factors. Mayo Clin Proc 81(2):159–166
Patrono C, Rocca B, De Stefano V (2013) Platelet activation and inhibition in polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Blood 121(10):1701–1711
Acknowledgements
We wish to thank all our colleagues in Allied Health Sciences School, Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Dr. NS conceived the manuscript and revised it. MM, SS, MG, and TV wrote the manuscript and prepared tables and figures.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
For this type of study, informed consent is not required.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maleknia, M., Shahrabi, S., Ghanavat, M. et al. Essential thrombocythemia: a hemostatic view of thrombogenic risk factors and prognosis. Mol Biol Rep 47, 4767–4778 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05536-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-020-05536-x