Abstract
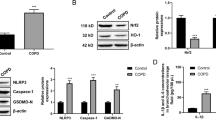
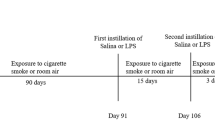
We sought to determine the circulatory level of atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and its receptor (Natriuretic peptide receptor-A) on different (7, 15, 30 and 45) days of cigarette smoke (CS) exposure-induced pulmonary inflammatory condition in experimental rats. The plasma ANP and lung cGMP levels were measured using a commercial ELISA kit. The total cells count (TC), neutrophil (N), and macrophage (M) were quantitated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) isolated from CS and control rat lungs. In addition, mRNA and protein expression profile of natriuretic peptide receptor-A (NPRA) was also quantitated in experimental groups. The TC, N, and M were gradually increased and reached maximum on the 45th day (p < 0.001 respectively) in BALF isolated from CS exposed rat compared with control. Further, Inflammatory markers of histamine and serotonin levels were also progressively increased and reached the maximum at 45 days of CS rats (p < 0.001 respectively) compared with control. The plasma ANP (9.07 ± 0.57 vs 22.01 ± 0.67 pmol/ml) and lung cGMP (8.66 ± 0.80 vs 21.33 ± 0.98 pg/ml) levels were up-regulated starting from 7th day of exposure and reach a maximum on 45 days CS exposed rats (p < 0.001 respectively) as compared with control. Moreover, mRNA and protein expression of NPRA was increased gradually and reached the maximum (threefold and 3.5-fold respectively) on 45th day of CS exposure. Our results demonstrate for the first time that ANP/NPRA an intrinsic anti-inflammatory system of the lung is getting up-regulated during CS exposure.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barua RS, Sharma M, Dileepan KN (2015) Cigarette smoke amplifies inflammatory response and atherosclerosis progression through activation of the H1R-TLR2/4-COX2 axis. Front Immunol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2015.00572
Dalrymple A, Ordoñez P, Thorne D et al (2015) An improved method for the isolation of rat alveolar type II lung cells: use in the comet assay to determine DNA damage induced by cigarette smoke. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 72:141–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2015.03.013
Divya T, Dineshbabu V, Soumyakrishnan S et al (2016) Celastrol enhances Nrf2 mediated antioxidant enzymes and exhibits anti-fibrotic effect through regulation of collagen production against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Chem Biol Interact 246:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2016.01.006
Dodd-o JM, Hristopoulos ML, Kibler K et al (2008) The role of natriuretic peptide receptor-A signaling in unilateral lung ischemia-reperfusion injury in the intact mouse. Am J Physiol 294:714–723. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00185.2007
Hamad AM, Clayton A, Islam B et al (2003) Guanylyl and airway smooth muscle function. Am J Physiol 285(2003):973–983. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00033.2003
Hodge-Bell KC, Lee KM, Renne RA et al (2007) Pulmonary inflammation in mice exposed to mainstream cigarette smoke. Inhal Toxicol 19:361–376. https://doi.org/10.1080/08958370601144076
Irwin DC, Van Patot MCT, Tucker A, Bowen R (2005) Direct ANP inhibition of hypoxia-induced inflammatory pathways in pulmonary microvascular and macrovascular endothelial monolayers. Am J Physiol 288:849–859. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00294.2004
Kalaiarasu LP, Subramanian V, Sowndharrajan B, Vellaichamy E (2016) Insight into the anti-inflammatory mechanism of action of atrial natriuretic peptide, a heart derived peptide hormone: involvement of COX-2, MMPs, and NF-kB pathways. Int J Pept Res Ther 22:451–463. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-016-9525-9
Kandasamy R, Park SJ, Boyapalle S et al (2010) Isatin down-regulates expression of atrial natriuretic peptide receptor A and inhibits airway inflammation in a mouse model of allergic asthma. Int Immunopharmacol 10:218–225. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2009.11.003
Lagente V, Manoury B, Nénan S et al (2005) Role of matrix metalloproteinases in the development of airway inflammation and remodeling. Braz J Med Biol Res 38:1521–1530. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0100-879X2005001000009
Lau WKW, Cui LY, Chan SCH et al (2016) The presence of serotonin in cigarette smoke: a possible mechanistic link to 5-HT-induced airway inflammation. Free Radic Res 50:495–502. https://doi.org/10.3109/10715762.2016.1145355
Manivasagam S, Subramanian V, Tumala A, Vellaichamy E (2016) Differential expression and regulation of anti-hypertrophic genes Npr1 and Npr2 during β-adrenergic receptor activation-induced hypertrophic growth in rats. Mol Cell Endocrinol 433:117–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2016.06.010
Menegali BT, Nesi RT, Souza PS et al (2009) The effects of physical exercise on the cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary oxidative response. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 22:567–573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pupt.2009.08.003
Mezzasoma L, Antognelli C, Talesa VN (2016) Atrial natriuretic peptide down-regulates LPS/ATP-mediated IL-1β release by inhibiting NF-kB, NLRP3 inflammasome and caspase-1 activation in THP-1 cells. Immunol Res 64:303–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12026-015-8751-0
