Abstract
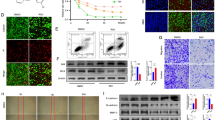
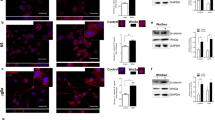
Alternations of environment signals such as neurotrophins may be the basis for malignant transformation of retinoblastoma (Rb), the most common primary intraocular malignancy in children. The aim of this study is to investigate the ability of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) to decrease the chemosensitivity of Rb cells to the common chemotherapeutic agents and to explore the role of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in such cellular process. The results showed that BDNF could induce higher expression of HIF-1α via activation of TrkB in human Y-79 retinoblastoma cells, which consequently contributed to its effect against chemotherapeutic agent-induced cytotoxicity and cell apoptosis. However, this protective effect could be potently reversed by knockdown of HIF-1α. Furthermore, BDNF strikingly prevented chemotherapeutic agent-induced alternations of apoptosis-related molecules, which could also be attenuated by silencing HIF-1α. Therefore, our findings demonstrated that BDNF could contribute to chemoresistance of Rb via modulation of HIF-1α expression, indicating that targeting at the BDNF-TrkB/HIF-1α signaling pathway might be a promising strategy for the treatment of retinoblastoma in the future.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
McCarthy N (2012) Retinoblastoma: epigenetic outcome. Nat Rev Cancer 12:80
Villegas VM, Hess DJ, Wildner A, Gold AS, Murray TG (2013) Retinoblastoma. Curr Opin Ophthalmol 24:581–588
Friedman DN, Sklar CA, Oeffinger KC, Kernan NA, Khakoo Y, Marr BP, Wolden SL, Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ (2013) Long-term medical outcomes in survivors of extra-ocular retinoblastoma: the Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) experience. Pediatr Blood Cancer 60:694–699
Stannard C, Sauerwein W, Maree G, Lecuona K (2013) Radiotherapy for ocular tumours. Eye (Lond) 27:119–127
Shields CL, Bianciotto CG, Jabbour P, Griffin GC, Ramasubramanian A, Rosenwasser R, Shields JA (2011) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for retinoblastoma: report no. 2, treatment complications. Arch Ophthalmol 129:1407–1415
Knudson AG (1971) Mutation and cancer: statistical study of retinoblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 68:820–823
Stephan H, Zakrzewski JL, Bölöni R, Grasemann C, Lohmann DR, Eggert A (2008) Neurotrophin receptor expression in human primary retinoblastomas and retinoblastoma cell lines. Pediatr Blood Cancer 50:218–222
Maisonpierre PC, Belluscio L, Friedman B, Alderson RF, Wiegand SJ, Furth ME, Lindsay RM, Yancopoulos GD (1990) NT-3, BDNF, and NGF in the developing rat nervous system: parallel as well as reciprocal patterns of expression. Neuron 5:501–509
Numakawa T, Suzuki S, Kumamaru E, Adachi N, Richards M, Kunugi H (2010) BDNF function and intracellular signaling in neurons. Histol Histopathol 25:237–258
Washiyama K, Muragaki Y, Rorke LB, Lee V, Feinstein SC, Radeke MJ, Blumberg D, Kaplan D, Trojanowski J (1996) Neurotrophin and neurotrophin receptor proteins in medulloblastomas and other primitive neuroectodermal tumors of the pediatric central nervous system. Am J Pathol 148:929–940
Chiappa SA, Chin LS, Zurawel RH, Raffel C (1999) Neurotrophins and Trk receptors in primitive neuroectodermal tumor cell lines. Neurosurgery 45:1148–1154
Jaboin J, Kim CJ, Kaplan DR, Thiele CJ (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB protects neuroblastoma cells from chemotherapy-induced apoptosis via phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase pathway. Cancer Res 62:6756–6763
Semenza GL (2010) HIF-1: upstream and downstream of cancer metabolism. Curr Opin Genet Dev 20:51–56
Semenza GL (2012) Hypoxia-inducible factors: mediators of cancer progression and targets for cancer therapy. Trends Pharmacol Sci 33:207–214
Lee J-W, Bae S-H, Jeong J-W, Kim S-H, Kim K-W (2004) Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) α: its protein stability and biological functions. Exp Mol Med 36:1–12
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:721–732
Nakamura K, Martin KC, Jackson JK, Beppu K, Woo C-W, Thiele CJ (2006) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor activation of TrkB induces vascular endothelial growth factor expression via hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:4249–4255
Hammond JB, Kruger NJ (1988) The bradford method for protein quantitation. Methods Mol Biol 3:25–32
Zhu X, Wang K, Zhang K, Zhu L, Zhou F (2014) Ziyuglycoside II induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through activation of ROS/JNK pathway in human breast cancer cells. Toxicol Lett 227:65–73
Friedman WJ, Greene LA (1999) Neurotrophin signaling via Trks and p75. Exp Cell Res 253:131–142
Roux PP, Barker PA (2002) Neurotrophin signaling through the p75 neurotrophin receptor. Prog Neurobiol 67:203–233
Johnson JE, Barde Y-A, Schwab M, Thoenen H (1986) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor supports the survival of cultured rat retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 6:3031–3038
Colafrancesco V, Parisi V, Sposato V, Rossi S, Russo MA, Coassin M, Lambiase A, Aloe L (2011) Ocular application of nerve growth factor protects degenerating retinal ganglion cells in a rat model of glaucoma. J Glaucoma 20:100–108
Frade JM, Bovolenta P, Rodriguez-Tebar A (1999) Neurotrophins and other growth factors in the generation of retinal neurons. Microsc Res Tech 45:243–251
Rohwer N, Cramer T (2011) Hypoxia-mediated drug resistance: novel insights on the functional interaction of HIFs and cell death pathways. Drug Resist Updat 14:191–201
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ, Simon MC (2010) Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol Cell 40:294–309
Patel J, Landers K, Mortimer RH, Richard K (2010) Regulation of hypoxia inducible factors (HIF) in hypoxia and normoxia during placental development. Placenta 31:951–957
Halterman MW, Federoff HJ (1999) HIF-1α and p53 promote hypoxia-induced delayed neuronal death in models of CNS ischemia. Exp Neurol 159:65–72
Greijer A, Van der Wall E (2004) The role of hypoxia inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) in hypoxia induced apoptosis. J Clin Pathol 57:1009–1014
Zhang Q, Zhang ZF, Rao JY, Sato JD, Brown J, Messadi DV, Le AD (2004) Treatment with siRNA and antisense oligonucleotides targeted to HIF-1alpha induced apoptosis in human tongue squamous cell carcinomas. Int J Cancer 111:849–857
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funds of Tongji University (2012KJ042), Shanghai Municipality Health and Family Planning Commission (201540304), and Hongkou District of Shanghai Municipality Health and Family Planning Commission (1402-11).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Jing, M., Ge, R. et al. Induction of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α by BDNF protects retinoblastoma cells against chemotherapy-induced apoptosis. Mol Cell Biochem 414, 77–84 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2660-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2660-y