Abstract
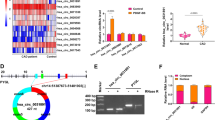
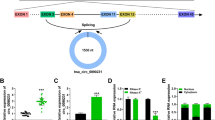
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) have been reported to play vital roles in atherosclerosis. However, the precise roles of circUBR4 in atherosclerosis remain unclear. The purpose of this study is to investigate the regulatory roles of circUBR4 in atherosclerosis. The expression levels of circUBR4, miR-185-5p, and Fibroblast growth factor receptor substrate 2 (FRS2) were analyzed by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) assay. Human vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) were treated with oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL) to mimic atherosclerosis condition in vitro. Cell proliferation was determined by 3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2, 5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazol-3-ium bromide (MTT), colony-forming, and 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) assays. Wound healing and transwell assays were used to assess cell migration. The interaction relationship between miR-185-5p and circUBR4 or FRS2 was confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter and RNA pull-down assays. CircUBR4 was overexpressed in atherosclerosis patients and VSMCs treated with ox-LDL, and the knockdown of circUBR4 abolished ox-LDL-induced enhanced effects on the proliferation and migration of VSMCs. MiR-185-5p, interacted with FRS2, was a target of circUBR4 in VSMCs. The silencing of miR-185-5p reversed the effects caused by circUBR4 knockdown on ox-LDL-induced VSMCs. In addition, overexpression of miR-185-5p suppressed the proliferation and migration of VSMCs by targeting FRS2. CircUBR4 contributed to ox-LDL-induced VSMC proliferation and migration through up-regulating FRS2 via miR-185-5p.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Please contact the correspondence author for the data request.
References
Torres N, Guevara-Cruz M, Velazquez-Villegas LA, Tovar AR (2015) Nutrition and atherosclerosis. Arch Med Res 46(5):408–426
Ceska R (2014) Introduction: atherosclerosis. Physiol Res 63(Suppl 3):xi
Badimon L, Vilahur G (2014) Thrombosis formation on atherosclerotic lesions and plaque rupture. J Intern Med 276(6):618–632
Zheng Y, Li Y, Liu G, Qi X, Cao X (2018) MicroRNA-24 inhibits the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells in patients with atherosclerosis by targeting importin-alpha3 and regulating inflammatory responses. Exp Ther Med 15(1):338–344
Chen L-L (2016) The biogenesis and emerging roles of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(4):205
Yu T, Wang Y, Fan Y, Fang N, Wang T, Xu T, Shu Y (2019) CircRNAs in cancer metabolism: a review. J Hematol Oncol 12(1):90
Zhang LL (2020) CircRNA-PTPRA promoted the progression of atherosclerosis through sponging with miR-636 and upregulating the transcription factor SP1. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(23):12437–12449
Zhang SA-O, Song G, Yuan J, Qiao S, Xu S, Si Z, Yang Y, Xu X, Wang A (2020) Circular RNA circ_0003204 inhibits proliferation, migration and tube formation of endothelial cell in atherosclerosis via miR-370-3p/TGFβR2/phosph-SMAD3 axis. J Biomed Sci 27:1–17
Yang L, Yang F, Zhao H, Wang M, Zhang Y (2019) Circular RNA circCHFR facilitates the proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle via miR-370/FOXO1/Cyclin D1 pathway. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 16:434–441
Lu Y, Thavarajah T, Gu W, Cai J, Xu Q (2018) Impact of miRNA in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 38(9):e159–e170
Li SH, Su SY, Liu JL (2015) Differential regulation of microRNAs in patients with ischemic stroke. Curr Neurovasc Res 12(3):214–221
Niu Y, Tang G (2019) miR-185-5p targets ROCK2 and inhibits cell migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett 17(6):5087–5093
Liu M, Lang N, Chen X, Tang Q, Liu S, Huang J, Zheng Y, Bi F (2011) miR-185 targets RhoA and Cdc42 expression and inhibits the proliferation potential of human colorectal cells. Cancer Lett 301(2):151–160
Tang H, Wang Z, Liu X, Liu Q, Xu G, Li G, Wu M (2012) LRRC4 inhibits glioma cell growth and invasion through a miR-185-dependent pathway. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 12(8):1032–1042
Jiang H, Zhang J, Du Y, Jia X, Yang F, Si S, Wang L, Hong B (2015) microRNA-185 modulates low density lipoprotein receptor expression as a key posttranscriptional regulator. Atherosclerosis 243(2):523–532
Yang M, Liu W, Pellicane C, Sahyoun C, Joseph BK, Gallo-Ebert C, Donigan M, Pandya D, Giordano C, Bata A et al (2014) Identification of miR-185 as a regulator of de novo cholesterol biosynthesis and low density lipoprotein uptake. J Lipid Res 55(2):226–238
Feinberg MW, Moore KJ (2016) MicroRNA regulation of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118(4):703–720
