Abstract
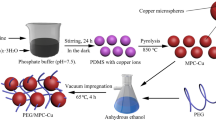
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) as phase change materials has been extensively studied. However, it is difficult to uniformly disperse the PEG in the unmodified matrix material owing to the impregnation problem. It is therefore challenging to overcome the shortcoming of low thermal conductivity. In order to solve this problem, carbon microspheres (CMPs) prepared by the hydrothermal method is firstly proposed as the supporting matrix for preparation of PEG composite. The PEG/CMPs composite is prepared via a mutual diffusion methodology in a high-temperature environment. The test result shows the CMPs nano-material has rich oxygen-based functional groups and can be uniformly dispersed in the PEG phase. As the carbon content increases, the CMPs become gradually connected in the PEG/CMPs composite, which can result in a network with good thermal conductivity. Compared with the thermal conductivity of pure PEG, the thermal conductivity of the composite is increased by 65.07%. Owing to the existence of hydrogen bonds in the composite, the crystallinity fraction of the PEG is in the range of 102–105%. It means that the test result is higher than the theoretical value of latent heat for the composite. Finally, its cycling performance was measured. After 500 thermal cycles, the phase transition temperature of the composite remains almost constant, and the latent heat values of the melting and freezing decrease by 1.05 and 1.45%, respectively. The PEG/CMPs composite would be a promising material for thermal energy storage applications and can be used in various engineering disciplines.










Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- T :
-
Temperature (°C)
- T C :
-
Crystallization temperature (°C)
- T C,P :
-
Peak temperature during crystallization process (°C)
- T M :
-
Melting temperature (°C)
- T M,P :
-
Peak temperature during melting process (°C)
- ∆T :
-
Supercooling between T M,P and T C,P (°C)
- F c :
-
Crystallization fraction (%)
- ∆H :
-
Latent heat (J g−1)
- Β :
-
Mass fraction of PEG in the composite (%)
- K :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- α :
-
Thermal diffusivity (m2 s−1)
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- C p :
-
Specific heat capacity (J kg−1 K−1)
References
Yuan Y, Zhang N, Tao W, Cao X, He Y. Fatty acids as phase change materials: a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2014;29:482–98.
Yuan Y, Gao X, Wu H, Zhang Z, Cao X. Coupled cooling method and application of latent heat thermal energy storage combined with pre-cooling of envelope: method and model development. Energy. 2017;119:817–33.
Zeng J, Cao Z, Yang D, Xu F, Sun L, Zhang X, Zhang L. Effects of MWNTs on phase change enthalpy and thermal conductivity of a solid-liquid organic PCM. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2009;95(2):507–12.
Yuan Y, Zhang H, Zhang N, Sun Q, Cao X. Effect of water content on the phase transition temperature, latent heat and water uptake of PEG polymers acting as endothermal-hydroscopic materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;126:699–708.
Pielichowska K, Pielichowski K. Phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Prog Mater Sci. 2014;65(10):67–123.
Sarı A, Alkan C, Biçer A. Synthesis and thermal properties of polystyrene-graft-PEG copolymers as new kinds of solid–solid phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Mater Chem Phys. 2012;133(1):87–94.
Sharma RK, Ganesan P, Tyagi VV, Mahlia TMI. Accelerated thermal cycle and chemical stability testing of polyethylene glycol (PEG) 6000 for solar thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2016;147:235–9.
Zhang L, Zhu J, Zhou W, Wang J, Wang Y. Thermal and electrical conductivity enhancement of graphite nanoplatelets on form-stable polyethylene glycol/polymethyl methacrylate composite phase change materials. Energy. 2012;39(1):294–302.
Zalba B, Marίn JM, Cabeza LF, Mehling H. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change: materials, heat transfer analysis and applications. Appl Therm Eng. 2003;23(3):251–83.
Wensel J, Wright B, Thomas D, Douglas W, Mannhalter B, Cross W, Hong H, Kellar J, Smith P, Roy W. Enhanced thermal conductivity by aggregation in heat transfer nanofluids containing metal oxide nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes. Appl Phys Lett. 2008;92(2):1–3.
Cui Y, Liu C, Hu S, Yu X. The experimental exploration of carbon nanofiber and carbon nanotube additives on thermal behavior of phase change materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2011;95(4):1208–12.
He L, Li J, Zhou C, Zhu H, Cao X, Tang B. Phase change characteristics of shape-stabilized PEG/SiO2 composites using calcium chloride-assisted and temperature-assisted sol gel methods. Sol Energy. 2014;103:448–55.
Ji P, Sun H, Zhong Y, Feng W. Improvement of the thermal conductivity of a phase change material by the functionalized carbon nanotubes. Chem Eng Sci. 2012;81:140–5.
Qian T, Li J, Ma H, Yang J. Adjustable thermal property of polyethylene glycol/diatomite shape-stabilized composite phase change material. Polym Compos. 2016;37(3):854–60.
Li J, He L, Liu T, Cao X, Zhu H. Preparation and characterization of PEG/SiO2 composites as shape-stabilized phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2013;118(11):48–53.
Karaman S, Karaipekli A, Sarı A, Biçer A. Polyethylene glycol (PEG)/diatomite composite as a novel form-stable phase change material for thermal energy storage. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2011;95(7):1647–53.
