Abstract
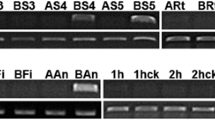
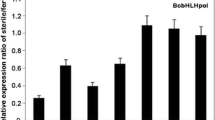
In this report a full length cDNA, Brassica campestris Male Fertile 21 (BcMF21) was successfully isolated from one of the cDNA-amplified fragment length polymorphism (cDNA-AFLP) transcript-derived fragments (TDFs), BBP10, that was found down-regulated in the flower buds of sterile plants in Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino genic male sterile (GMS) AB line system (Bcajh 97-01A/B). BcMF21 protein structure analysis showed a signal peptide at the N-terminus; two protein kinase C phosphorylation sites, five N-myristoylation sites and one casein kinase II phosphorylation site. The promoter region of BcMF21, a 779 bp upstream of ATG was isolated by thermal asymmetric interlaced-PCR (TAIL-PCR). Bioinformatics analysis revealed that the promoter of BcMF21 contained several classical cis-acting elements and three pollen specific elements. Transient expression analysis showed that the promoter could drive green fluorescence protein (GFP) expression. Quantitative reverse transcript-PCR analysis revealed that BcMF21 was specifically expressed in flower buds. The transcript level of BcMF21 was much lower in the sterile flower buds than in the fertile flower buds in ‘Bcajh 97-01A/B’ system. In situ hybridization further showed that BcMF21 was only expressed in the tetrads and the microspores at the tetrad stage and the uninucleate stage. In addition, phylogenetic analysis demonstrated that the BcMF21 was relative conserved within family Crucifereae and might be originated from the ancestor diploid B. campestris within genus Brassica according to the Triangle of U theory.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BcMF21 :
-
Brassica campestris male fertile 21
- cDNA-AFLP:
-
cDNA-amplified fragment length polymorphism
- ORF:
-
Open reading frame
- qRT-PCR:
-
Quantitative reverse transcript polymerase chain reaction
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- TAIL-PCR:
-
Thermal asymmetric interlaced-PCR
References
Becker JD, Boavida LC, Carneiro J, Haury M, Feijo JA (2003) Transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis tissues reveals the unique characteristics of the pollen transcriptome. Plant Physiol 133:713–725
Honys D, Twell D (2003) Comparative analysis of the Arabidopsis polleb transcriptome. Plant Physiol 132:640–652
Honys D, Twell D (2004) Transcriptome analysis of haploid male gametophyte development in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 5:R85
Pina C, Pinto F, Feijo J, Becker J (2005) Gene family analysis of the Arabidopsis pollen transcriptome reveals biological implications for cell growth, division control, and gene expression regulation. Plant Physiol 138:744–756
Ma H, Sundaresan V (2010) Development of flowering plant gametophytes. Curr Top Dev Biol 91:379–412
Olmedilla A (2010) Microspore embryogenesis. In: Pua EC, Davey MR (eds) Plant development biology–biotechnological perspectives. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Chang F, Wang Y, Wang, Ma H (2011) Molecular control of microsporogenesis in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:66–73
Yang X, Makaroff CA, Ma H (2003) The Arabidopsis MALE MEIOCYTE DEATH 1 gene encodes a PHD-finger protein that is required for male meiosis. Plant Cell 15:1281–1295
Zhou S, Wang Y, Li W, Zhao Z, Ren Y, Gu S, Wang Y, Lin Q, Wang D, Jiang L, Su N, Zhang X, Liu L, Cheng Z, Lei C, Wang J, Guo X, Wu F, Ikehashi H, Wang H, Wan J (2011) Pollen Semi-Sterility 1 encodes a Kinesin-like protein important for male meiosis, anther dehiscence and fertility in Rice. Plant Cell 23:111–129
Zeng CJT, Lee YRJ, Liu B (2009) The WD4 repeat protein NEDD1 functions in microtubule organization during cell division in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 21:1129–1140
