Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to explore the mechanism of Nobiletin attenuating Alzheimer’s disease (AD) by inhibiting neuroinflammation.
Methods
The expression of inflammatory cytokines and HMGB-1 in serum of AD patients were examined. Microglia (MGs) were treated with different doses of Nobiletin before LPS and Nigericin induction. Cell viability and apoptosis were determined by CCK-8 and TUNEL assays, respectively. APP/PS1 mice were gavaged with Nobiletin, and Morris water maze (MWM) was established to record swimming speed, escape latency, the number of platform crossings, and time spent in the platform quadrant. MGs activation in brain tissues was evaluated by immunofluorescence. The expression of pyroptosis-related proteins, inflammatory cytokines, and HMGB-1 was determined in the hippocampus and MGs.
Results
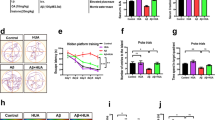
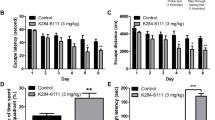
The levels of inflammatory cytokines and HMGB-1 were high in serum of AD patients. Treatment with different concentrations of Nobiletin prominently enhanced cell viability and reduced apoptosis and the expression of inflammatory cytokine and pyroptosis-related proteins in LPS + Nigericin-induced MGs. Gavage of different doses of Nobiletin into APP/PS1 mice shortened the escape latency in mice, diminished MGs activation in brain tissues, and remarkably elevated the number of platform crossings and the time spent in the platform quadrant without obvious change in swimming speed, suggesting that Nobiletin improved the spatial learning and memory abilities in APP/PS1 mice. The expression of pyroptosis-related proteins, HMGB-1, and inflammatory cytokines was decreased dramatically by Nobiletin in the hippocampus of APP/PS1 mice.
Conclusions
Nobiletin can inhibit neuroinflammation by inhibiting HMGB-1, pyroptosis-related proteins, and inflammatory cytokines, thus mitigating AD.




Similar content being viewed by others
Code Availability
Not applicable.
Data Availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Al Rahim M, Nakajima A, Saigusa D, Tetsu N, Maruyama Y, Shibuya M, Yamakoshi H, Tomioka Y, Iwabuchi Y, Ohizumi Y, Yamakuni T (2009) 4’-Demethylnobiletin, a bioactive metabolite of nobiletin enhancing PKA/ERK/CREB signaling, rescues learning impairment associated with NMDA receptor antagonism via stimulation of the ERK cascade. Biochemistry 48(32):7713–7721
Braidy N, Behzad S, Habtemariam S, Ahmed T, Daglia M, Nabavi SM, Sobarzo-Sanchez E, Nabavi SF (2017) Neuroprotective Effects of Citrus Fruit-Derived Flavonoids, Nobiletin and Tangeretin in Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s Disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 16(4):387–397
Cai M, Lee JH, Yang EJ (2019) Electroacupuncture attenuates cognition impairment via anti-neuroinflammation in an Alzheimer’s disease animal model. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):264
Cajas YN, Canon-Beltran K, Ladron de Guevara M, de la Millan MG, Ramos-Ibeas P, Gutierrez-Adan A, Rizos D, Gonzalez EM (2020) Antioxidant Nobiletin Enhances Oocyte Maturation and Subsequent Embryo Development and Quality. Int J Mol Sci 21(15)
Chaney A, Williams SR, Boutin H (2019) In vivo molecular imaging of neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 149(4):438–451
Chen DB, Gao HW, Peng C, Pei SQ, Dai AR, Yu XT, Zhou P, Wang Y, Cai B (2020) Quinones as preventive agents in Alzheimer’s diseases: focus on NLRP3 inflammasomes. J Pharm Pharmacol 72(11):1481–1490
Coleman LG Jr, Zou J, Crews FT (2020) Microglial depletion and repopulation in brain slice culture normalizes sensitized proinflammatory signaling. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):27
Crapser JD, Spangenberg EE, Barahona RA, Arreola MA, Hohsfield LA, Green KN (2020) Microglia facilitate loss of perineuronal nets in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. EBioMedicine 58:102919
Dardenne AD, Wulff BC, Wilgus TA (2013) The alarmin HMGB-1 influences healing outcomes in fetal skin wounds. Wound Repair Regen 21(2):282–291
Dey R, Bishayi B (2019) Dexamethasone exhibits its anti-inflammatory effects in S. aureus induced microglial inflammation via modulating TLR-2 and glucocorticoid receptor expression. Int Immunopharmacol 75:105806
Doganyigit Z, Okan A, Kaymak E, Pandir D, Silici S (2020) Investigation of protective effects of apilarnil against lipopolysaccharide induced liver injury in rats via TLR 4/ HMGB-1/ NF-kappaB pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 125:109967
