Abstract
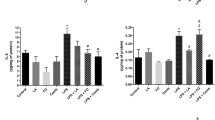
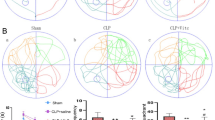
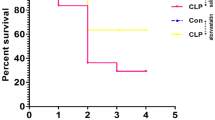
Oxidative stress and inflammation seem to be the main factors responsible for cognitive impairment in sepsis. Genistein (GEN) is claimed to exert many beneficial effects on health, however, its possible effects on brain sepsis remains unclear. Here, we assess the influence and underling mechanisms of GEN on cognitive impairments in cecal ligation and puncture (CLP)-induced septic model. Rats were randomly divided into Sham, Sham + GEN, CLP, CLP + GEN gropus. Rats were treated with GEN (15 mg/kg at 0 and 12 h after CLP, i.p). Twenty-four hours after CLP, protein levels of cytokines, NF-kB and Nrf2, myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity, oxidative damage to lipids and proteins, the activities of antioxidant enzymes and the expression of Nrf2-target genes were evaluated in the hippocampus. At 10 days after sepsis induction, behavioral tests were conducted to evaluate cognitive impairment. The results indicate that GEN can enhance survival percentage and improve cognitive function. Genistein administration significantly reduced TNF-α and IL-1β levels, MPO activity and protein level of NF-kB in the hippocampus of septic rats. Genistein also decreased the levels of oxidative stress parameters (MDA and protein carbonyls) and elevated the activities of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) in septic rats. Furthermore, nuclear Nrf2 and the expression of HO-1 and NQO-1 were also elevated by GEN treatment. These findings suggest that GEN improves cognition impairment in septic rats via decreasing inflammatory responses and oxidative stress, and activation of the Nrf2 pathway.
Graphical Abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Aras AB, Guven M, Akman T et al (2015) Genistein exerts neuroprotective effect on focal cerebral ischemia injury in rats. Inflammation 38(3):1311–1321
Arnalich F, Garcia-Palomero E, López J et al (2000) “Predictive value of nuclear factor κB activity and plasma cytokine levels in patients with sepsis”. Infect Immun 68(4):1942–1945
Bannister JV, Calabrese L (1987) Assays for superoxide dismutase. Methods Biochem Anal 32:279–313
Barichello T, Machado RA, Constantino L et al (2007) “Antioxidant treatment prevented late memory impairment in an animal model of sepsis”. Crit Care Med 35(9):2186–2190
Basu S, Eriksson M (1998) Oxidative injury and survival during endotoxemia. FEBS Lett 438(3):159–160
Byun EB, Sung NY, Yang MS et al (2014) Anti-inflammatory effect of gamma-irradiated genistein through inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway in lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophages. Food Chem Toxicol 74:255–264
Cassol-Jr OJ, Comim CM, Silva BR et al (2010) Treatment with cannabidiol reverses oxidative stress parameters, cognitive impairment and mortality in rats submitted to sepsis by cecal ligation and puncture. Brain Res 1348:128–138
Catalão CHR, Santos-Junior NN, da Costa LHA et al (2020) Simvastatin prevents long-term cognitive deficits in sepsis survivor rats by reducing neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Neurotox Res 38(4):871–886
Della Giustina A, Goldim MP, Danielski LG et al (2020) Fish oil-rich lipid emulsion modulates neuroinflammation and prevents long-term cognitive dysfunction after sepsis. Nutrition 70:110417
Della Giustina A, Goldim MP, Danielski LG et al (2017) Alpha-lipoic acid attenuates acute neuroinflammation and long-term cognitive impairment after polymicrobial sepsis. Neurochem Int 108:436–447
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Kostov RV, Kazantsev AG (2018) “The role of Nrf2 signaling in counteracting neurodegenerative diseases”. FEBS J 285(19):3576–3590