Gusti A, Baumberger N, Nowack M, Pusch S, Eisler H, Potuschak T, De Veylder L, Schnittger A, Genschik P (2009) The Arabidopsis thaliana F-box protein FBL 17 is essential for progression through the second mitosis during pollen development. PLoS One 4:e4780
Aarts MG, Kerjzer CJ, Stietkema WJ, Pereira A (1995) Mocecular characterization of the CER1 gene of arabidopsis involved in epicuticular wax biosynthesis and pollen fertility. Plant Cell 7:2115–2127
Huang L, Cao J, Zhang A, Ye Y, Zhang Y, Liu T (2009) The polygalacturonase gene BcMF2 from Brassica campestris is associated with intine development. J Exp Bot 60:301–313
Huang L, Ye Y, Zhang Y, Zhang A, Liu T, Cao J (2009) BcMF9, a novel polygalacturonase gene, is required for both Brassica campestris intine and exine formation. Ann Bot 104:1339–1351
Quilichini TD, Friedmann MC, Samuels AL, Douglas CJ (2010) ATP-binding cassette transporter G26 is required for male fertility and pollen exine formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 154:678–690
Wang YQ, Ye WZ, Cao J, Yu XL, Xiang X, Lu G (2005) Cloning and characterization of the microspore development-related gene BcMF2 in Chinese Cabbage Pak-Choi (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino). J Integr Plant Biol 47:863–872
Huang L, Cao J, Ye W, Liu T, Jiang L, Ye Y (2008) Transcriptional differences between the male-sterile mutant bcms and wild-type Brassica campestris ssp.chinensis reveal genes related to pollen development. Plant Biol 10:342–355
Huang L, Ye W, Liu T, Cao J (2009) Characterization of the male-sterile line ‘Bcajh97-01A/B’ and identification of candidate genes for genic male sterility in Chinese cabbage-pak-choi. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 134:632–640
Huang L, Zhao X, Liu T, Dong H, Cao J (2010) Developmental characteristics of floral organs and pollen of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis). Plant Syst Evol 286:103–115
Huang L, Cao J, Zhang YC, Ye YQ (2007) Characterization of a novel gene, BcMF7 that is expressed preferentially in pollen of Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino. Sci China C Life Sci 50:497–504
Huang L, Cao J, Zhang AH, Ye YQ (2008) Characterization of a putative pollen-specific arabinogalactan protein gene, BcMF8, from Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. Mol Biol Rep 35:631–639
Huang L, Cao J, Zhang AH, Zhang YC, Ye YQ (2008) Characterization of BcMF10, a novel gene involved in pollen wall development of Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis. Funct Plant Biol 35:1194–1204
Huang L, Liu Y, Yu X, Xiang X, Cao J (2011) A polygalacturonase inhibitory protein gene (BcMF19) expressed during pollen development in Chinese cabbage-pak-choi. Mol Biol Rep 38:545–552
Liu LC, Wang YQ, Zhang T, Huang L, Xiang X, Cao J (2007) Isolation and characterization of the microspore-related gene BcMF4 in Chinese cabbage-pak-choi and its functional identification in Arabidopsis. J Hortic Sci Biotech 82:133–139
Li Y, Cao J (2008) Morphological and functional characterization of BcMF13 in the antisense-silenced plants of Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis var. parachinensis. Mol Biol Rep 36:929–937
Li Y, Cao J, Huang L, Yu XL, Xiang X (2008) BcMF13, a new reproductive organ-specific gene from Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis, affects pollen development. Mol Biol Rep 35:207–214
Zhang Q, Cao J, Liu HZ, Huang L, Xiang X, Yu XL (2008) Characterization and functional analysis of a novel PCP gene BcMF5 from Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino). J Plant Physiol 165:445–455
Zhang Q, Huang L, Liu T, Yu X, Cao J (2008) Functional analysis of a pollen-expressed polygalacturonase gene BcMF6 in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. chinensis Makino). Plant Cell Rep 27:1207–1215
