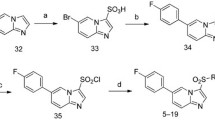
Abstract
The c-Met tyrosine kinase plays an important role in human cancers. Preclinical studies demonstrated that c-Met is over-expressed, mutated and amplified in a variety of human tumor types and design of more potent c-Met inhibitors is a priority. In this study, 14 molecular dynamics simulations of potent type II c-Met inhibitors were run to resolve the critical interactions responsible for high affinity of ligands towards c-Met considering the essential flexibility of protein–ligand interactions. Residues Phe1223 and Tyr1159, involved in pi-pi interactions were recognized as the most effective residues in the ligand binding in terms of binding free energies. Hydrogen bond interaction with Met1160 was also found necessary for effective type II ligand binding to c-Met.
Graphic abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332
Collins I, Workman P (2006) New approaches to molecular cancer therapeutics. Nat Chem Biol 2:689–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio840
Birchmeier C, Gherardi E (1998) Developmental roles of HGF/SF and its receptor, the c-Met tyrosine kinase. Trends Cell Biol 8:404–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0962-8924(98)01359-2
Lv P-C, Yang Y-S, Wang Z-C (2019) Recent progress in the development of small molecule c-met inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem 19:1276–1288. https://doi.org/10.2174/1568026619666190712205353
Zhang Y, Xia M, Jin K, Wang S, Wei H, Fan C, Wu Y, Li X, Li X, Li G (2018) Function of the c-Met receptor tyrosine kinase in carcinogenesis and associated therapeutic opportunities. Mol Cancer 17:45. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-018-0796-y
Merchant M, Ma X, Maun HR, Zheng Z, Peng J, Romero M, Huang A, Yang N-y, Nishimura M, Greve J (2013) Monovalent antibody design and mechanism of action of onartuzumab, a MET antagonist with anti-tumor activity as a therapeutic agent. PNAS USA 110:E2987–E2996. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1302725110
Yuan H, Liu Q, Zhang L, Hu S, Chen T, Li H, Chen Y, Xu Y, Lu T (2018) Discovery, optimization and biological evaluation for novel c-Met kinase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 143:491–502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.11.073
Yang Y, Zhang Y, Yang L, Zhao L, Si L, Zhang H, Liu Q, Zhou J (2017) Discovery of imidazopyridine derivatives as novel c-Met kinase inhibitors: Synthesis, SAR study, and biological activity. Bioorg Chem 70:126–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2016.12.002
Cui JJ, Shen H, Tran-Dubé M, Nambu M, McTigue M, Grodsky N, Ryan K, Yamazaki S, Aguirre S, Parker M, Li Q, Zou H, Christensen J (2013) Lessons from (S)-6-(1-(6-(1-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl) [1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b]pyridazin-3-yl)ethyl)quinoline (PF-04254644), an inhibitor of receptor tyrosine kinase c-met with high protein kinase selectivity but broad phosphodiesterase family inhibition leading to myocardial degeneration in rats. J Med Chem 56:6651–6665. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm400926x
El-Wakil MH, Ashour HM, Saudi MN, Hassan AM, Labouta IM (2018) Design, synthesis and molecular modeling studies of new series of antitumor 1, 2, 4-triazines with potential c-Met kinase inhibitory activity. Bioorg Chem 76:154–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioorg.2017.11.006
Cui H, Peng X, Liu J, Ma C, Ji Y, Zhang W, Geng M, Li Y (2016) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of c-Met kinase inhibitors bearing 2-oxo-1, 2-dihydroquinoline scaffold. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 26:4483–4486. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2016.07.077
Zhao Y, Zhang J, Zhuang R, He R, Xi J, Pan X, Shao Y, Pan J, Sun J, Cai Z (2017) Synthesis and evaluation of a series of pyridine and pyrimidine derivatives as type II c-Met inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 25:3195–3205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2017.04.003
Parikh PK, Ghate MD (2018) Recent advances in the discovery of small molecule c-Met Kinase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 143:1103–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.08.044
Damghani T, Sedghamiz T, Sharifi S, Pirhadi S (2020) Critical c-Met-inhibitor interactions resolved from molecular dynamics simulations of different c-Met complexes. J Mol Struct 1203:127456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molstruc.2019.127456
Asses Y, Leroux V, Tairi-Kellou S, Dono R, Maina F, Maigret B (2009) Analysis of c-Met kinase domain complexes: a new specific catalytic site receptor model for defining binding modes of ATP-competitive ligands. Chem Biol Drug Des 74:560–570. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-0285.2009.00895.x
Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L (2018) SWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:W296–W303. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky427
