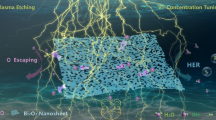
Abstract
Electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution is an exercisable way to achieve large-scale application of hydrogen energy. It is of great significance to develop an effect, stable, and cost-effective electrocatalyst. Here, we applied the two-dimensional (2D) bismuth (Bi) to the electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution, and proposed the strategies to enhance the catalytic performance of the catalyst. Due to more active sites located along the edges of 2D structure, Bi nanosheets revealed a higher electrocatalytic activity (overpotential of −958 mV vs RHE at 10 mA cm−2, Tafel slope of 122 mV/dec) than the bulk counterpart. To further evaluate the electrocatalytic performance of Bi nanosheets, the typical parameters measured in different H+ concentration (C[H+]) are carried out. The improved catalytic activity obtained in 0.5 M H2SO4 is attributed to enhancing the hydrogen adsorption and accelerating the charge transport on the surface of catalyst. Moreover, the durability of Bi nanosheets has been texted, where the current is not evident fluctuation during the 40,000 s electrolysis measurement indicating its excellent stability. The present work expands the application of Bi in the catalysis and provides the simple strategies to improve its hydrogen evolution performance.

Highlights
-
The Bismuth nanosheet are successfully exfoliated by the sonication assisted liquid-phase exfoliation.
-
The exfoliated 2D Bi has the enhanced electrocatalytic activity compared to the bulk counterpart.
-
Bi nanosheets show an excellent durability in the long-term stability test.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mallouk TE (2013) Water electrolysis: divide and conquer. Nat Chem 5:362–363
Kadi MW, Mohamed RM (2019) Synthesis of BaCeO3 nanoneedles and the effect of V, Ag, Au, Pt doping on the visible light hydrogen evolution in the photocatalytic water splitting reaction. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 91:138–145
Turner JA (2004) Sustainable hydrogen production. Science 305:972–974
Kibsgaard J, Chorkendorff I (2019) Considerations for the scaling-up of water splitting catalysts. Nat Energy 4:430
An L, Han X, Li Y, Hou C, Wang H, Zhang Q (2019) ZnS–CdS–TaON nanocomposites with enhanced stability and photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 91:82–91
Zhu J, Hu L, Zhao P, Lee LYS, Wong K-Y (2019) Recent advances in electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution using nanoparticles. Chem Rev 120:851–918
Yan J, Huang Y, Zhang L, Zhou M, Yang P, Chen W, Deng X, Yang H (2020) Preparation of MoS2-Graphene-NiO@Ni foam composite by sol coating for (photo) electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution reaction. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 93:462–470
Yan Y, Xia B, Xu Z, Wang X (2014) Recent development of molybdenum sulfides as advanced electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Catal 4:1693–1705
Di J, Yan C, Handoko AD, Seh ZW, Li H, Liu Z (2018) Ultrathin two-dimensional materials for photo-and electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Mater Today 21:749–770
Li X, Fang Y, Wang J, Wei B, Qi K, Hoh HY, Hao Q, Sun T, Wang Z, Yin Z (2019) High-yield electrochemical production of large-sized and thinly layered NiPS3 flakes for overall water splitting. Small 15:1902427
Zhang P, Xiang H, Tao L, Dong H, Zhou Y, Hu TS, Chen X, Liu S, Wang S, Garaj S (2019) Chemically activated MoS2 for efficient hydrogen production. Nano Energy 57:535–541
Gao Q, Jin Y, Jin Y, Wang X, Ye Z, Hong Z, Zhi M (2018) Synthesis of amorphous MoSx and MoSx/carbon nanotubes composite aerogels as effective hydrogen evolution reaction catalysts. J Sol-Gel Sci Techn 88:227–235
