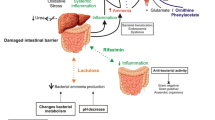
Abstract
Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a prevalent complication of the central nervous system (CNS) that is caused by acute or chronic liver failure. This study was designed to evaluate the effects of thymoquinone (TQ) on thioacetamide (TAA)-induced HE in rats, and determine the consequential behavioral, biochemical, and histological changes. HE was induced in male Wistar rats by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of 200 mg/kg TAA once every 48 h for 14 consecutive days. Control groups received the normal saline containing 5 % DMSO. Thymoquinone (5, 10, and 20 mg/kg) was administered for ten consecutive days intraperitoneally (i.p.) after HE induction and it was continued until the end of the tests. Then, the passive avoidance memory, extracellular single unit, BBB permeability, and brain water content were evaluated. Moreover, hippocampal tissues were used for evaluation of oxidative stress index, inflammatory biomarkers, and histological parameters following HE. As result of the treatment, TQ improved passive avoidance memory, increased the average number of simultaneous firing of spikes/bins, improved the integrity of BBB, and decreased brain water content in the animal model of HE. Furthermore, the results indicated that treatment with TQ decreased the levels of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) but increased the levels of glutathione (GSH) and anti-inflammatory cytokine (IL-10) of the surviving cells in the hippocampal tissues. This study demonstrates that TQ may have beneficial therapeutic effects on cognitive, oxidative stress, neuroinflammatory, and histological complications of HE in rat.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that supports the findings of this study could be accessed through the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Abulfadl YS, El-Maraghy NN, Ahmed AAE, Nofal S, Badary OA (2018) Protective effects of thymoquinone on D-galactose and aluminum chloride induced neurotoxicity in rats: biochemical, histological and behavioral changes. Neurol Res 40:324–333
Ahmad A et al (2013) A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: A miracle herb. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 3:337–352
Algandaby MM (2018) Antifibrotic effects of crocin on thioacetamide-induced liver fibrosis in mice. Saudi J Biol Sci 25:747–754
Alhebshi A, Gotoh M, Suzuki I (2013) Thymoquinone protects cultured rat primary neurons against amyloid β-induced neurotoxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 433:362–367
Al-Majed AA, Al-Omar FA, Nagi MN (2006) Neuroprotective effects of thymoquinone against transient forebrain ischemia in the rat hippocampus European. J Pharmacol 543:40–47
Bai T, Yang Y, Wu Y-L, Jiang S, Lee JJ, Lian L-H, Nan J-X (2014) Thymoquinone alleviates thioacetamide-induced hepatic fibrosis and inflammation by activating LKB1–AMPK signaling pathway in mice. Int Immunopharmacol 19:351–357
Bakiri Y, Hamilton NB, Káradóttir R, Attwell D (2008) Testing NMDA receptor block as a therapeutic strategy for reducing ischaemic damage to CNS white matter. Glia 56:233–240
Bargi R, Asgharzadeh F, Beheshti F, Hosseini M, Sadeghnia HR, Khazaei M (2017) The effects of thymoquinone on hippocampal cytokine level, brain oxidative stress status and memory deficits induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Cytokine 96:173–184
Beutler E (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Beutler E, Kelly BM (1963) The effect of sodium nitrite on red cell GSH. Experientia 19(2):96–97
Beyazcicek E, Ankarali S, Beyazcicek O, Ankarali H, Demir S, Ozmerdivenli R (2016) Effects of thymoquinone, the major constituent of Nigella sativa seeds, on penicillin-induced epileptiform activity in rats. Neurosciences 21:131
Bratlid D, Winsnes A (1971) Determination of conjugated and unconjugated bilirubin by methods based on direct spectrophotometry and chloroform-extraction. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 28(1):41–48
Butterworth RF (2011) Hepatic encephalopathy: a central neuroinflammatory disorder? Hepatology 53:1372–1376
Cauli O et al (2011) Brain region-selective mechanisms contribute to the progression of cerebral alterations in acute liver failure in rats. Gastroenterology 140:638–645