Fang J, Wang H, Zhou J et al (2018) “Baicalin provides neuroprotection in traumatic brain injury mice model through Akt/Nrf2 pathway.“ Drug design, development and therapy 12: 2497
Gu M, Mei X-L, Zhao Y-N (2021) Sepsis and cerebral dysfunction: BBB damage, neuroinflammation, oxidative stress, apoptosis and autophagy as key mediators and the potential therapeutic approaches. Neurotox Res 39(2):489–503
Hsu BG, Lee RP, Yang FL, Harn HJ, Chen HI (2006) “Post-treatment with N-acetylcysteine ameliorates endotoxin shock-induced organ damage in conscious rats. " Life Sci 79(21):2010–2016
Hu Q-p, Huang X-y, Feng W et al (2021) “Genistein Protects Epilepsy-Induced Brain Injury Through Regulating The JAK2/STAT3 and Keap1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathways in The Developing Rats.“
Huang Y-H, Zhang Q-H (2010) Genistein reduced the neural apoptosis in the brain of ovariectomised rats by modulating mitochondrial oxidative stress. Br J Nutr 104(9):1297–1303
Ibrahim AS, El-Shishtawy MM, Peña A Jr, Liou GI (2010) Genistein attenuates retinal inflammation associated with diabetes by targeting of microglial activation. Mol Vis 16:2033–2042
Kawai T, Akira S (2007) Signaling to NF-kappaB by Toll-like receptors. Trends Mol Med 13(11):460–469
Lee YW, Lee WH (2008) Protective effects of genistein on proinflammatory pathways in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Nutr Biochem 19(12):819–825
Liu H, Zhong H, Yin Y, Jiang Z (2017) Genistein has beneficial effects on hepatic steatosis in high fat-high sucrose diet-treated rats. Biomed Pharmacother 91:964–969
Liu SF, Malik AB (2006) NF-κB activation as a pathological mechanism of septic shock and inflammation. Am J Physiology-Lung Cell Mol Physiol 290(4):L622–L645
Ma Q (2013) Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426
Nguyen T, Nioi P, Pickett CB (2009) “The Nrf2-antioxidant response element signaling pathway and its activation by oxidative stress”. J Biol Chem 284(20):13291–13295
Oeckinghaus A, Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2011) “Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways”. Nat Immunol 12(8):695–708
Prauchner CA (2017) Oxidative stress in sepsis: Pathophysiological implications justifying antioxidant co-therapy. Burns 43(3):471–485
Qian L, Weng X-W, Chen W, Sun C-H, Wu J (2014) TREM-1 as a potential therapeutic target in neonatal sepsis. Int J Clin Exp Med 7(7):1650
Reis PA, Alexandre PC, D’Avila JC et al (2017) “Statins prevent cognitive impairment after sepsis by reverting neuroinflammation, and microcirculatory/endothelial dysfunction.“ Brain, behavior, and immunity. 60:293–303
Ritter C, Andrades ME, Reinke A, Menna-Barreto S, Moreira JC, Dal-Pizzol F (2004) “Treatment with N-acetylcysteine plus deferoxamine protects rats against oxidative stress and improves survival in sepsis”. Crit Care Med 32(2):342–349
Schwalm MT, Pasquali M, Miguel SP et al (2014) Acute brain inflammation and oxidative damage are related to long-term cognitive deficits and markers of neurodegeneration in sepsis-survivor rats. Mol Neurobiol 49(1):380–385
Sener G, Toklu H, Ercan F, Erkanli G (2005) Protective effect of beta-glucan against oxidative organ injury in a rat model of sepsis. Int Immunopharmacol 5(9):1387–1396
Soltani Z, Khaksari M, Jafari E, Iranpour M, Shahrokhi N (2015) “Is genistein neuroprotective in traumatic brain injury?“ Physiology & behavior 152:26–31
Suzuki K, Ota H, Sasagawa S, Sakatani T, Fujikura T (1983) Assay method for myeloperoxidase in human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Anal Biochem 132(2):345–352
Tang G, Yang H, Chen J et al (2017) Metformin ameliorates sepsis-induced brain injury by inhibiting apoptosis, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Oncotarget 8(58):97977
