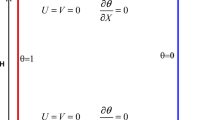Abstract
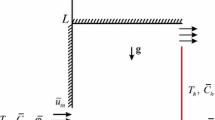
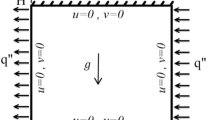
The objective of this study is to extend the attention of the incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics method (ISPH) in the heat transfer field. The ISPH method for the natural convection heat transfer under the Boussinesq approximation in various environments: pure-fluid, nanofluid, and non-Darcy porous medium is introduced. We adopted the improved analytical method for calculating the kernel renormalization factor and its gradient based on a quintic kernel function for the wall boundary treatment in the ISPH method. The proposed method requires no dummy particle layer to meet the impermeability condition and makes the heat flux over the wall boundary easy to implement. We performed four different numerical simulations of natural convection in cavities with increasing complexity in modeling and implementation: the natural convection in a square cavity with constant differentially heated wall temperature, natural convection with the heat flux from the bottom wall for a wide range of Rayleigh numbers, natural convection in a non-Darcy porous cavity fully filled with nanofluid in different flow regimes, and natural convection in a partially layered porous cavity. The results showed excellent agreement with results from literatures and the in-house P1–P1 finite element method code.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lucy LB (1977) A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron J 82:1013–1024
Gingold RA, Monaghan JJ (1977) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 181:375–389
Koshizuka S, Oka Y (1996) Moving-particle semi-implicit method for fragmentation of incompressible fluid. Nucl Sci Eng 123:421–434
Aly AM (2012) An Improved incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics to simulate fluid–soil–structure interactions. Kyushu University. https://wiki.manchester.ac.uk/s
Amdahl DL (1993) Modeling aerodynamic problems using smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH). SAE Technical Paper, No. 932512. https://doi.org/10.4271/932512
Hu XY, Adams NA (2006) A multi-phase SPH method for macroscopic and mesoscopic flows. J Comput Phys 213:844–861
Monaghan JJ (1994) Simulating free surface flows with SPH. J Comput Phys 110:399–406
Fourey G, Oger G, Touzé DL, Alessandrini B (2010) Violent fluid–structure interaction simulations using a coupled SPH/FEM method. In: IOP conference series: materials science and engineering, vol 10, p 012041
Cummins SJ, Rudman M (1999) An SPH projection method. J Comput Phys 152:584–607
Shao S, Lo EYM (2003) Incompressible SPH method for simulating newtonian and non-newtonian flows with a free surface. Adv Water Resour 26:787–800
Khayyer A, Gotoh H, Shao SD (2008) Corrected incompressible SPH method for accurate water-surface tracking in breaking waves. Coast Eng 55:236–250
Asai M, Sonoda AMA, Sakai YY (2012) A Stabilized incompressible SPH method by relaxing the density invariance condition. J Appl Math Mech 2012:24
Aly AM, Lee SW (2014) Numerical simulations of impact flows with incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J Mech Sci Technol 28:2179–2188
Gotoh H, Khayyer A (2016) A Current achievements and future perspectives for projection-based particle methods with applications in ocean engineering. J Ocean Eng Mar Energy 2016:1–28
Shadloo MS, Oger G, Le Touzé D (2016) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics method for fluid flows, towards industrial applications: motivations, current state, and challenges. Comput Fluids 136:11–34
Basak T, Roy S, Thirumalesha C (2007) Finite element analysis of natural convection in a triangular enclosure: effects of various thermal boundary conditions. Chem Eng Sci 62:2623–2640
Oztop HF, Varol Y, Pop I (2009) Investigation of natural convection in triangular enclosure filled with porous media saturated with water near 4°C. Energ Convers Manag 50:1473–1480
Sieres J, Campo A, Ridouane EH, Fernándes-Seara J (2007) Effect of surface radiation on buoyant convection in vertical triangular cavities with variable aperture angles. Int J Heat Mass Transf 50:5139–5149
Varol Y, Oztop HF, Pop I (2009) Entropy generation due to natural convection in non-uniformly heated porous isosceles triangular enclosures at different positions. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:1193–1205
Varol Y, Oztop HF, Pop I (2009) Natural convection in right-angle porous trapezoidal enclosure partially cooled from inclined wall. Int Commun Heat Mass 36:6–15
Chamkha AJ, Ismael MA (2014) Natural convection in differentially heated partially porous layered cavities filled with a nanofluid. Numer Heat Transf Appl 65:1089–1113
Chamkha AJ, Mansour MA, Ahmed SE (2010) Double-diffusive natural convection in inclined finned triangular porous enclosures in the presence of heat generation/absorption effects. Heat Mass Transf 46:757–768
Aly AM (2017) Natural convection over circular cylinders in a porous enclosure filled with a nanofluid under thermo-diffusion effects. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 70:88–103
Nguyen MT, Aly AM, Lee SW (2015) Natural convection in a non-Darcy porous cavity filled with cu–water nanofluid using the characteristic-based split procedure in finite-element method. Numer Heat Transf Appl 67:224–247
