Abstract
Resistance to radiotherapy is a major limitation for the successful treatment of colorectal cancer (CRC). Recently, accumulating evidence supports a critical role of epigenetic regulation in tumor cell survival upon irradiation. Lysine Demethylase 4B (KDM4B) is a histone demethylase involved in the oncogenesis of multiple human cancers but the underlying mechanisms have not been fully elucidated. Here we show that KDM4B is overexpressed in human colorectal cancer (CRC) tumors and cell lines. In CRC cells, KDM4B silencing induces spontaneous double-strand breaks (DSBs) formation and potently sensitizes tumor cells to irradiation. A putative mechanism involved suppression of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) signaling pathway, which is essential for efficient repair of damaged DNA. Overexpression of STAT3 in KMD4B knockdown cells largely attenuates DNA damage triggered by KDM4B silencing and increases cell survival upon irradiation. Moreover, we find evidence that transcription factor CAMP Responsive Element Binding Protein (CREB) is a key regulator of KMD4B expression by directly binding to a conserved region in KMD4B promoter. Together, our findings illustrate the significance of CREB–KDM4B–STAT3 signaling cascade in DNA damage response, and highlight that KDM4B may potentially be a novel oncotarget for CRC radiotherapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ross W, Lynch P, Raju G, Rodriguez A, Burke T, Hafemeister L, Hawk E, Wu X, Dubois RN, Mishra L (2012) Biomarkers, bundled payments, and colorectal cancer care. Genes Cancer 3:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1177/1947601912448958
Migliore L, Migheli F, Spisni R, Coppede F (2011) Genetics, cytogenetics, and epigenetics of colorectal cancer. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:792362. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/792362
Shadad AK, Sullivan FJ, Martin JD, Egan LJ (2013) Gastrointestinal radiation injury: symptoms, risk factors and mechanisms. World J Gastroenterol 19:185–198. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v19.i2.185
Lao VV, Grady WM (2011) Epigenetics and colorectal cancer. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 8:686–700. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2011.173
Crea F, Nobili S, Paolicchi E, Perrone G, Napoli C, Landini I, Danesi R, Mini E (2011) Epigenetics and chemoresistance in colorectal cancer: an opportunity for treatment tailoring and novel therapeutic strategies. Drug Resist Updat 14:280–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2011.08.001
van Engeland M, Derks S, Smits KM, Meijer GA, Herman JG (2011) Colorectal cancer epigenetics: complex simplicity. J Clin Oncol 29:1382–1391. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2010.28.2319
Fodor BD, Kubicek S, Yonezawa M, O’Sullivan RJ, Sengupta R, Perez-Burgos L, Opravil S, Mechtler K, Schotta G, Jenuwein T (2006) Jmjd2b antagonizes H3K9 trimethylation at pericentric heterochromatin in mammalian cells. Genes Dev 20:1557–1562. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.388206
Yang J, Jubb AM, Pike L, Buffa FM, Turley H, Baban D, Leek R, Gatter KC, Ragoussis J, Harris AL (2010) The histone demethylase JMJD2B is regulated by estrogen receptor alpha and hypoxia, and is a key mediator of estrogen induced growth. Cancer Res 70:6456–6466. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0413
Whetstine JR, Nottke A, Lan F, Huarte M, Smolikov S, Chen Z, Spooner E, Li E, Zhang G, Colaiacovo M, Shi Y (2006) Reversal of histone lysine trimethylation by the JMJD2 family of histone demethylases. Cell 125:467–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.03.028
Young LC, McDonald DW, Hendzel MJ (2013) Kdm4b histone demethylase is a DNA damage response protein and confers a survival advantage following gamma-irradiation. J Biol Chem 288:21376–21388. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M113.491514
Khoury-Haddad H, Guttmann-Raviv N, Ipenberg I, Huggins D, Jeyasekharan AD, Ayoub N (2014) PARP1-dependent recruitment of KDM4D histone demethylase to DNA damage sites promotes double-strand break repair. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E728–E737. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1317585111