Garcia-Morales G, Huerta-Reyes M, Gonzalez-Cortazar M, Zamilpa A, Jimenez-Ferrer E, Silva-Garcia R, Roman-Ramos R, Aguilar-Rojas A (2015) Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-acetylcholinesterase activities of Bouvardia ternifolia: potential implications in Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Pharm Res 38(7):1369–1379
Gyengesi E, Munch G (2020) In search of an anti-inflammatory drug for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol 16(3):131–132
Hagenlocher Y, Gommeringer S, Held A, Feilhauer K, Koninger J, Bischoff SC, Lorentz A (2019) Nobiletin acts anti-inflammatory on murine IL-10(-/-) colitis and human intestinal fibroblasts. Eur J Nutr 58(4):1391–1401
Han C, Guo L, Yang Y, Guan Q, Shen H, Sheng Y, Jiao Q (2020a) Mechanism of microRNA-22 in regulating neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav 10(6):e01627
Han C, Yang Y, Guan Q, Zhang X, Shen H, Sheng Y, Wang J, Zhou X, Li W, Guo L, Jiao Q (2020b) New mechanism of nerve injury in Alzheimer’s disease: beta-amyloid-induced neuronal pyroptosis. J Cell Mol Med 24(14):8078–8090
Han C, Hu Q, Yu A, Jiao Q, Yang Y (2021) Mafenide derivatives inhibit neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease by regulating pyroptosis. J Cell Mol Med 25(22):10534–10542
Jang A, Liew H, Kim YM, Choi H, Kim S, Lee SH, Ohshima T, Mikoshiba K, Suh YH (2013) p35 deficiency accelerates HMGB-1-mediated neuronal death in the early stages of an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Curr Alzheimer Res 10(8):829–843
Jojua N, Sharikadze N, Zhuravliova E, Zaalishvili E, Mikeladze DG (2015) Nobiletin restores impaired hippocampal mitochondrial bioenergetics in hypothyroidism through activation of matrix substrate-level phosphorylation. Nutr Neurosci 18(5):225–231
Li W, Wang X, Niu X, Zhang H, He Z, Wang Y, Zhi W, Liu F (2016) Protective Effects of Nobiletin Against Endotoxic Shock in Mice Through Inhibiting TNF-alpha, IL-6, and HMGB1 and Regulating NF-kappaB Pathway. Inflammation 39(2):786–797
Li H, Zhao XK, Cheng YJ, Zhang Q, Wu J, Lu S, Zhang W, Liu Y, Zhou MY, Wang Y, Yang J, Cheng ML (2019a) Gasdermin D-mediated hepatocyte pyroptosis expands inflammatory responses that aggravate acute liver failure by upregulating monocyte chemotactic protein 1/CC chemokine receptor-2 to recruit macrophages. World J Gastroenterol 25(44):6527–6540
Li L, Ismael S, Nasoohi S, Sakata K, Liao FF, McDonald MP, Ishrat T (2019b) Thioredoxin-Interacting Protein (TXNIP) Associated NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Human Alzheimer’s Disease Brain. J Alzheimers Dis 68(1):255–265
Liu P, Li YW, Wang XS, Zou X, Zhang DZ, Wang DX, Li SZ (2013) High serum interleukin-6 level is associated with increased risk of delirium in elderly patients after noncardiac surgery: a prospective cohort study. Chin Med J (Engl) 126(19):3621–3627
Liu Z, Guo S, Dong Q (2020) Nobiletin suppresses IL-21/IL-21 receptor-mediated inflammatory response in MH7A fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLS): An implication in rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol 875:172939
Lu Y, Zhang C, Bucheli P, Wei D (2006) Citrus flavonoids in fruit and traditional Chinese medicinal food ingredients in China. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 61(2):57–65
Munster BC, Aronica E, Zwinderman AH, Eikelenboom P, Cunningham C, Rooij SE (2011) Neuroinflammation in delirium: a postmortem case-control study. Rejuvenation Res 14(6):615–622
Nakajima A, Ohizumi Y, Yamada K (2014) Anti-dementia Activity of Nobiletin, a Citrus Flavonoid: A Review of Animal Studies. Clin Psychopharmacol Neurosci 12(2):75–82
Nakajima A, Aoyama Y, Shin EJ, Nam Y, Kim HC, Nagai T, Yokosuka A, Mimaki Y, Yokoi T, Ohizumi Y, Yamada K (2015) Nobiletin, a citrus flavonoid, improves cognitive impairment and reduces soluble Abeta levels in a triple transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease (3XTg-AD). Behav Brain Res 289:69–77
Nakajima A, Ohizumi Y (2019) Potential Benefits of Nobiletin, A Citrus Flavonoid, against Alzheimer’s Disease and Parkinson’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 20(14)
Nazem A, Sankowski R, Bacher M, Al-Abed Y (2015) Rodent models of neuroinflammation for Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroinflammation 12:74
Nizami S, Millar V, Arunasalam K, Zarganes-Tzitzikas T, Brough D, Tresadern G, Brennan PE, Davis JB, Ebner D, Di Daniel E (2021) A phenotypic high-content, high-throughput screen identifies inhibitors of NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Sci Rep 11(1):15319
