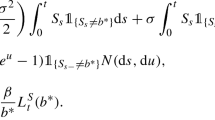Abstract
In this paper, we consider a two-dimensional reduced form contagion model with regime-switching interacting default intensities. The model assumes that the intensities of the default times are driven by macro-economy described by a homogenous Markov chain and that the default of one firm may trigger a positive jump, associated with the state of Markov chain, in the default intensity of the other firm. The intensities before the default of the other firm are modeled by a two-dimensional regime-switching shot noise process with common shocks. By using the idea of “change of measure” and some closed-form formulas for the joint conditional Laplace transforms of the regime-switching shot noise processes and the integrated regime-switching shot noise processes, we derive the two-dimensional conditional and unconditional joint distributions of the default times. Based on these results, we can express the single-name credit default swap (CDS) spread, the first and second-to-default CDS spreads on two underlyings in terms of fundamental matrix solutions of linear, matrix-valued, ordinary differential equations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang A, Bekaert G (2002a) Regime switches in interest rates. J Bus Econ Stat 20:163–182
Ang A, Bekaert G (2002b) Short rate nonlinearities and regime switches. J Econ Dyn Control 26:1243–1274
Brigo D, Pallavicini A, Torresetti R (2007) Calibration of CDO tranches with the dynamical generalized Poisson loss model. Risk 20:70–75
Buffington J, Elliott RJ (2002) American options with regime switching. Int J Theor Appl Financ 5:497–514
Collin-Dufresne P, Goldstein R, Hugonnier J (2004) A general formula for valuing defaultable securities. Econometrica 72(5):1377–1407
Cossette H, Marceau E (2000) The discrete-time model with correlated classes of businesses. Insur Math Econ 26:133–149
Dassios A, Jang J (2003) Pricing of catastrophe reinsurance & derivatives using the Cox process with shot noise intensity. Financ Stoch 7(1):73–95
Davies A (2004) Credit spread modeling with regime-switching techniques. J Fixed Income 14(3):36–48
Davies A (2008) Credit spread determinants: an 85 year perspective. J Financ Mark 11:180–197
Davis M, Lo V (2001) Infectious defaults. Quant Financ 1:382–387
Di Graziano G, Rogers LCG (2009) A dynamic approach to the modelling of correlation credit derivatives using Markov chains. Int J Theor Appl Financ 12:45–62
Ding XW, Giesecke K, Tomecek PI (2009) Time-changed birth processes and multiname credit derivatives. Oper Res 57(4):990–1005
Duffie D, Gârleanu N (2001) Risk and valuation of collateralized debt obligations. Financ Anal J 57(1):41–59
Elliott RJ, Aggoun L, Moore JB (1994) Hidden Markov models: estimation and control. Springer, Berlin
Duffie D, Filipovic D, Schachermayer W (2003) Affine processes and applications in finance. Ann Appl Probab 13(3):984–1053
Elliott RJ, Leunglung C, Siu TK (2005) Option pricing and Esscher transform under regime switching. Ann Financ 1:423–432
Errais E, Giesecke K, Goldberg LR (2010) Affine point processes and portfolio credit risk. SIAM J Financ Math 1:642–665
Gaspar RM, Schmidt T (2010) Credit risk modeling with shot-noise processes. Working paper
Giesecke K, Goldberg L (2004) Sequential defaults and incomplete information. J Risk 7(1):1–26
Giesecke K, Zhu S (2013) Transform analysis for point processes and applications in credit risk. Math Finance 23(4):742–762
Giesecke K, Goldberg L, Ding X (2011a) A top down approach to multi-name credit. Oper Res 59(2):283–300
Giesecke K, Longstaff FA, Schaefer S, Ilya Strebulaev I (2011b) Corporate bond default risk: a 150-year perspective. J Financ Econ 102:233–250
Hackbarth D, Miao JJ, Morellec E (2006) Capital structure, credit risk, and macroeconomic conditions. J Financ Econ 82:519–550
Hardy MR (2001) A regime-switching model of long-term stock returns. N Am Actuar J 5(2):41–53
Jarrow R, Yu F (2001) Counterparty risk and the pricing of defaultable securities. J Finance 56:1765–1799
Kusuoka S (1999) A remark on default risk models. Adv Math Econ 1:69–82
Leung KS, Kwok YK (2009) Counterparty risk for credit default swaps: Markov chain interacting intensities model with stochastic intensity. Asia-Pac Financ Mark 16:169–181
Lindskog F, McNeil A (2003) Common Poisson shock models: applications to insurance and credit risk modelling. Astin Bull 33:209–238
Ma J, Yun YY (2010) Correlated intensity, counter party risks, and dependent mortalities. Insur Math Econ 47:337–351
Siu TK (2010) Bond pricing under a Markovian regime-switching jump-augmented Vasicek model via stochastic flows. Appl Math Comput 216(11):3184–3190
Siu TK, Erlwein C, Mamon RS (2008) The pricing of credit default swaps under a Markov-modulated Merton’s structural model. N Am Actuar J 12(1):19–46
Yu F (2007) Correlated defaults in intensity-based models. Math Financ 17:155–173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, Y., Yuen, K.C., Wang, G. et al. A Reduced-Form Model for Correlated Defaults with Regime-Switching Shot Noise Intensities. Methodol Comput Appl Probab 18, 459–486 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-014-9431-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11009-014-9431-6