Song JH, Zhang LX, Cao J (2009) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel pollen predominantly membrane protein gene BcMF12 from Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis. Mol Biol Rep 36:2307–2314
Cao J, Cao S, Yi Q (1995) RAPD analysis on genomic DNA of Chinese cabbage and the other groups of Brassica. Acta Hort Sin 22:47–52
Liu YG, Whittier RF (1995) Thermal asymmetric interlaced PCR: automatable amplification and sequencing of insert end fragments from PI and YAC clones for chromosome walking. Genomics 25:674–681
Krause K, Kilbienski I, Mulisch M, Rödiger A, Schäfer A, Krupinska K (2005) DNA-binding proteins of the Whirly family in Arabidopsis thaliana are targeted to the organelles. FEBS Lett 579:3707–3712
Yang C, Vizcay-Barrena G, Conner K, Wilson ZA (2007) MALE STERILITY1 is required for tapetal development and pollen wall biosynthesis. Plant Cell 19:3530–3548
Zhang J, Weiler S, Oh KJ, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ (2000) Posttranslational N-myristoylation of BID as a molecular switch for targeting mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 290:1761–1765
Pierrea M, Traversoa JA, Boissona B, Domenichinib S, Bouchezc D, Giglionea C, Meinnela T (2007) N-Myristoylation regulates the SnRK1 pathway in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2804–2821
Newton AC (1995) Protein kinase C: structure, function, and regulation. J Biol Chem 270:28495–28498
Larsson C (2006) Protein kinase C and the regulation of the actin cytoskeleton. Cell Signal 18:276–284
Ahmed K, Allende JE, Issinger OG (2001) Protein kinase CK2 - from structure to regulation. Kluwer academic publishers, The Netherlands
Ogiso E, Takahashi Y, Sasaki T, Yano M, Izawa T (2010) The role of casein kinase II in flowering time regulation has diversified during evolution. Plant Physiol 152:808–820
Bate N, Twell D (1998) Functional architecture of a late pollen promoter: pollen-specific transcription is developmentally regulated by multiple stage-specific and co-dependent activator elements. Plant Mol Biol 37:859–869
Rogers HJ, Bate N, Combe J, Sullivan J, Sweetman J, Swan C, Lonsdale DM, Twell D (2001) Functional analysis of cis-regulatory elements within the promoter of the tobacco late pollen gene g10. Plant Mol Biol 45:577–585
Mascarenhas JP (1990) Gene activity during pollen development. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 41:317–338
Xu SX, Liu GS, Chen RD (2006) Characterization of an anther- and tapetum-specific gene and its highly specific promoter isolated from tomato. Plant Cell Rep 25:231–240
Chen L, Tu Z, Hussain J, Cong L, Yan Y, Jin L, Yang G, He G (2010) Isolation and heterologous transformation analysis of a pollen-specific promoter from wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Mol Biol Rep 37:737–744
Filichkin SA, Leonard JM, Monteros A, Liu PP, Nonogaki H (2004) A novel endo-β-mannanase gene in tomato LeMAN5 is associated with anther and pollen development. Plant Physiol 134:1080–1087
Nagaharu U (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Parkin IA, Lydiate DJ (1997) Conserved patterns of chromosome pairing and recombination in Brassica napus crosses. Genome 40:496–504
Liu AH, Wang JB, Zhu YG (2003) RAPS analysis on the genome evolution of polyploids in Brassica. Acta Phytotaxon Sin 41:520–530
Udall J, Ouijada P, Osborn TC (2005) Detection of chromosomal rearrangement derived from homoeologous recombination in four mapping populations of Brassica napus L. Genetics 169:967–979
Acknowledgment
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30871715).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, J., Yu, X., Miao, Y. et al. Sequence characterization and expression pattern of BcMF21, a novel gene related to pollen development in Brassica campestris ssp. chinensis . Mol Biol Rep 39, 7319–7326 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1563-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1563-6