Abstract
Context
The role of ecological processes governing community structure are dependent on the spatial distances among local communities and the degree of habitat heterogeneity at a given spatial scale. Also, they depend on the dispersal ability of the targeted organisms collected throughout a landscape window.
Objectives
We assessed the relative importance of spatial and environmental factors shaping edaphic (Collembola) and epigeous (Carabidae) communities at different scales.
Methods
The sampling sites were four different landscape windows (1 km2 square each) in a Mediterranean cork-oak landscape in Portugal. Variance partitioning methods were used to disentangle the relative effects of spatial variables and environmental variables (habitat: data on % of vegetation cover types; management: data on forestry and pasture interventions; landscape: data on landscape metrics e.g., patch size, shape and configuration) across different spatial scales.
Results
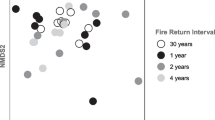
The relative effects of environmental and spatial factors at different scales varied between Collembola and Carabidae. The pure effect of the environmental component was only significant for carabid beetles and explained a higher percentage of their community variance compared to collembolan communities. The pure effects of the spatial component were generally higher than the environmental component for both groups of soil fauna. Carabid communities responded to landscape features related to the patch connectivity of open areas (grasslands) as well as the shape of cork-oak habitat patches integrating the agro-forest mosaic.
Conclusions
Community patterns of surface-dwelling soil fauna may be partly predicted by some features of the landscape, while soil-dwelling communities require ecological assessments at finer spatial scales.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
AströmJ Bengtsson J (2011) Patch size matters more than dispersal distance in a mainland–island metacommunity. Oecologia 167:747–757
Baars MA (1979) Catches in pitfall traps in relation to mean densities of carabid beetles. Oecologia 41:25–46
Barbaro L, van Halder I (2009) Linking bird, carabid beetle and butterfly life-history traits to habitat fragmentation in mosaic landscapes. Ecography 32:321–333
Bardgett RD, Bowman WD, Kaufmann R, Schmidt SK (2005) A temporal approach to linking aboveground and belowground ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 20:634–641
Beisner B, Peres-Neto P, Lindstro E, Barnett A, Longhi ML (2006) The role of environmental and spatial processes in structuring lake communities from bacteria to fish. Ecology 87:2985–2991
Bengtsson G, Hedlund K, Rundgren S (1994) Food-and density-dependent dispersal: evidence from a soil collembolan. J Anim Ecol 63:513–520
Berg MP (2010) Spatio-temporal structure in soil communities and ecosystem processes. In: Verhoef HA, Morin PJ (eds) Community ecology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 69–80
Berg MP, Bengtsson J (2007) Temporal and spatial variability in soil food web structure. Oikos 116:1789–1804
Berg MP, Kiers ET, Driessen G, van Der Heijden M, Kooi BW, Kuenen F, Liefting M, Verhoef HA, Ellers J (2010) Adapt or disperse: understanding species persistence in a changing world. Glob Change Biol 16:587–598
Bivand R (2013) SPDEP: spatial dependence: weighting schemes, statistics and models. R package version 0.5-59/r491 http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/spdep/
Blanchet FG, Legendre P, Borcard D (2008) Forward selection of explanatory variables. Ecology 89:2623–2632
Boieiro M, Carvalho JC, Cardoso P, Aguiar CAS, Rego C, Faria e Silva I, Amorim I, Pereira R, Azevedo FEB, Borges PAV, Serrano ARM (2013) Spatial factors play a major role as determinants of endemic ground Beetle Beta diversity of Madeira Island Laurisilva. PLoS One 8:1–10
Borcard D, Legendre P, Drapeau P (1992) Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology 73:1045–1055
Bowler DE, Benton TG (2011) Testing the interaction between environmental variation and dispersal strategy on population dynamics using a soil mite experimental system. Oecologia 166:111–119
Bray JR, Curtis JT (1957) An ordination of upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol Monogr 27:325–349
Brose U (2003) Bottom-up control of carabid beetle communities in early successional wetlands: mediated by vegetation structure or plant diversity? Oecologia 135:407–413
Chase JM, Bengtsson J (2010) Increasing spatio-temporal scales: meta-community ecology. In: Verhoef HA, Morin PJ (eds) community ecology. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 57–68