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera-a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20084
Da Silva AWS, Vranken WF (2012) ACPYPE-Antechamber python parser interface. BMC Res notes 5:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-5-367
Kumari R, Kumar R, Consortium OSDD, Lynn A (2014) g_mmpbsa-A GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations. J Chem Inf Model 54:1951–1962. https://doi.org/10.1021/ci500020m
Baker NA, Sept D, Joseph S, Holst MJ, McCammon JA (2001) Electrostatics of nanosystems: application to microtubules and the ribosome. PNAS USA 98:10037–10041. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.181342398
Castiglione F, Crupi V, Majolino D, Mele A, Rossi B, Trotta F, Venuti V (2012) Effect of cross-linking properties on the vibrational dynamics of cyclodextrins-based polymers: an experimental–numerical study. J Phys Chem 116:7952–7958. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp303006a
Brewster ME, Loftsson T (2007) Cyclodextrins as pharmaceutical solubilizers. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 59:645–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2007.05.012
Pronk S, Páll S, Schulz R, Larsson P, Bjelkmar P, Apostolov R, Shirts MR, Smith JC, Kasson PM, van der Spoel D (2013) GROMACS 4.5: a high-throughput and highly parallel open source molecular simulation toolkit. J Bioinform 29:845–854. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btt055
Chen K, Kurgan L (2009) Investigation of atomic level patterns in protein—small ligand interactions. PLoS ONE 4:e4473. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0004473
Aftabuddin M, Kundu S (2007) Hydrophobic, hydrophilic, and charged amino acid networks within protein. Biophys J 93:225–231. https://doi.org/10.1529/biophysj.106.098004
http://manual.gromacs.org/documentation/2019/reference-manual/index.html.
Norman MH, Liu L, Lee M, Xi N, Fellows I, D’Angelo ND, Dominguez C, Rex K, Bellon SF, Kim T-S (2012) Structure-based design of novel class II c-Met inhibitors: 1. Identification of pyrazolone-based derivatives. J Med Chem 55:1858–1867. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm201330u
Matsumoto S, Miyamoto N, Hirayama T, Oki H, Okada K, Tawada M, Iwata H, Nakamura K, Yamasaki S, Miki H (2013) Structure-based design, synthesis, and evaluation of imidazo [1, 2-b] pyridazine and imidazo [1, 2-a] pyridine derivatives as novel dual c-Met and VEGFR2 kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 21:7686–7698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmc.2013.10.028
Smith BD, Kaufman MD, Leary CB, Turner BA, Wise SC, Ahn YM, Booth RJ, Caldwell TM, Ensinger CL, Hood MM (2015) Altiratinib inhibits tumor growth, invasion, angiogenesis, and microenvironment-mediated drug resistance via balanced inhibition of MET, TIE2, and VEGFR2. Mol Cancer Ther 14:2023–2034. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-14-1105
Hong DS, LoRusso P, Hamid O, Janku F, Kittaneh M, Catenacci DVT, Chan E, Bekaii-Saab T, Gadgeel SM, Loberg RD, Amore BM, Hwang YC, Tang R, Ngarmchamnanrith G, Kwak EL (2019) Phase I study of AMG 337, a highly selective small-molecule MET inhibitor, in patients with advanced solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 25:2403. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-1341
D’Angelo ND, Bellon SF, Booker SK, Cheng Y, Coxon A, Dominguez C, Fellows I, Hoffman D, Hungate R, Kaplan-Lefko P (2008) Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of potent c-Met inhibitors. J Med Chem 51:5766–5779. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm8006189
Cai Z-W, Wei D, Schroeder GM, Cornelius LA, Kim K, Chen X-T, Schmidt RJ, Williams DK, Tokarski JS, An Y (2008) Discovery of orally active pyrrolopyridine-and aminopyridine-based Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:3224–3229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2008.04.047
Yan SB, Peek VL, Ajamie R, Buchanan SG, Graff JR, Heidler SA, Hui Y-H, Huss KL, Konicek BW, Manro JR (2013) LY2801653 is an orally bioavailable multi-kinase inhibitor with potent activity against MET, MST1R, and other oncoproteins, and displays anti-tumor activities in mouse xenograft models. Invest New Drugs 31:833–844. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10637-012-9912-9
Williams DK, Chen X-T, Tarby C, Kaltenbach R, Cai Z-W, Tokarski JS, An Y, Sack JS, Wautlet B, Gullo-Brown J (2010) Design, synthesis and structure–activity relationships of novel biarylamine-based Met kinase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 20:2998–3002. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2010.01.042
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the [Vice Chancellor of Research, Shiraz University of Medical Sciences] under Grant [Number 98-01-12-20089].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Damghani, T., Elyasi, M., Pirhadi, S. et al. Type II c-Met inhibitors: molecular insight into crucial interactions for effective inhibition. Mol Divers 26, 1411–1423 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10267-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11030-021-10267-7