Berry WL, Janknecht R (2013) KDM4/JMJD2 histone demethylases: epigenetic regulators in cancer cells. Cancer Res 73:2936–2942. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-4300
Chen L, Fu L, Kong X, Xu J, Wang Z, Ma X, Akiyama Y, Chen Y, Fang J (2014) Jumonji domain-containing protein 2B silencing induces DNA damage response via STAT3 pathway in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer 110:1014–1026. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2013.808
Marti TM, Hefner E, Feeney L, Natale V, Cleaver JE (2006) H2AX phosphorylation within the G1 phase after UV irradiation depends on nucleotide excision repair and not DNA double-strand breaks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:9891–9896. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0603779103
Xiong H, Zhang ZG, Tian XQ, Sun DF, Liang QC, Zhang YJ, Lu R, Chen YX, Fang JY (2008) Inhibition of JAK1, 2/STAT3 signaling induces apoptosis, cell cycle arrest, and reduces tumor cell invasion in colorectal cancer cells. Neoplasia 10:287–297
Barry SP, Townsend PA, Knight RA, Scarabelli TM, Latchman DS, Stephanou A (2010) STAT3 modulates the DNA damage response pathway. Int J Exp Pathol 91:506–514. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2613.2010.00734.x
Young LC, Hendzel MJ (2013) The oncogenic potential of Jumonji D2 (JMJD2/KDM4) histone demethylase overexpression. Biochem Cell Biol 91:369–377. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2012-0054
Yang Q, Zhu Q, Lu X, Du Y, Cao L, Shen C, Hou T, Li M, Li Z, Liu C, Wu D, Xu X, Wang L, Wang H, Zhao Y, Yang Y, Zhu WG (2017) G9a coordinates with the RPA complex to promote DNA damage repair and cell survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 114:E6054–E6063. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700694114
Roos WP, Thomas AD, Kaina B (2016) DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat Rev Cancer 16:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2015.2
Xu Y, Ayrapetov MK, Xu C, Gursoy-Yuzugullu O, Hu Y, Price BD (2012) Histone H2A.Z controls a critical chromatin remodeling step required for DNA double-strand break repair. Mol Cell 48:723–733. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.09.026
Price BD, D’Andrea AD (2013) Chromatin remodeling at DNA double-strand breaks. Cell 152:1344–1354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.011
Zheng H, Chen L, Pledger WJ, Fang J, Chen J (2014) p53 promotes repair of heterochromatin DNA by regulating JMJD2b and SUV39H1 expression. Oncogene 33:734–744. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.6
Pregi N, Belluscio LM, Berardino BG, Castillo DS, Canepa ET (2017) Oxidative stress-induced CREB upregulation promotes DNA damage repair prior to neuronal cell death protection. Mol Cell Biochem 425:9–24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2858-z
Ipenberg I, Guttmann-Raviv N, Khoury HP, Kupershmit I, Ayoub N (2013) Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) selectively regulates the stability of KDM4B/JMJD2B histone demethylase. J Biol Chem 288:14681–14687. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.C113.462770
Fu L, Chen L, Yang J, Ye T, Chen Y, Fang J (2012) HIF-1alpha-induced histone demethylase JMJD2B contributes to the malignant phenotype of colorectal cancer cells via an epigenetic mechanism. Carcinogenesis 33:1664–1673. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgs217
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) 81660096.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2018_3345_MOESM1_ESM.eps
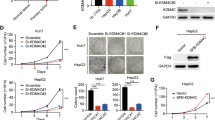
Supplementary Figure 1. KDM4B silencing doesn’t induce cell death or proliferation arrest. Growth curves of KDM4B knockdown or control knockdown cells. 10,000 cells were cultured for up to 72 h and the number of cells overtime were calculated. Data represent the mean ± s.e.m. for three independent experiments. No significant difference was observed between groups. Supplementary material 1 (EPS 1910 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, WW., Hu, Q., Liu, ZR. et al. KDM4B promotes DNA damage response via STAT3 signaling and is a target of CREB in colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 449, 81–90 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3345-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3345-5