Chisholm C, Lindo Z, Gonzalez A (2011) Metacommunity diversity depends on connectivity and patch arrangement in heterogeneous habitat networks. Ecography 34:415–424
Chust G, Pretus JL, Ducrot D, Bedos A, Deharveng L (2003) Response of soil fauna to landscape heterogeneity: determining optimal scales for biodiversity modeling. Conserv Biol 17:1712–1723
Chust G, Pretus JL, Ducrot D, Ventura D (2004) Scale dependency of insect assemblages in response to landscape pattern. Landscape Ecol 19:41–57
Chust G Pretus JL, Ducrot D, Bedos A, Deharveng L (2003) Identification of landscape units from an insect perspective. Ecography 26:257–268
Clarke KR (1993) Nonparametric multivariate analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol 18:117–143
Cliff AD, Ord JK (1973) Spatial autocorrelation. Pion, London
Costanza JK, Moody A, Peet RK (2011) Multi-scale habitat heterogeneity as a predictor of plant species richness. Landscape Ecol 26:851–864
Cottenie K (2005) Integrating environmental and spatial processes in ecological community dynamics. Ecol Lett 8:1175–1182
Cushman SA, McGarigal K (2002) Hierarchical, multi-scale decomposition of species-environment relationships. Landscape Ecol 17:637–646
Desender K, Turin H (1989) Loss of habitat and changes in the composition of the ground and tiger beetle fauna in four West European countries since 1950 (Coleoptera: Carabidae, Cicindelidae). Biol Conserv 48:277–294
Diekötter T, Wamser S, Wolters V, Birkhofer K (2010) Landscape and management effects on structure and function of soil arthropod communities in winter wheat. Agric Ecosyst Environ 137:108–112
Dormann CF, Elith J, Bacher S, Buchmann C, Carl G, Carré G, GarcíaMarquéz JR, Gruber B, Lafourcade B, Leitão PJ, Münkemüller T, McClean C, Osborne P, Reineking B, Schröder B, Skidmore A, Zurell D, Lautenbach S (2013) Collinearity: a review of methods to deal with it and a simulation study evaluating their performance. Ecography 36:27–46
Dray S (2013) spacemakeR: spatial modelling. R package version 0.0–5/r113 http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/sedar/
Dray S, Legendre P, Peres-Neto PR (2006) Spatial modelling: a comprehensive framework for principal coordinate analysis of neighbour matrices (PCNM). Ecol Modell 196:483–493
Dray S, Legendre P, Blanchet FG (2013) packfor: forward selection with permutation (Canoco p. 46). R package version 0.0-8/r109. http://R-Forge.R-project.org/projects/sedar/
Driscoll DA, Kirkpatrick JB, McQuillan PB, Bonham KJ (2010) Classic metapopulations are rare among common beetle species from a naturally fragmented landscape. J Anim Ecol 79:294–303
Ettema CH, Wardle DA (2002) Spatial soil ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 17:177–183
Flohre A, Fischer C, Aavik T, Bengtsson J, Berendse F, Bommarco R, Ceryngier P, Clement LW, Dennis C, Eggers S, Emmerson M, Geiger F, Guerrero I, Hawro V, Inchausti P, Liira J, Morales MB, Oñate JJ, Pärt T, Weisser WW, Winqvist C, Thies C, Tscharntke T (2011) Agricultural intensification and biodiversity partitioning in European landscapes comparing plants, carabids, and birds. Ecol Appl 21:1772–1781
Hamazaki T (1996) Effects of patch shape on the number of organisms. Landscape Ecol 11:299–306
Hedlund K, Griffiths B, Christensen S, Scheu S, Setälä H, Tscharntke T, Verhoef H (2004) Trophic interactions in changing landscapes: responses of soil food webs. Basic Appl Ecol 5:495–503
Heiniger C, Barot S, Ponge JF, Salmon S, Botton-Divet L, Carmignac D, Dubs F (2014) Effect of habitat spatiotemporal structure on collembolan diversity. Pedobiologia 57:103–117
Heino J (2013) Environmental heterogeneity, dispersal mode and co-occurrence in stream macroinvertebrates. Ecol Evol 3:344–355
Hopkin SP (1997) Biology of the springtails. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Ingimarsdóttir M, Caruso T, Ripa J, Magnúsdóttir OB, Migliorini M, Hedlund K (2012) Primary assembly of soil communities: disentangling the effect of dispersal and local environment. Oecologia 170:745–754
Jonason D, Smith HG, Bengtsson J, Birkhofer K (2013) Landscape simplification promotes weed seed predation by carabid beetles. Landscape Ecol 28:478–494
Kotze DJ, O’Hara RB (2003) Species decline–but why? Explanations of carabid beetle (Coleoptera, Carabidae) declines in Europe. Oecologia 135:138–148
Kotze DJ, Brandmayr P, Casale A, Dauffy-Richard E, Dekoninck W, Koivula MJ, Lövei GL, Mossakowski D, Noordijk J, Paarmann W, Pizzolotto R, Saska P, Schwerk A, Serrano J, Szyszko J, Taboada A, Turin H, Venn S, Vermeulen R, Zetto T (2011) Forty years of carabid beetle research in Europe–from taxonomy, biology, ecology and population studies to bioindication, habitat assessment and conservation. ZooKeys 100:55–148
