Abstract
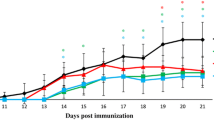
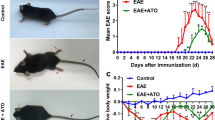
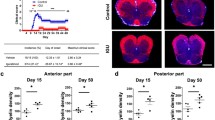
Inflammatory demyelination in the central nervous system (CNS) is a hallmark of multiple sclerosis (MS) and its animal model, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE). Besides MS disease-modifying therapy, targeting myelin sheath protection/regeneration is currently a hot spot in the treatment of MS. Here, we attempt to explore the therapeutic potential of Bilobalide (BB) for the myelin protection/regeneration in EAE model. The results showed that BB treatment effectively prevented worsening and demyelination of EAE, accompanied by the inhibition of neuroinflammation that should be closely related to T cell tolerance and M2 macrophages/microglia polarization. BB treatment substantially inhibited the infiltration of T cells and macrophages, thereby alleviating the enlargement of neuroinflammation and the apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in CNS. The accurate mechanism of BB action and the feasibility of clinical application in the prevention and treatment of demyelination remain to be further explored.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- MS:
-
Multiple sclerosis
- EAE:
-
Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis
- BB:
-
Bilobalide
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- PPMS:
-
Primary progressive multiple sclerosis
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
- BBB:
-
Blood-brain barrier
- CPZ:
-
Cuprizone
- MOG:
-
Myelin oligodendrocyte glycolipid
- p.i.:
-
Post-immunization
- NS:
-
Normal saline
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- LFB:
-
Luxol fast blue
- H&E:
-
Haematoxylin/eosin
- MNCs:
-
Mononuclear cells
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium
- DMSO:
-
Dimethyl sulfoxide
- TLR-4:
-
Toll-like receptor 4
- TGF-β:
-
Transforming growth factor β
References
Aboul-Enein F, Lassmann H (2005) Mitochondrial damage and histotoxic hypoxia: a pathway of tissue injury in inflammatory brain disease? Acta Neuropathol 109:49–55
Akdis CA, Blaser K (1999) IL-10-induced anergy in peripheral T cell and reactivation by microenvironmental cytokines: two key steps in specific immunotherapy. FASEB J 13:603–609
Aronson NN, Backes M, Kuranda MJ (1989) Rat liver chitobiase: purification, properties, and role in the lysosomal degradation of Asn-linked glycoproteins. Arch Biochem Biophys 272:290–300
Baecher-Allan C, Kaskow BJ, Weiner HL (2018) Multiple sclerosis: mechanisms and immunotherapy. Neuron 97:742–768
Bevan RJ, Evans R, Griffiths L, Watkins LM, Rees MI, Magliozzi R, Allen I, McDonnell G, Kee R, Naughton M, Fitzgerald DC, Reynolds R, Neal JW, Howell OW (2018) Meningeal inflammation and cortical demyelination in acute multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 84:829–842
Bonora M, De Marchi E, Patergnani S, Suski JM, Celsi F, Bononi A, Giorgi C, Marchi S, Rimessi A, Duszyński J, Pozzan T, Wieckowski MR, Pinton P (2014) Tumor necrosis factor-α impairs oligodendroglial differentiation through a mitochondria-dependent process. Cell Death Differ 21:1198–1208
Correale J, Gaitán MI, Ysrraelit MC, Fiol MP (2017) Progressive multiple sclerosis: from pathogenic mechanisms to treatment. Brain 140:527–546
Dargahi N, Apostolopoulos V, de Courten M, Matsoukas J, Androutsou M-E, Katsara M, Tselios T (2017) Multiple sclerosis: immunopathology and treatment update. Brain Sci 7:78
Dendrou CA, Fugger L, Friese MA (2015) Immunopathology of multiple sclerosis. Nat Rev Immunol 15:545–558
Gilli F, Li L, Campbell SJ, Anthony DC, Pachner AR (2015) The effect of B-cell depletion in the Theiler’s model of multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 359:40–47
Hawker K, O’Connor P, Freedman MS, Calabresi PA, Antel J, Simon J, Hauser S, Waubant E, Vollmer T, Panitch H, Zhang JM, Chin P, Smith CH (2009) Rituximab in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis: results of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled multicenter trial. Ann Neurol 66(4):460–471
Hua J, Yin N, Yang B, Zhang J, Ding J, Fan Y, Hu G (2017) Ginkgolide B and bilobalide ameliorate neural cell apoptosis in α-synuclein aggregates. Biomed Pharmacother 96:792–797
Jana A, Pahan K (2007) Oxidative stress kills human primary oligodendrocytes via neutral sphingomyelinase: implications for multiple sclerosis. J NeuroImmune Pharmacol 2:184–193