Nithiarasu P, Sundararajan T, Seetharamu KN (1998) Finite element analysis of transient natural convection in an odd-shaped enclosure. Int J Numer Methods H 8:199–216
Aly AM (2015) Modeling of multi-phase flows and natural convection in a square cavity using an incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Int J Numer Method Heat 25:513–533
Aly AM, Asai M (2015) Modelling of non-Darcy flows through porous media using extended incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. Numer Heat Transf B Fundam 67:255–279
Aly AM, Chamkha AJ, Lee SW, Al-Mudhaf A (2016) On mixed convection in an inclined lid-driven cavity with sinusoidal heated walls using the ISPH method. Int J Comput Therm 8:337–354
Leroy A, Violeau D, Ferrand M, Joly A (2015) Buoyancy modelling with incompressible SPH for laminar and turbulent flows. Int J Numer Methods Fluid 78:455–474
Cleary PW, Monaghan JJ (1999) Conduction modelling using smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J Comput Phys 148:227–264
Chaniotis AK, Poulikakos D, Koumoutsakos P (2002) Remeshed smoothed particle hydrodynamics for the simulation of viscous and heat conducting flows. J Comput Phys 182:67–90
Danis ME, Orhan M, Ecder A (2013) ISPH modelling of transient natural convection. Int J Comput Fluid D 27:15–31
Szewc K, Pozorski J, Taniére A (2011) Modeling of natural convection with smoothed particle hydrodynamics: non-Boussinesq formulation. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:4807–4816
Morris JP, Fox PJ, Zhu Y (1997) Modeling low Reynolds number incompressible flows using SPH. J Comput Phys 136:214–226
Yildiz M, Rock RA, Suleman A (2009) SPH with the multiple boundary tangent method. Int J Numer Methods Eng 77:1416–1438
Leroy A, Violeau D, Ferrand M, Kassiotis C (2014) Unified semi-analytical wall boundary conditions applied to 2-D incompressible SPH. J Comput Phys 261:106–129
De Leffe M, Le Touze D, Alessandrini B (2009) Normal flux method at the boundary for SPH. 4th Int SPHERIC Workshop (SPHERIC 2009), Nantes, France
Feldman J, Bonet J (2007) Dynamic refinement and boundary contact forces in SPH with applications in fluid flow problems. Int J Numer Methods Eng 72:295–324
Monaco AD, Manenti S, Gallati M, Sibilla S, Agate G, Guandalini R (2011) SPH modeling of solid boundaries through a semi-analytic approach. Eng Appl Comput Fluid 5:1–15
Ferrandd M, Laurence DR, Rogers BD, Violearu D, Kassiotis C (2013) Unified semi-analytical wall boundary conditions for inviscid, laminar or turbulent flows in the meshless SPH method. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 71:446–472
Mayrhofer A, Rogers BD, Violeau D, Ferrand M (2013) Investigation of wall bounded flows using SPH and the unified semi-analytical wall boundary conditions. Comput Phys Commun 184:2515–2527
Macià F, González LM, Cercos-pita JL, Souto-iglesias A (2012) A boundary integral SPH formulation: consistency and applications to ISPH and WCSPH. Prog Theor Phys 128:439–462
Ellero M, Serrano M, Espanol P (2007) Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics. J Comput Phys 226(2):1731–1752
Chorin AJ (1968) Numerical solution of the Navier–Stokes equations. Math Comput 22:745–762
Lind SJ, Xu R, Stansby PK, Rogers BD (2012) Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics for free-surface flows: a generalised diffusion-based algorithm for stability and validations for impulsive flows and propagating waves. J Comput Phys 231:1499–1523
Skillen A, Lind S, Stansby PK, Rogers BD (2013) Incompressible smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) with reduced temporal noise and generalised Fickian smoothing applied to body–water slam and efficient wave–body interaction. Comput Method Appl M 265:163–173
Brookshaw L (1985) A method of calculating radiative heat diffusion in particle simulations. Proc Astron Soc Aust 6:207–210
Kulasegaram S, Bonet J, Lewis WR, Profit M (2004) A variational formulation based contact algorithm for rigid boundaries in two-dimensional SPH applications. Comput Mech 33:316–325
Davis GDV (1983) Natural convection of air in a square cavity: a bench mark numerical solution. Int J Numer Methods Fluids 3:249–264
Nguyen MT, Aly AM, Lee SW (2016) Unsteady natural convection heat transfer in a nanofluid-filled square cavity with various heat source conditions. Adv Mech Eng 8(5):1–18
Nithiarasu P, Seetharamu KN, Sundararajan T (1997) Natural convective heat transfer in a fluid saturated variable porosity medium. Int J Heat Mass Transf 40:3955–3967
Maxwell J (1904) A treatise on electricity and magnetism, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Brinkman HC (1952) The Viscosity of concentrated suspensions and solutions. J Chem Phys 20:571
Beckermann C, Ramadhyani S, Viskanta R (1987) Natural convection flow and heat transfer between a fluid layer and a porous layer inside a rectangular enclosure. J Heat Transf 109:363–370
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the University of Ulsan, Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, M.T., Aly, A.M. & Lee, SW. ISPH modeling of natural convection heat transfer with an analytical kernel renormalization factor. Meccanica 53, 2299–2318 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-018-0825-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-018-0825-3