Legendre P, Gallagher ED (2001) Ecologically meaningful transformations for ordination of species data. Oecologia 129:271–280
Legendre P, Legendre L (2012) Numerical ecology. In: Vidmar L (ed) Developments in environmental modelling, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Legendre P, Borcard D, Roberts DW (2012) Variation partitioning involving orthogonal spatial eigenfunction submodels. Ecology 93:1234–1240
Leibold MA, Holyoak M, Mouquet N, Amarasekare P, Chase JM, Hoopes MF, Holt RD, Shurin JB, Law R, Tilman D, Loreau M, Gonzalez A (2004) The metacommunity concept: a framework for multi-scale community ecology. Ecol Lett 7:601–613
Lemessa D, Hambäck PA, Hylander K (2014) The effect of local and landscape level land-use compositionon predatory arthropods in a tropical agricultural landscape. Landscape Ecol 30:167–180
Lindberg N, Bengtsson J (2005) Population responses of oribatid mites and collembolans after drought. Appl Soil Ecol 28:163–174
Lindo Z, Winchester NN (2009) Spatial and environmental factors contributing to patterns in arboreal and terrestrial oribatid mite diversity across spatial scales. Oecologia 160:817–825
Lövei GL, Sunderland KD (1996) Ecology and behavior of ground beetles (Coleoptera, Carabidae). Annu Rev Entomol 41:231–256
Martins da Silva P, Aguiar CAS, Niemelä J, Sousa JP, Serrano ARM (2008) Diversity patterns of ground-beetles (Coleoptera: Carabidae) along a gradient of land-use disturbance. Agric Ecosyst Environ 124:270–274
Martins da Silva P, Aguiar CAS, Niemelä J, Sousa JP, Serrano ARM (2009) Cork-oak woodlands as key-habitats for biodiversity conservation in Mediterranean landscapes: a case study using rove and ground beetles (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae, Carabidae). Biodivers Conserv 18:605–619
Martins da Silva P, Berg MP, Serrano ARM, Dubs F, Sousa JP (2012) Environmental factors at different spatial scales governing soil fauna community patterns in fragmented forests. Landscape Ecol 27:1337–1349
McGarigal K, Cushman SA, Neel MC, Ene E (2002) FRAGSTATS: spatial pattern analysis program for categorical maps. Computer software program produced by the authors at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst. www.umass.edu/landeco/research/fragstats/fragstats.html. Accessed 10 Sept 2009
Moran P (1948) The interpretation of statistical maps. J R Stat Soc Ser B 10:243–251
Myers JA, Chase JM, Jiménez I, Jørgensen PM, Araujo-Murakami A, Paniagua-Zambrana N, Seidel R (2013) Beta-diversity in temperate and tropical forests reflects dissimilar mechanisms of community assembly. Ecol Lett 16:151–157
Nabe-Nielsen J, Sibly RM, Forchhammer MC, Forbes VE, Topping CJ (2010) The effects of landscape modifications on the long-term persistence of animal populations. PLoS One 5:1–7
Niemelä J, Kotze DJ (2009) Carabid beetle assemblages along urban to rural gradients: a review. Landsc Urban Plan 92:65–71
Niemelä J, Haila Y, Halme E, Pajunen T, Punttila P (1992) Heterogeneity in the spatial distribution of carabid beetles in the southern Finnish taiga. J Biogeogr 19:173–181
Ojala R, Huhta V (2001) Dispersal of microarthropods in forest soil. Pedobiologia 45:443–450
Oksanen J, Blanchet FG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara RB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2013) vegan: community ecology package. R package version 2.0-8. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Peres-Neto PR, Legendre P, Dray S, Borcard D (2006) Variation partitioning of species data matrices: estimation and comparison of fractions. Ecology 87:2614–2625
Ponge JF, DubsF Gillet S, Sousa JP, Lavelle P (2006) Decreased biodiversity in soil springtail communities: the importance of dispersal and landuse history in heterogeneous landscapes. Soil Biol Biochem 38:1158–1161
Puech C, Poggi S, Baudry J, Aviron S (2014) Do farming practices affect natural enemies at the landscapescale? Landscape Ecol 30:125–140
Querner P, Bruckner A, Drapela T, Moser D, Zaller JG, Frank T (2013) Landscape and site effects on Collembola diversity and abundance in winter oilseed rape fields in eastern Austria. Agric Ecosyst Environ 164:145–154
R Core Team (2013) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/
Rantalainen M-L, Fritze H, Haimi J, Pennanen T, Setälä H (2005) Colonisation of newly established habitats by soil decomposer organisms: the effect of habitat corridors in relation to colonisation distance and habitat size. Appl Soil Ecol 28:67–77
Ribera I, Dolédec S, Downie IS, Foster GN (2001) Effect of land disturbance and stress on species traits of ground beetle assemblages. Ecology 82:1112–1129