Tuon L, Comim CM, Petronilho F et al (2008) Time-dependent behavioral recovery after sepsis in rats. Intensive Care Med 34(9):1724–1731
Van Gool WA, Van de Beek D, Eikelenboom P (2010) “Systemic infection and delirium: when cytokines and acetylcholine collide”. The Lancet 375(9716):773–775
Wang S, Wei H, Cai M et al (2014) Genistein attenuates brain damage induced by transient cerebral ischemia through up-regulation of ERK activity in ovariectomized mice. Int J Biol Sci 10(4):457
Widmann CN, Heneka MT (2014) “Long-term cerebral consequences of sepsis”. Lancet Neurol 13(6):630–636
Xin X, Chen C, Hu Y-Y, Feng Q (2019) Protective effect of genistein on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Biomed Pharmacother 117:109047
Xiong C-q, Zhou H-c, Wu J, Guo N-Z (2019) The protective effects and the involved mechanisms of tanshinone IIA on sepsis-induced brain damage in mice. Inflammation 42(1):354–364
Xu X-e, Li M-z, Yao E-s et al (2020) Morin exerts protective effects on encephalopathy and sepsis-associated cognitive functions in a murine sepsis model. Brain Res Bull 159:53–60
Xu X-e, Liu L, Wang Y-c et al (2019) Caspase-1 inhibitor exerts brain-protective effects against sepsis-associated encephalopathy and cognitive impairments in a mouse model of sepsis. Brain Behav Immun 80:859–870
Yi L, Chang M, Zhao Q et al (2020) Genistein-3’-sodium sulphonate protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced lung vascular endothelial cell apoptosis and acute lung injury via BCL-2 signalling. J Cell Mol Med 24(1):1022–1035
Zamani-Garmsiri F, Emamgholipour S, Rahmani Fard S, Ghasempour G, Jahangard Ahvazi R, Meshkani R (2021a) “Polyphenols:Potential anti-inflammatory agents for treatment of metabolic disorders.“ Phytother Res
Zamani-Garmsiri F, Hashemnia SMR, Shabani M, Bagherieh M, Emamgholipour S, Meshkani R (2021b) Combination of metformin and genistein alleviates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in high-fat diet-fed mice. J Nutr Biochem 87:108505
Zarbato GF, de Souza Goldim MP, Della Giustina A et al (2018) Dimethyl fumarate limits neuroinflammation and oxidative stress and improves cognitive impairment after polymicrobial sepsis. Neurotox Res 34(3):418–430
Zhang N, Zhao W, Hu Z-J et al (2021) “Protective effects and mechanisms of high-dose vitamin C on sepsis-associated cognitive impairment in rats”. Sci Rep 11(1):1–10
Funding
This study was supported by the Health Commission of Hubei Province scientific research project (WJ2021M184).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.B: Performed the experiments, wrote the manuscript.
C.M: Performed the experiments, wrote the manuscript.
X.Z; analyzed the data.
T.W: analyzed the data.
L.Y: contributed to the interpretation of the results.
Q.C: contributed to the interpretation of the results.
A.A: Performed the experiments, contributed to the interpretation of the results, wrote the paper.
H.C: revised the manuscript.
X.H: Conceived and designed the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
This study was performed in line with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Approval was granted by the Ethics Committee of Maternal and Child Health Hospital of Hubei Province (Date 22/2/2021/No 1GW22012).
Informed consent
This study is on animal model and therefore informed consent is not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Nnote
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, B., Chen, M., Xia, Z. et al. Genistein attenuates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress and improves cognitive impairment in a rat model of sepsis-associated encephalopathy: potential role of the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Metab Brain Dis 38, 339–347 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01076-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01076-4