Abstract
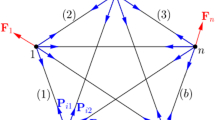
The coupling between form and forces, their structural morphology, is a key point for tensegrity systems. In the first part of this paper we describe the design process of the simplest tensegrity system which was achieved by Kenneth Snelson. Some other simple cells are presented and tensypolyhedra are defined as tensegrity systems which meet polyhedra geometry in a stable equilibrium state. A numerical model giving access to more complex systems, in terms of number of components and geometrical properties, is then evoked. The third part is devoted to linear assemblies of annular cells which can be folded. Some experimental models of the tensegrity ring which is the basic component of this “hollow rope” have been realized and are examined.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Motro R (1983) Formes et forces dans les systèmes constructifs. Cas des systèmes réticulés spatiaux autocontraints. (2 volumes). Thèse d’Etat. Université Montpellier II. 2 Juin 1983
Schenk M (2005) Statically balanced tensegrity mechanisms. A literature review. Department of BioMechanical Engineering. Delft University of Technology. August 2005
Snelson K (1965) Continuous tension, discontinuous compression structures. US Patent No 3,169,611, Feb 16, 1965
Vassart N, Motro R (1999) Multi parameter form finding method. Application to tensegrity systems. Int J Space Struct 14(2):131–146
Motro R, Smaili A, Foucher O (2002) Form controlled method for tensegrity formfinding: Snelson and Emmerich examples. In: Obrebski JB (ed) International IASS symposium on lightweight structures in civil engineering, contemporary problems, Warsaw, Poland, June 2002. Micropublisher, Warsaw, pp 243–248
Foucher O (2001) Polyèdres et tenségrité. Master, Université Montpellier II
Belkacem S (1987) Recherche de forme par relaxation dynamique de systèmes réticulés spatiaux autocontraints, PhD thesis, Université Paul Sabatier, Toulouse
Li Zhang, Maurin B, Motro R (2006) Form-finding of non regular tensegrity systems. J Struct Eng 132(4):1435–1440
Eberly D (1999) Distance between two line segments in 3D. Magic Software Inc
Motro R (2003) Tensegrity: structural systems for the future. Hermés Penton Sciences, Paris. ISBN 1903996376 (UK)
Pugh A (1976) An introduction to tensegrity. University of California
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Motro, R. Structural morphology of tensegrity systems. Meccanica 46, 27–40 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-010-9379-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-010-9379-8