Peng Z, Li X, Xing D, Du X, Wang Z, Liu G, Li X (2018) Nobiletin alleviates palmitic acidinduced NLRP3 inflammasome activation in a sirtuin 1dependent manner in AML12 cells. Mol Med Rep 18(6):5815–5822
Pirzada RH, Javaid N, Choi S (2020) The Roles of the NLRP3 Inflammasome in Neurodegenerative and Metabolic Diseases and in Relevant Advanced Therapeutic Interventions. Genes (Basel) 11(2)
Qi G, Mi Y, Fan R, Li R, Liu Z, Liu X (2019) Nobiletin Protects against Systemic Inflammation-Stimulated Memory Impairment via MAPK and NF-kappaB Signaling Pathways. J Agric Food Chem 67(18):5122–5134
Scott XO, Stephens ME, Desir MC, Dietrich WD, Keane RW, de Rivero Vaccari JP (2020) The Inflammasome Adaptor Protein ASC in Mild Cognitive Impairment and Alzheimer’s Disease. Int J Mol Sci 21(13)
Shao P (2021) MiR-216a-5p ameliorates learning-memory deficits and neuroinflammatory response of Alzheimer’s disease mice via regulation of HMGB1/NF-kappaB signaling. Brain Res 1766:147511
Song X, Cui Z, He J, Yang T, Sun X (2021) kappaopioid receptor agonist, U50488H, inhibits pyroptosis through NLRP3 via the Ca(2+)/CaMKII/CREB signaling pathway and improves synaptic plasticity in APP/PS1 mice. Mol Med Rep 24(1)
Spangenberg EE, Green KN (2017) Inflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: Lessons learned from microglia-depletion models. Brain Behav Immun 61:1–11
Thawkar BS, Kaur G (2019) Inhibitors of NF-kappaB and P2 × 7/NLRP3/Caspase 1 pathway in microglia: Novel therapeutic opportunities in neuroinflammation induced early-stage Alzheimer’s disease. J Neuroimmunol 326:62–74
Wang H, Guo Y, Qiao Y, Zhang J, Jiang P (2020) Nobiletin Ameliorates NLRP3 Inflammasome-Mediated Inflammation Through Promoting Autophagy via the AMPK Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 57(12):5056–5068
Wu SY, Pan BS, Tsai SF, Chiang YT, Huang BM, Mo FE, Kuo YM (2020) BDNF reverses aging-related microglial activation. J Neuroinflammation 17(1):210
Xia P, Pan Y, Zhang F, Wang N, Wang E, Guo Q, Ye Z (2018) Pioglitazone Confers Neuroprotection Against Ischemia-Induced Pyroptosis due to its Inhibitory Effects on HMGB-1/RAGE and Rac1/ROS Pathway by Activating PPAR. Cell Physiol Biochem 45(6):2351–2368
Xu J, Jiang Y, Wang J, Shi X, Liu Q, Liu Z, Li Y, Scott MJ, Xiao G, Li S, Fan L, Billiar TR, Wilson MA, Fan J (2014) Macrophage endocytosis of high-mobility group box 1 triggers pyroptosis. Cell Death Differ 21(8):1229–1239
Xu YJ, Zheng L, Hu YW, Wang Q (2018) Pyroptosis and its relationship to atherosclerosis. Clin Chim Acta 476:28–37
Zhang L, Zhou Z, Zhai W, Pang J, Mo Y, Yang G, Qu Z, Hu Y (2019) Safflower yellow attenuates learning and memory deficits in amyloid beta-induced Alzheimer’s disease rats by inhibiting neuroglia cell activation and inflammatory signaling pathways. Metab Brain Dis 34(3):927–939
Zhang Y, Deng XH, Lebaschi AH, Wada S, Carballo CB, Croen B, Ying L, Rodeo SA (2020) Expression of alarmins in a murine rotator cuff tendinopathy model. J Orthop Res 38(11):2513–2520
Acknowledgements
Thanks for all the contributors.
Funding
Thanks for the support of the grant from the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangxi Province (Grant No.20202BABL206005 and Grant No.20202BAB216014) and Science and technology plan of Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission (202210013 for Chai Wen).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CW conceived the ideas. ZP designed the experiments. XZB performed the experiments. ZHL analyzed the data. CW and ZP provided critical materials. XZB and ZHL wrote the manuscript. MZJ supervised the study. CW, NHB and XRX revised the manuscript. All the authors have read and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This experiment was admitted by the Ethics Committee of Jiangxi provincial People’s Hospital and complied with the Declaration of Helsinki. The study was allowed by the Animal Research and Ethics Committee of Jiangxi provincial People’s Hospital, and all experiments followed the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The author declares they have no competing interest.
Note
F, forward; R, reverse.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, W., Zhang, J., Xiang, Z. et al. Potential of nobiletin against Alzheimer’s disease through inhibiting neuroinflammation. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1145–1154 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00932-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00932-7