Cauli O, Rodrigo R, Boix J, Piedrafita B, Agusti A, Felipo V (2008) Acute liver failure-induced death of rats is delayed or prevented by blocking NMDA receptors in brain. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 295:G503–G511
Chehl N, Chipitsyna G, Gong Q, Yeo CJ, Arafat HA (2009) Anti-inflammatory effects of the Nigella sativa seed extract, thymoquinone in pancreatic cancer cells. HPB 11:373–381
Chen Y-C et al (2012) Alterations in NADPH oxidase expression and blood–brain barrier in bile duct ligation-treated young rats effects of melatonin. Neurochem Int 60:751–758
Chen J-R, Wang B-N, Tseng G-F, Wang Y-J, Huang Y-S, Wang T-J (2014) Morphological changes of cortical pyramidal neurons in hepatic encephalopathy. BMC Neurosci 15:15
Coltart I, Tranah TH, Shawcross DL (2013) Inflammation and hepatic encephalopathy. Arch Biochem Biophys 536:189–196
de Miranda AS et al (2017) A neuroprotective effect of the glutamate receptor antagonist MK801 on long-term cognitive and behavioral outcomes secondary to experimental cerebral malaria. Mol Neurobiol 54:7063–7082
Dhanda S, Sandhir R (2018) Blood-brain barrier permeability is exacerbated in experimental model of hepatic encephalopathy via MMP-9 activation and downregulation of tight junction proteins. Mol Neurobiol 55:3642–3659
Durand F, Nadim MK (2016) Management of acute-on-chronic liver failure. Thieme Medical Publishers, New York, pp 141–152
Ebrahimi SS, Oryan S, Izadpanah E, Hassanzadeh K (2017) Thymoquinone exerts neuroprotective effect in animal model of Parkinson’s disease. Toxicol Lett 276:108–114
El Khiat A et al (2019) Kinetic deterioration of short memory in rat with acute hepatic encephalopathy: involvement of astroglial and neuronal dysfunctions. Behav Brain Res 367:201–209
El-Marasy SA, El-Shenawy SM, El-Khatib AS, El-Shabrawy OA, Kenawy SA (2012) Effect of Nigella sativa and wheat germ oils on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats . Bull Fac Pharm Cairo Univ 50:81–88
Fanoudi S, Alavi MS, Hosseini M, Sadeghnia HR (2019) Nigella sativa and thymoquinone attenuate oxidative stress and cognitive impairment following cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Metab Brain Dis 34:1001–1010
Felipo V (2013) Hepatic encephalopathy: effects of liver failure on brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:851
Gow AG (2017) Hepatic encephalopathy. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract 47:585–599
Haghparast A, Naderi N, Khani A, Lashgari R, Motamedi F (2010) Formalin-induced differential activation of nucleus cuneiformis neurons in the rat: an electrophysiological study. J Pain 11:32–43
Hermenegildo C, Monfort P, Felipo V (2000) Activation of N-methyl‐D‐aspartate receptors in rat brain in vivo following acute ammonia intoxication: Characterization by in vivo brain microdialysis. Hepatology 31:709–715
Hernandez-Rabaza V et al (2016) Neuroinflammation increases GABAergic tone and impairs cognitive and motor function in hyperammonemia by increasing GAT-3 membrane expression. Reversal by sulforaphane by promoting M2 polarization of microglia. J Neuroinflamm 13:83
Hernández-Rabaza V, Cabrera-Pastor A, Taoro-González L, Malaguarnera M, Agustí A, Llansola M, Felipo V (2016) Hyperammonemia induces glial activation, neuroinflammation and alters neurotransmitter receptors in hippocampus, impairing spatial learning: reversal by sulforaphane. J Neuroinflamm 13:41
Hossen MJ, Yang WS, Kim D, Aravinthan A, Kim J-H, Cho JY (2017) Thymoquinone: an IRAK1 inhibitor with in vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory activities. Sci Rep 7:1–12
Khaksari M, Mahmmodi R, Shahrokhi N, Shabani M, Joukar S, Aqapour M (2013) The effects of shilajit on brain edema, intracranial pressure and neurologic outcomes following the traumatic brain injury in rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16:858
Kosenko E, Venediktova N, Kaminsky Y, Montoliu C, Felipo V (2003) Sources of oxygen radicals in brain in acute ammonia intoxication in vivo. Brain Res 981:193–200
Lashgari R, Motamedi F, Asl SZ, Shahidi S, Komaki A (2006) Behavioral and electrophysiological studies of chronic oral administration of L-type calcium channel blocker verapamil on learning and memory in rats. Behav Brain Res 171:324–328
Lu L et al (2020) BabaoDan cures hepatic encephalopathy by decreasing ammonia levels and alleviating inflammation in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 249:112301