Ricklefs RE (1987) Community diversity: relative roles of local and regional processes. Science 235:167–171
Salmon S, Ponge JF, Gachet S, Deharveng L, Lefebvre N, Delabrosse F (2014) Linking species, traits and habitat characteristics of Collembola at European scale. Soil Biol Biochem 75:73–85
Sarthou J-P, Badoz A, Vaissière B, Chevallier A, Rusch A (2014) Local more than landscape parameters structure natural enemy communities during their overwintering in semi-natural habitats. Agric Ecosyst Environ 194:17–28
Sattler T, Duelli P, Obrist MK, ArlettazR Moretti M (2010) Response of arthropod species richness and functional groups to urban habitat structure and management. Landscape Ecol 25:941–954
Schuldt A, Assmann T, Schaefer M (2013) Scale-dependent diversity patterns affect spider assemblages of two contrasting forest ecosystems. Acta Oecol 49:17–22
Siqueira T, Bin LM, Roque FO, Pepinelli M, Ramos RC, Marques Couceiro SR, Trivinho-Strixino S, Cottenie K (2012) Common and rare species respond to similar niche processes in macroinvertebrate metacommunities. Ecography 35:183–192
Smith TW, Lundholm JT (2010) Variation partitioning as a tool to distinguish between niche and neutral processes. Ecography 33:648–655
Sousa JP, Gama MM, Pinto C, Keating A, Calhôa F, Lemos M, Castro C, Luz T, Leitão P, Dias S (2004) Effects of land-use on Collembola diversity patterns in a Mediterranean landscape. Pedobiologia 48:609–622
Tanner J (2003) Patch shape and orientation influences on seagrass epifauna are mediated by dispersal abilities. Oikos 100:517–524
Thompson R, Townsend C (2006) A truce with neutral theory: local deterministic factors, species traits and dispersal limitation together determine patterns of diversity in stream invertebrates. J Anim Ecol 75:476–484
Turner MG, Gardner RH, O’Neill RV (2001) Pattern and process: landscape ecology in theory and practice. Springer, New York
van de Meutter F, de Meester L, Stoks R (2007) Metacommunity structure of pond macroinvertebrates: effects of dispersal mode and generation time. Ecology 88:1687–1695
Vandewalle M, de Bello F, Berg MP, Bolger T, Dolédec S, Dubs F, Feld CK, Harrington R, Harrison PA, Lavorel S, Martins da Silva P, Moretti M, Niemelä J, Santos P, Sattler T, Sousa JP, Sykes MT, Vanbergen AJ, Woodcock BA (2010) Functional traits as indicators of biodiversity response to land use changes across ecosystems and organisms. Biodivers Conserv 19:2921–2947
Woltz JM, Isaacs R, Landis DA (2012) Landscape structure and habitat management differentially influence insect natural enemies in anagricultural landscape. Agric Ecosyst Environ 152:40–49
Woodcock BA, Redhead J, Vanbergen AJ, Hulmes L, Hulmes S, Peyton J, Nowakowski M, Pywell RF, Heard MS (2010) Impact of habitat type and landscape structure on biomass, species richness and functional diversity of ground beetles. Agric Ecosyst Environ 139:181–186
Wu J (2004) Effects of changing scale on landscape pattern analysis: scaling relations. Landscape Ecol 19:125–138
Wu J, Hobbs R (2002) Key issues and research priorities in landscape ecology: an idiosyncratic synthesis. Landscape Ecol 17:355–365
Wu J, Loucks OL (1995) From balance-of-nature to hierarchical patch dynamics: a paradigm shift in ecology. Q Rev Biol 70:439–466
Yaacobi G, Ziv Y, Rosenzweig ML (2007) Effects of interactive scale-dependent variables on beetle diversity patterns in a semi-arid agricultural landscape. Landscape Ecol 22:687–703
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to António Keating, Filipa Calhôa, Marco Lemos, Catarina Castro and Tiago Luz for their assistance during field work and sorting soil fauna are indebted to Manuela da Gama, Cristina Pinto and Carlos Aguiar for their assistance in the identification of Collembola and Carabidae, and to Eva Ivitis for the extraction of landscape parameters in FRAGSTATS. We are very thankful to two anonymous reviewers who helped us to improve a previous version of the manuscript. This work was supported by the EU BIOASSESS project (Contract No. EVK4—1999-00280) and the RUBICODE Coordination Action Project (Contract No. 036890). P. Martins da Silva was supported by the Portuguese Foundation for Science and Technology (SFRH/BD/37976/2007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martins da Silva, P., Berg, M.P., da Silva, A.A. et al. Soil fauna through the landscape window: factors shaping surface-and soil-dwelling communities across spatial scales in cork-oak mosaics. Landscape Ecol 30, 1511–1526 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0206-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10980-015-0206-4