Mezzasoma L, Talesa VN, Romani R, Bellezza I (2021) Anp and bnp exert anti-inflammatory action via npr-1/cgmp axis by interfering with canonical, non-canonical, and alternative routes of inflammasome activation in human thp1 cells. Int J Mol Sci 22:1–17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22010024
Mohapatra SS, Lockey RF, Vesely DL, Gower WR (2004) Natriuretic peptides and genesis of asthma: An emerging paradigm? J Allergy Clin Immunol 114:520–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2004.05.028
Nojiri T, Inoue M, Maeda H et al (2013) Low-dose human atrial natriuretic peptide for the prevention of postoperative cardiopulmonary complications in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients undergoing lung cancer surgery. Eur J Cardio-Thorac Surg 44:98–103. https://doi.org/10.1093/ejcts/ezs646
Nojiri T, Hosoda H, Tokudome T et al (2014) Atrial natriuretic peptide inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 29:24–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pupt.2014.01.003
Okamoto A, Nojiri T, Konishi K et al (2017) Atrial natriuretic peptide protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis via vascular endothelial cells in mice. Respir Res 18:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-016-0492-7
Pandey KN (2011) Guanylyl cyclase/atrial natriuretic peptide receptor-A: role in the pathophysiology of cardiovascular regulation. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 89:557–573. https://doi.org/10.1139/y11-054
Perrault T, Gutkowska J (1995) Role of Atrial natriuretic factor in lung physiology and pathology. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 151:226–242. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.151.1.7812560
Sakurai H, Nozaki M, Traber KSLD, Traber DL (2005) Atrial natriuretic peptide release associated with smoke inhalation and physiological responses to thermal injury in sheep. Burns 31:737–743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2005.03.002
Shergis JL, Di YM, Zhang AL et al (2014) Therapeutic potential of Panax ginseng and ginsenosides in the treatment of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Complement Ther Med 22:944–953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ctim.2014.08.006
Tanabe M, Ueda M, Endo M, Kitajima M (1996) The effect of atrial natriuretic peptide on pulmonary acid injury in a pig model. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 154:1351–1356. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.154.5.8912747
Valença SS, Pimenta WA, Rueff-Barroso CR et al (2009) Involvement of nitric oxide in acute lung inflammation induced by cigarette smoke in the mouse. Nitric Oxide 20:175–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.niox.2008.11.003
Vellaichamy E, Kaur K, Pandey KN (2007) Enhanced activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in mice lacking natriuretic peptide receptor-A. Peptides 28:893–899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2006.12.009
Vollmar AM (2005) The role of atrial natriuretic peptide in the immune system. Peptides 26:1086–1094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2004.08.034
Wang X, Xu W, Mohapatra S et al (2008) Prevention of airway inflammation with topical cream containing imiquimod and small interfering RNA for natriuretic peptide receptor. Genet Vaccines Ther 6:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-0556-6-7
Wang D, Tao K, Xion J et al (2016) TAK-242 attenuates acute cigarette smoke-induced pulmonary inflammation in mouse via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 472:508–515. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.03.001
Xing J, Birukova AA (2010) ANP attenuates inflammatory signaling and Rho pathway of lung endothelial permeability induced by LPS and TNFα. Microvasc Res 79:56–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mvr.2009.11.006
Zhang W, Cao X, Chen D et al (2011) Plasmid-encoded NP73-102 modulates atrial natriuretic peptide receptor signaling and plays a critical role in inducing tolerogenic dendritic cells. Genet Vaccines Ther 9:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1479-0556-9-3
Acknowledgements
Dr. EV greatly acknowledges UGC-SAP DRS-II (F.5/2015/DRS-II (SAP-II)), India for the financial support. AB wishes to thank the UGC-SAP DRS-II (GCCO/A5/UGC-SAP-II) for junior research fellowship (JRF) also thanks the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) (F.No.45/28/2020-BIO/BMS) for senior research fellowship (SRF).
Funding
Dr. EV greatly acknowledges UGC-SAP DRS-II (F.5/2015/DRS-II (SAP-II)), India, for the financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All the animals studies were approved by the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC) of the University of Madras IAEC No: 01/01/2018 and were performed in accordance with CPCSEA guidelines.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Babu, A.A., Vellaichamy, E. Enhanced Activation of Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP) and Natriuretic Peptide Receptor-A (NPRA) in Chronic Cigarette Smoke-Induced Lung Inflammation in Experimental Rats. Int J Pept Res Ther 27, 2543–2550 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-021-10271-3
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10989-021-10271-3