Malaguarnera M, Pistone G, Trovato B, Scuderi M, Vinci M, Romano M, Marletta F (1996) Electrophysiological alterations in hepatic encephalopathy detected by brain mapping. Panminerva Med 38:84–88
Mohammadian F, Firouzjaei MA, Haghani M, Shabani M, Moosavi SMS, Mohammadi F (2019) Inhibition of inflammation is not enough for recovery of cognitive impairment in hepatic encephalopathy: Effects of minocycline and ibuprofen. Brain Res Bull 149:96–105
Monfort P, Erceg S, Piedrafita B, Llansola M, Felipo V (2007) Chronic liver failure in rats impairs glutamatergic synaptic transmission and long-term potentiation in hippocampus and learning ability European. J Neurosci 25:2103–2111
Montoliu C, Llansola M, Felipo V (2015) Neuroinflammation and neurological alterations in chronic liver diseases. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2:138–144
Mustafa HN, El Awdan SA, Hegazy GA (2013) Protective role of antioxidants on thioacetamide-induced acute hepatic encephalopathy: biochemical and ultrastructural study. Tissue Cell 45:350–362
Obara-Michlewska M, Tuszyńska P, Albrecht J (2013) Ammonia upregulates kynurenine aminotransferase II mRNA expression in rat brain: a role for astrocytic NMDA receptors? Metab Brain Dis 28:161–165
O’Connor CA, Cernak I, Vink R (2005) Both estrogen and progesterone attenuate edema formation following diffuse traumatic brain injury in rats. Brain Res 1062:171–174
Oja SS, Saransaari P, Korpi ER (2017) Neurotoxicity of ammonia. Neurochem Res 42:713–720
Ott P, Clemmesen O, Larsen FS (2005) Cerebral metabolic disturbances in the brain during acute liver failure: from hyperammonemia to energy failure and proteolysis. Neurochem Int 47:13–18
Paxinos G, Watson C (2006) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates: hard cover edition
Racanelli V, Rehermann B (2006) The liver as an immunological organ. Hepatology 43:S54–S62
Radad K, Hassanein K, Al-Shraim M, Moldzio R, Rausch W-D (2014) Thymoquinone ameliorates lead-induced brain damage in Sprague Dawley rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 66:13–17
Rahmani AH, Almatroudi A, Babiker AY, Khan AA, Alsahli MA (2019) Thymoquinone, an active constituent of black seed attenuates CCl4 induced liver injury in mice via modulation of antioxidant enzymes, PTEN, P53 and VEGF protein Open access. Maced J Med Sci 7:311
Randolph C et al (2009) Neuropsychological assessment of hepatic encephalopathy: ISHEN practice guidelines. Liver Int 29:629–635
Said AM, Waheed RM, Khalifa OA (2019) Protective role of rosemary ethanolic extract on thioacetamide induced hepatic encephalopathy: biochemical and molecular studies . Aust J Basic Appl Sci 13:1–6
Salahshoor M, Haghjoo M, Roshankhah S, Makalani F, Jalili C (2018) Effect of thymoquinone on reproductive parameter in morphine-treated male mice. Adv Biomed Res 7:18
Sawara K, Desjardins P, Chatauret N, Kato A, Suzuki K, Butterworth RF (2009) Alterations in expression of genes coding for proteins of the neurovascular unit in ischemic liver failure. Neurochem Int 55:119–123
Sawasaki Y, Yamada N, Nakajima H (1976) Developmental features of cerebellar hypoplasia and brain bilirubin levels in a mutant (Gunn) rat with hereditary hyperbilirubinaemia 1. J Neurochem 27:577–583
Saxena N, Bhatia M, Joshi YK, Garg PK, Dwivedi SN, Tandon RK (2002) Electrophysiological and neuropsychological tests for the diagnosis of subclinical hepatic encephalopathy and prediction of overt encephalopathy. Liver 22:190–197
Sayeed MSB, Asaduzzaman M, Morshed H, Hossain MM, Kadir MF, Rahman MR (2013) The effect of Nigella sativa Linn. seed on memory, attention and cognition in healthy human volunteers. J Ethnopharmacol 148:780–786
Schauwecker PE (2010) Neuroprotection by glutamate receptor antagonists against seizure-induced excitotoxic cell death in the aging brain. Exp Neurol 224:207–218
Sedaghat R, Roghani M, Khalili M (2014) Neuroprotective effect of thymoquinone, the nigella sativa bioactive compound, in 6-hydroxydopamine-induced hemi-parkinsonian rat model. Iran J Pharm Res 13:227
Seyan AS, Hughes RD, Shawcross DL (2010) Changing face of hepatic encephalopathy: role of inflammation and oxidative stress. World J Gastroenterol 16:33–47
Shahrokhi N, Khaksari M, Soltani Z, Mahmoodi M, Nakhaee N (2010) Effect of sex steroid hormones on brain edema, intracranial pressure, and neurologic outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 88:414–421
