Abstract
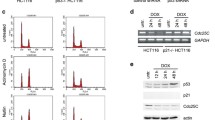
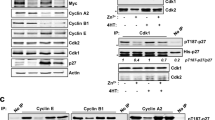
The Murine double-minute clone 2 (Mdm2) onco-protein is the principal regulator of the tumour suppressor, p53. Mdm2 acts as an E3-type ubiquitin ligase that mediates the ubiquitylation and turnover of p53 under normal, unstressed circumstances. In response to cellular stress, such as DNA damage, the Mdm2–p53 interaction is disrupted. Part of the mechanism of uncoupling p53 from Mdm2-mediated degradation involves hypo-phosphorylation of a cluster of phosphorylated serine residues in the central acidic domain of Mdm2. Here, we show that two of the residues within this domain that are phosphorylated in vivo, Ser-260 and Ser-269, are phosphorylated by CK2 in vitro. Treatment of cells with the CK2 inhibitor, 4,5,6,7-tetrabromo-2-azabenzimidazole (TBB), leads to the induction of p53 and downstream targets of p53 including Mdm2 itself and p21. These data are consistent with the idea that CK2-mediated phosphorylation of Mdm2 may regulate Mdm2-mediated p53 turnover.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michael D, Oren M: The p53-Mdm2 module and the ubiquitin system. Semin Cancer Biol 13: 49–58, 2003
Vousden KH, Lu X: Live or let die: The cell’s response to p53. Nature Rev Cancer 2: 594–604, 2002
Argentini M, Barboule N, Wasylyk B: The contribution of the acidic domain of MDM2 to p53 and MDM2 stability. Oncogene 20: 1267–1275, 2001
Kawai H, Wiederschain D, Yuan Z-M: Critical contribution of the MDM2 acidic domain to p53 ubiquitination. Mol Cell Biol 23: 4939–4947, 2003
Meulmeester E, Frenk R, Stad R, de Graaf P, Marine J-C, Vousden KH, Jochemsen AG: Critical role for a central part of Mdm2 in the ubiquitylation of p53. Mol Cell Biol 23: 4929–4938, 2003
Midgley CA, Desterro JM, Saville MK, Howard S, Sparks A, Hay RT, Lane DP: An N-terminal p14ARF peptide blocks Mdm2-dependent ubiquitination in vitro and can activate p53 in vivo. Oncogene 19: 2312–2323, 2000
Ganguli G, Wasylyk B: p53-independent functions of Mdm2. Mol Cancer Res 1: 1027–1035, 2003
Blattner C, Hay TJ, Meek DW, Lane DP: Hypophosphorylation of Mdm2 augments p53 stability. Mol Cell Biol 22: 6170–6182, 2002
Winter M, Milne D, Dias S, Kulikov R, Knippschild U, Blattner C, Meek D: Protein kinase CK1-delta phosphorylates key sites in the acidic domain of Mdm2 that regulate p53 turnover. Biochemistry 43: 16356–16364, 2004
Litchfield DW: Protein kinase CK2: Structure, regulation and role in cellular decisions of life and death. Biochem J 369: 1–15, 2003
Meggio F, Pinna LA: One thousand and one substrates of protein kinase CK2? FASEB J 17: 349–368, 2003
Pinna LA: Protein kinase CK2: A challenge to canons. J Cell Sci 115: 3873–3878, 2002
Keller DM, Zeng X, Wang Y, Zhang QH, Kapoor M, Shu H, Goodman R, Lozano G, Zhao Y, Lu H: A DNA damage-induced p53 serine 392 kinase complex contains CK2, hSpt16, and SSRP1. Mol Cell 7: 283–292, 2001
Ghavidel A, Schultz MC: TATA binding protein-associated CK2 transduces DNA damage signals to the RNA polymerase III transcriptional machinery. Cell 106: 575–584, 2001
Maldonado E, Allende JE: Phosphorylation of yeast TBP by protein kinase CK2 reduces its specific binding to DNA. FEBS Lett 443: 256–260, 1999
Burch L, Scott M, Pohler E, Meek D, Hupp T: Phage-peptide display identifies the death-activated protein kinase family as a novel modifier of the p53-inducible gene products MDM2 and p21WAF1. J Mol Biol 337: 115–128, 2004
Kurki S, Peltonen K, Kiviharju T, Latonen L, Ojala P, Meek D, Laiho M: Nucleolar protein NPM interacts with HDM2 and protects tumor suppressor protein p53 from HDM2-mediated degradation. Cancer Cell 5: 465–475, 2004
Gotz C, Kartarius S, Scholtes P, Nastainczyk W, Montenarh M: Identification of a CK2 phosphorylation site in mdm2. Eur J Biochem 266: 493–501, 1999
Hjerrild M, Milne D, Dumaz N, Hay T, Issinger OG, Meek D: Phosphorylation of murine double minute clone 2 (MDM2) protein at serine-267 by protein kinase CK2 in vitro and in cultured cells. Biochem J 355: 347–356, 2001
Sarno S, Moro S, Meggio F, Zagotto G, Dal Ben D, Ghisellini P, Battistutta R, Zanotti G, Pinna LA: Toward the rational design of protein kinase casein kinase-2 inhibitors. Pharmacol Ther 93: 159–168, 2002
Sarno S, Reddy H, Meggio F, Ruzzene M, Davies SP, Donella-Deana A, Shugar D, Pinna LA: Selectivity of 4,5,6,7-tetrabromobenzotriazole, an ATP site-directed inhibitor of protein kinase CK2 (‘casein kinase-2′). FEBS Lett 496: 44–48, 2001
Leveillard T, Wasylyk B: The Mdm2 C-terminal region binds TAFII250 and is required for Mdm2 regulation of the cyclin A promoter. J Biol Chem. 272: 30651–30661, 1997
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Allende-Vega, N., Dias, S., Milne, D. et al. Phosphorylation of the acidic domain of Mdm2 by protein kinase CK2. Mol Cell Biochem 274, 85–90 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-3074-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-005-3074-4