Jayaraman A, Soni A, Prabhakar BS, Holterman M, Jayaraman S (2017) The epigenetic drug Trichostatin a ameliorates experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis via T cell tolerance induction and impaired influx of T cells into the spinal cord. Neurobiol Dis 108:1–12
Jiang M, Li J, Peng Q, Liu Y, Liu W, Luo C, Peng J, Li J, Yung KKL, Mo Z (2014a) Neuroprotective effects of bilobalide on cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury are associated with inhibition of pro-inflammatory mediator production and down-regulation of JNK1/2 and p38 MAPK activation. J Neuroinflammation 11:1–17
Jiang Z, Jiang JX, Zhang GX (2014b) Macrophages: a double-edged sword in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunol Lett 160:17
Kaskow BJ, Baecher-Allan C (2018) Effector t cells in multiple sclerosis. CSH Perspect Med 8(4):a029025
Kim S, Steelman AJ, Koito H, Li J (2011) Astrocytes promote TNF-mediated toxicity to oligodendrocyte precursors. J Neurochem 116:53–66
Krieglstein J, Ausmeier F, El-Abhar H, Lippert K, Welsch M, Rupalla K, Henrich-Noack P (1995) Neuroprotective effects of Ginkgo biloba constituents. Eur J Pharm Sci 3:39–48
Li L, Zhao Y, Du F, Yang J, Xu F, Niu W, Ren Y, Li C (2012) Intestinal absorption and presystemic elimination of various chemical constituents present in GBE50 extract, a standardized extract of Ginkgo biloba leaves. Curr Drug Metab 13:494–509
Li WZ, Wu WY, Huang H, Wu YY, Yin YY (2013) Protective effect of bilobalide on learning and memory impairment in rats with vascular dementia. Mol Med Rep 8:935–941
Liu CY, De Guo S, Yu JZ, Li YH, Zhang H, Feng L, Chai Z, Yuan HJ, Yang WF, Feng QJ, Xiao BG, Ma CG (2015) Fasudil mediates cell therapy of EAE by immunomodulating encephalomyelitic T cells and macrophages. Eur J Immunol 45:142–152
Liu XW, Yang JL, Niu W, Wei JW, Olaleye OE, Wen Q, Duan XN, Huang YH, Wang FQ, Du FF, Zhong CC, Li YF, Xu F, Gao Q, Li L, Li C (2018) Human pharmacokinetics of ginkgo terpene lactones and impact of carboxylation in blood on their platelet-activating factor antagonistic activity. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39:1935–1946
Lutterotti A, Martin R (2013) Antigen-specific tolerization approaches in multiple sclerosis. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 23:9–20
Mahurkar S, Suppiah V, O’Doherty C (2014) Pharmacogenomics of interferon beta and glatiramer acetate response: a review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev 13:178–186
Markus R, Reutens DC, Kazui S, Read S, Wright P, Pearce DC, Tochon-Danguy HJ, Sachinidis JI, Donnan GA (2004) Hypoxic tissue in ischaemic stroke: persistence and clinical consequences of spontaneous survival. Brain 127:1427–1436
Martin R, Sospedra M, Rosito M, Engelhardt B (2016) Current multiple sclerosis treatments have improved our understanding of MS autoimmune pathogenesis. Eur J Immunol 46:2078–2090
Mc Guire C, Prinz M, Beyaert R, van Loo G (2013) Nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in multiple sclerosis pathology. Trends Mol Med 19:604–613
Nakazawa T, Nakazawa C, Noda K, Hafezi-Moghadam A, Hisatomi T, Benowitz LI, Michaud N, Miller JW, She H, Matsubara A (2006) Tumor necrosis factor- mediates Oligodendrocyte death and delayed retinal ganglion cell loss in a mouse model of glaucoma. J Neurosci 26:12633–12641
Ng CC, Duke RK, Hinton T, Johnston GAR (2017) Effects of bilobalide, ginkgolide B and picrotoxinin on GABAA receptor modulation by structurally diverse positive modulators. Eur J Pharmacol 806:83–90
Ontaneda D, Thompson AJ, Fox RJ, Cohen JA (2017) Progressive multiple sclerosis: prospects for disease therapy, repair, and restoration of function. Lancet 389:1357–1366
Pinto M, Gomes AS, Bastos ML, Costa VM, Reis-Mendes A, Sousa E, Carvalho F, Carvalho RA, Remião F (2016) Naphthoquinoxaline metabolite of mitoxantrone is less cardiotoxic than the parent compound and it can be a more cardiosafe drug in anticancer therapy. Arch Toxicol 91:1871–1890
Ransohoff RM, Giannini C, Bunyan RF, Lucchinetti CF, Brück W, Weigand SD, Moll NM, Scheithauer BW, Mandrekar J, Popescu BFG, Lassmann H, Roemer SF, Parisi JE (2011) Inflammatory cortical demyelination in early multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 365:2188–2197
Reich DS, Lucchinetti CF, Calabresi PA (2018) Multiple Sclerosis. N Engl J Med 378:169–180