Shawcross DL, Davies NA, Williams R, Jalan R (2004) Systemic inflammatory response exacerbates the neuropsychological effects of induced hyperammonemia in cirrhosis. J Hepatol 40:247–254
Shooshtari MK, Sarkaki A, Mansouri SMT, Badavi M, Khorsandi L, Dehcheshmeh MG, Farbood Y (2019) Protective effects of Chrysin against memory impairment, cerebral hyperemia and oxidative stress after cerebral hypoperfusion and reperfusion in rats. Metab Brain Dis 35:401–412
Tabeshpour J, Mehri S, Abnous K, Hosseinzadeh H (2020) Role of oxidative stress, MAPKinase and apoptosis pathways in the protective effects of thymoquinone against acrylamide-induced central nervous system toxicity in rat. Neurochem Res 45:254–267
Tahamtan M, Aghaei I, Pooladvand V, Sheibani V, Khaksari M, Shabani M (2017) Characterization of the CA1 pyramidal neurons in rat model of hepatic cirrhosis: insights into their electrophysiological properties. Metab Brain Dis 32:881–889
Tavakkoli A, Mahdian V, Razavi BM, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Review on clinical trials of black seed (Nigella sativa) and its active constituent thymoquinone. J Pharmacopuncture 20:179
Umar S, Zargan J, Umar K, Ahmad S, Katiyar CK, Khan HA (2012) Modulation of the oxidative stress and inflammatory cytokine response by thymoquinone in the collagen induced arthritis in Wistar rats. Chem Biol Interact 197:40–46
Umar S, Hedaya O, Singh AK, Ahmed S (2015) Thymoquinone inhibits TNF-α-induced inflammation and cell adhesion in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts by ASK1 regulation. Toxicol Appl Pharmcol 287:299–305
Vickers NJ (2017) Animal communication: when i’m calling you, will you answer too? Curr Biol 27:R713–R715
Wang L-Q, Zhou H-J, Pan C-F, Zhu S-M, Xu L-M (2011) Expression of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α in rats with thioacetamide-induced acute liver failure and encephalopathy: correlation with brain edema. Asian Biomed 5:205–215
Wang F, Lei X, Zhao Y, Yu Q, Li Q, Zhao H, Pei Z (2019) Protective role of thymoquinone in sepsis–induced liver injury in BALB/c mice. Exp Ther Med 18:1985–1992
Wijdicks EF (2016) Hepatic encephalopathy New England. J Med 375:1660–1670
Acknowledgements
This article was extracted from Miss Somayeh Hajipour’s Ph.D. thesis. This study was financially supported by the Research Affairs Deputy of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (grant No. APRC- 9617).
Funding
The authors did not receive any financial support from any organization for the submitted work. The authors have no affiliation with any organization with a direct or indirect financial interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have participated in (a) conception and design, or analysis and interpretation of the data; (b) drafting the article or revising it critically for important intellectual content; and (c) approval of the final version.
1. SH analyzed the electrophysiological data and contributed in writing the manuscript.
2. AS designed, guided, and supervised the project and monitored the electrophysiological records.
3. MD was responsible for confirming the TAA-induced HE, analyzed the liver enzyme changes, and revised the article.
4. MR was responsible for the biochemical factors analyses.
5. LKH performed and interpreted the histological examinations of the brains.
6. YF was responsible for monitoring and approving the behavioral tests in different experimental groups.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors. The ethics governing the use and conduct of experiments on animals were strictly observed, and all the procedures used in this study were done according to the National Institute of Health (NIH) and were approved by the Local Ethics Committee of Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences (AJUMS) (Ethics code: IR.AJUMS.REC.1396.684).
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the contents of this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hajipour, S., Sarkaki, A., Dianat, M. et al. The effects of thymoquinone on memory impairment and inflammation in rats with hepatic encephalopathy induced by thioacetamide. Metab Brain Dis 36, 991–1002 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00688-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00688-6