Tafrihi M, Hasheminasab E (2019) MiRNAs: biology, biogenesis, their web-based tools, and databases. MicroRNA 8(1):4–27
Qi M, Xin S (2019) FGF signaling contributes to atherosclerosis by enhancing the inflammatory response in vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Med Rep 20(1):162–170
Chen J, Dai M, Wang Y (2014) Paeonol inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by high glucose via Ras-Raf-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in coculture model. Evid Based Complement Altern Med eCAM 2014:484269
Miura S, Matsuo Y, Saku K (2004) Simvastatin suppresses coronary artery endothelial tube formation by disrupting Ras/Raf/ERK signaling. Atherosclerosis 175(2):235–243
Xu Y, Wang J, Qiu M, Xu L, Li M, Jiang F, Yin R, Xu L (2015) Upregulation of the long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes proliferation and migration of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Tumour Biol J Int Soc Oncodev Biol Med 36(3):1643–1651
Zheng HK, Dong MH, Liu GH, An Z, Zhang L, Shan RT, Zhang WQ (2020) Dysregulation of the urothelial cancer associated 1 long noncoding RNA promotes proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells by modulating expression of P27KIP1/CDK2. Genet Test Mol Biomark 24(4):204–211
Gao LN, Zhou X, Lu YR, Li K, Gao S, Yu CQ, Cui YL (2018) Dan-Lou prescription inhibits foam cell formation induced by ox-LDL via the TLR4/NF-kappaB and PPARgamma signaling pathways. Front Physiol 9:590
Chaabane C, Coen M, Bochaton-Piallat ML (2014) Smooth muscle cell phenotypic switch: implications for foam cell formation. Curr Opin Lipidol 25(5):374–379
Hofmann A, Brunssen C, Poitz DM, Langbein H, Strasser RH, Henle T, Ravens U, Morawietz H (2017) Lectin-like oxidized low-density lipoprotein receptor-1 promotes endothelial dysfunction in LDL receptor knockout background. Atheroscler Suppl 30:294–302
Obermayer G, Afonyushkin T, Binder CJ (2018) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein in inflammation-driven thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost JTH 16(3):418–428
Wang B, Ge Z, Cheng Z, Zhao Z (2017) Tanshinone IIA suppresses the progression of atherosclerosis by inhibiting the apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells and the proliferation and migration of macrophages induced by ox-LDL. Biol Open 6(4):489–495
Zhang X, Shi H, Wang Y, Hu J, Sun Z, Xu S (2017) Down-regulation of hsa-miR-148b inhibits vascular smooth muscle cells proliferation and migration by directly targeting HSP90 in atherosclerosis. Am J Transl Res 9(2):629–637
Hu W, Han Q, Zhao L, Wang L (2019) Circular RNA circRNA_15698 aggravates the extracellular matrix of diabetic nephropathy mesangial cells via miR-185/TGF-beta1. J Cell Physiol 234(2):1469–1476
Fang M, Li Y, Wu Y, Ning Z, Wang X, Li X (2019) miR-185 silencing promotes the progression of atherosclerosis via targeting stromal interaction molecule 1. Cell Cycle 18(6–7):682–695
Iorio MV, Croce CM (2017) MicroRNA dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics. A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med 9(6):852
Chen PY, Simons M, Friesel R (2009) FRS2 via fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 is required for platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta-mediated regulation of vascular smooth muscle marker gene expression. J Biol Chem 284(23):15980–15992
Zhang J, Gao F, Ni T, Lu W, Lin N, Zhang C, Sun Z, Guo H, Chi J (2019) Linc-POU3F3 is overexpressed in in-stent restenosis patients and induces VSMC phenotypic transformation via POU3F3/miR-449a/KLF4 signaling pathway. Am J Transl Res 11(7):4481–4490
Funding
This work was supported by Scientific research project approved by Heilongjiang Provincial Health Committee in 2019 (No. 2019-253).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CS, JL and YL were responsible for the conception and design of the research. CS, YL and LL performed the experiments. CS, JL and GH interpreted the results of the experiments. CS analysed the data, prepared the figures, and drafted the manuscript. JL, YL, LL, and GH edited and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the report.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no financial conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent participate
Written informed consent was obtained from patients with approval by the Institutional Review Board in Yantai City Municipal Government Hospital.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, C., Li, J., Li, Y. et al. Circular RNA circUBR4 regulates ox-LDL-induced proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells through miR-185-5p/FRS2 axis. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 3899–3910 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04207-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04207-0