Rizzo FR, Musella A, De Vito F, Fresegna D, Bullitta S, Vanni V, Guadalupi L, Stampanoni Bassi M, Buttari F, Mandolesi G, Centonze D, Gentile A (2018) Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1β modulate synaptic plasticity during Neuroinflammation. Neural Plast 2018:8430123
Robinson AP, Harp CT, Noronha A, Miller SD (2014) The experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of MS: utility for understanding disease pathophysiology and treatment. Handb Clin Neurol 122:173–189
Rossi R, Basilico F, Rossoni G, Riva A, Morazzoni P, Mauri PL (2009) Liquid chromatography/atmospheric pressure chemical ionization ion trap mass spectrometry of bilobalide in plasma and brain of rats after oral administration of its phospholipidic complex. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:224–227
Sabatino JJ, Zamvil SS (2018) T cells take aim at a ubiquitous autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. Sci Transl Med 10:1–4
Schwartz RH (1997) T cell clonal anergy. Curr Opin Immunol 9:351–357
Schwarzkopf TM, Hagl S, Eckert GP, Klein J (2013) Neuroprotection by bilobalide in ischemia: improvement of mitochondrial function. Pharmazie 68:584–589
Simons M, Nave K-A (2015) Oligodendrocytes: myelination and axonal support. CSH Perspect Biol 8:a020479
Steinman L (2015) The re-emergence of antigen-specific tolerance as a potential therapy for MS. Mult Scler J 21:1223–1238
Sui RX, Miao Q, Wang J, Wang Q, Song LJ, Yu JW, Cao L, Xiao W, Xiao BG, Ma CG (2019) Protective and therapeutic role of Bilobalide in cuprizone-induced demyelination. Int Immunopharmacol 66:69–81
Voet S, Prinz M, van Loo G (2018) Microglia in central nervous system inflammation and multiple sclerosis pathology. Trends Mol Med 25(2):112–123
Willer CJ, Dyment DA, Risch NJ, Sadovnick AD, Ebers GC (2003) Twin concordance and sibling recurrence rates in. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100:12877–12882
Wingerchuk DM, Carter JL (2014) Multiple sclerosis: current and emerging disease-modifying therapies and treatment strategies. Mayo Clin Proc 89:225–240
Xiao BG, Ma CG, Xu LY, Link H, Lu CZ (2008) IL-12/IFN-γ/NO axis plays critical role in development of Th1-mediated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Mol Immunol 45(6):1191–1196
Yin Y, Wang M, Li W, Cao M, Zhu Z, Ren Y, Wu W, Wang Y (2013) Protective effects of bilobalide on Aβ25–35 induced learning and memory impairments in male rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 106:77–84
Zhang Y, Li X, Ciric B, Ma CG, Gran B, Rostami A, Zhang GX (2017) Effect of Fingolimod on neural stem cells: a novel mechanism and broadened application for neural repair. Mol Ther 25:401–415
Zheng Y, Wu Z, Yi F, Orange M, Yao M, Yang B, Liu J, Zhu H (2018) By activating Akt/eNOS Bilobalide B inhibits autophagy and promotes angiogenesis following focal cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Cell Physiol Biochem 47:604–616
Zhou JM, Gu SS, Mei WH, Zhou J, Wang ZZ, Xiao W (2016) Ginkgolides and bilobalide protect BV2 microglia cells against OGD/reoxygenation injury by inhibiting TLR2/4 signalling pathways. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:1037–1053
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81473577 and 81371414), and Research Project Supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China (2014-7).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Cun-Gen Ma and Bao-Guo Xiao designed the experiments and checked all experimental data and analyses; Qiang Miao, Ruo-Xuan Sui, Qing-Xian Han, Si-Si Ren, and Jing Wang are involved in the establishment of the animal model and drug intervention; Xiao-Xue Zhang and Jing Wang carried out western blot; Qing Wang, Jing-Wen Yu, and Jie-Zhong Yu carried out immunohistopathology and immunohistochemistry; Liang Cao and Wei Xiao have prepared and identified bilobalide for use in this experiment.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None of the authors has any potential financial and non-financial conflicts of interest related to this manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, Q., Zhang, XX., Han, QX. et al. The therapeutic potential of bilobalide on experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) mice. Metab Brain Dis 35, 793–807 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00555-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00555-w