Feng L, Zheng J, Yang H, Guo Y, Li W, Li X. Preparation and characterization of polyethylene glycol/active carbon composites as shape-stabilized phase change materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2011;95(2):644–50.
Wang W, Yang X, Fang Y, Ding J. Preparation and performance of form-stable polyethylene glycol/silicon dioxide composites as solid–liquid phase change materials. Appl Energy. 2009;86(2):170–4.
Xie X, Mai Y, Zhou X. Dispersion and alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix: a review. Mater Sci Eng R Rep. 2005;49(4):89–112.
Tang Y, Alva G, Huang X, Su D, Liu L, Fang G. Thermal properties and morphologies of MA–SA eutectics/CNTs as composite PCMs in thermal energy storage. Energy Build. 2016;127:603–10.
Li M, Chen M, Wu Z, Liu J. Carbon nanotube grafted with polyalcohol and its influence on the thermal conductivity of phase change material. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;83(7):325–9.
Salvetat JP, Briggs GAD, Bonard JM, Bacsa RR, Kulik AJ, Stöckli T, Burnham NA, Forró L. Elastic and shear moduli of single-walled carbon nanotube ropes. Phys Rev Lett. 1999;82(5):944–7.
Li H, Jiang M, Li Q, Li D, Chen Z, Hu W, Huang J, Xu X, Dong L, Xie H, Xiong C. Aqueous preparation of polyethylene glycol/sulfonated graphene phase change composite with enhanced thermal performance. Energy Convers Manag. 2013;75:482–7.
Meng X, Zhang H, Sun L, Xu F, Jiao Q, Zhao Z, Zhang J, Zhou H, Sawada Y, Liu Y. Preparation and thermal properties of fatty acids/CNTs composite as shape-stabilized phase change materials. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2012;111(1):377–84.
Cavallaro G, De Lisi R, Lazzara G, Milioto S. Polyethylene glycol/clay nanotubes composites thermal properties and structure. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2013;112:383–9.
Wang J, Xie H, Xin Z, Li Y, Chen L. Enhancing thermal conductivity of palmitic acid based phase change materials with carbon nanotubes as fillers. Sol Energy. 2010;84(2):339–44.
Cavallaro G, Lazzara G, Milioto S. Sustainable nanocomposites based on halloysite nanotubes and pectin/polyethylene glycol blend. Polym Degrad Stab. 2013;98:2529–36.
Zheng M, Liu Y, Xiao Y, Zhu Y, Guan Q, Yuan D, Zhang J. An easy catalyst-free hydrothermal method to prepare monodisperse carbon microspheres on a large scale. J Phys Chem C. 2009;113(19):8455–9.
Wang Q, Li H, Chen L, Huang X. Monodispersed hard carbon spherules with uniform nanopores. Carbon. 2001;39(14):2211–4.
Mi Y, Hu W, Dan Y, Liu Y. Synthesis of carbon micro-spheres by a glucose hydrothermal method. Mater Lett. 2008;62(8):1194–6.
Mehrali M, Latibari ST, Mehrali M, Mahlia TMI. Effect of carbon nanospheres on shape stabilization and thermal behavior of phase change materials for thermal energy storage. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;88:206–13.
Ryu J, Suh Y-W, Suh DJ, Ahn DJ. Hydrothermal preparation of carbon microspheres from mono-saccharides and phenolic compounds. Carbon. 2010;48(7):1990–8.
Wang C, Feng L, Li W, Zheng J, Tian W, Li X. Shape-stabilized phase change materials based on polyethylene glycol/porous carbon composite: the influence of the pore structure of the carbon materials. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2012;105:21–6.
Wang J, Yang M, Lu Y, Jin Z, Tan L, Gao H, Fan S, Dong W, Wang G. Surface functionalization engineering driven crystallization behavior of polyethylene glycol confined in mesoporous silica for shape-stabilized phase change materials. Nano Energy. 2016;19:78–87.
Tang B, Qiu M, Zhang S. Thermal conductivity enhancement of PEG/SiO2 composite PCM by in situ Cu doping. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2012;105:242–8.
Feng L, Song P, Yan S, Wang H, Wang J. The shape-stabilized phase change materials composed of polyethylene glycol and graphitic carbon nitride matrices. Thermochim Acta. 2015;612:19–24.
Qian T, Li J, Ma H, Yang J. The preparation of a green shape-stabilized composite phase change material of polyethylene glycol/SiO2 with enhanced thermal performance based on oil shale ash via temperature-assisted sol–gel method. Sol Energy Mater Sol C. 2015;132:29–39.
Chen W, Yan L, Bangal R. Preparation of graphene by the rapid and mild thermal reduction of graphene oxide induced by microwaves. Carbon. 2010;48:1146–52.
Han D, Yan L, Chen W, Li W. Preparation of chitosan/graphene oxide composite film with enhanced mechanical strength in the wet state. Carbohydr Polym. 2011;83:653–8.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Program of Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51378426) and the Youth Science and Technology Innovation Team of Sichuan Province of Building Environment and Energy Efficiency (No. 2015TD0015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Q., Yuan, Y., Zhang, H. et al. Thermal properties of polyethylene glycol/carbon microsphere composite as a novel phase change material. J Therm Anal Calorim 130, 1741–1749 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6535-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-017-6535-6