Lloret V, Rivero-Crespo MÁ, Vidal-Moya JA, Wild S, Doménech-Carbó A, Heller BS, Shin S, Steinrück H-P, Maier F, Hauke F (2019) Few layer 2D pnictogens catalyze the alkylation of soft nucleophiles with esters. Nat Commun 10:1–11
Wang X, Bai L, Lu J, Zhang X, Liu D, Yang H, Wang J, Chu PK, Ramakrishna S, Yu XF (2019) Rapid activation of platinum with black phosphorus for efficient hydrogen evolution. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:19060–19066
Li L, Yu Y, Ye GJ, Ge Q, Ou X, Wu H, Feng D, Chen XH, Zhang Y (2014) Black phosphorus field-effect transistors. Nat Nanotechnol 9:372
Hu J, Chen D, Mo Z, Li N, Xu Q, Li H, He J, Xu H, Lu J (2019) Z‐Scheme 2D/2D heterojunction of black phosphorus/monolayer Bi2WO6 nanosheets with enhanced photocatalytic activities. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:2073–2077
Zhang L, Ding LX, Chen GF, Yang X, Wang H (2019) Ammonia synthesis under ambient conditions: selective electroreduction of dinitrogen to ammonia on black phosphorus nanosheets. Angew Chem 131:2638–2642
Bai L, Wang X, Tang S, Kang Y, Wang J, Yu Y, Zhou ZK, Ma C, Zhang X, Jiang J (2018) Black phosphorus/platinum heterostructure: a highly efficient photocatalyst for solar‐driven chemical reactions. Adv Mater 30:1803641
Tian B, Tian B, Smith B, Scott M, Hua R, Lei Q, Tian Y (2018) Supported black phosphorus nanosheets as hydrogen-evolving photocatalyst achieving 5.4% energy conversion efficiency at 353 K. Nat Commun 9:1–11
Abate Y, Akinwande D, Gamage S, Wang H, Snure M, Poudel N, Cronin SB (2018) Recent progress on stability and passivation of black phosphorus. Adv Mater 30:1704749
Kistanov AA, Khadiullin SK, Zhou K, Dmitriev SV, Korznikova EA (2019) Environmental stability of bismuthene: oxidation mechanism and structural stability of 2D pnictogens. J Mater Chem C 7:9195–9202
Mayorga‐Martinez CC, Gusmão R, Sofer Z, Pumera M (2019) Pnictogen‐based enzymatic phenol biosensors: phosphorene, arsenene, antimonene, and bismuthene. Angew Chem Int Ed 58:134–138
Nagao T, Sadowski J, Saito M, Yaginuma S, Fujikawa Y, Kogure T, Ohno T, Hasegawa Y, Hasegawa S, Sakurai T (2004) Nanofilm allotrope and phase transformation of ultrathin Bi film on Si (111)−7×7. Phys Rev Lett 93:105501
Medina-Ramos J, DiMeglio JL, Rosenthal J (2014) Efficient reduction of CO2 to CO with high current density using in situ or ex situ prepared Bi-based materials. J Am Chem Soc 136:8361–8367
Liu X, Zhang S, Guo S, Cai B, Yang SA, Shan F, Pumera M, Zeng H (2020) Advances of 2D bismuth in energy sciences. Chem Soc Rev 49:263–285
Zhang Y, Zuo L, Huang Y, Zhang L, Lai F, Fan W, Liu T (2015) In-situ growth of few-layered MoS2 nanosheets on highly porous carbon aerogel as advanced electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction. ACS Sustain Eng 3:3140–3148
Walker ES, Na SR, Jung D, March SD, Kim J-S, Trivedi T, Li W, Tao L, Lee ML, Liechti KM (2016) Large-area dry transfer of single-crystalline epitaxial bismuth thin films. Nano Lett 16:6931–6938
Lukowski MA, Daniel AS, Meng F, Forticaux A, Li L, Jin S (2013) Enhanced hydrogen evolution catalysis from chemically exfoliated metallic MoS2 nanosheets. J Am Chem Soc 135:10274–10277
Shao G, Xue XX, Wu B, Lin YC, Ouzounian M, Hu TS, Xu Y, Liu X, Li S, Suenaga K (2020) Template‐assisted synthesis of metallic 1T′‐Sn0.3W0.7S2 nanosheets for hydrogen evolution reaction. Adv Funct Mater 30:1906069
Aktürk E, Aktürk OÜ, Ciraci S (2016) Single and bilayer bismuthene: stability at high temperature and mechanical and electronic properties. Phys Rev B 94:014115
Su P, Xu W, Qiu Y, Zhang T, Li X, Zhang H (2018) Ultrathin bismuth nanosheets as highly efficient electrocatalyst for CO2 reduction. ChemSusChem 11:848–853
Yang B, Burch R, Hardacre C, Headdock G, Hu P (2014) Understanding the optimal adsorption energies for catalyst screening in heterogeneous catalysis. ACS Catal 4:182–186
Sabatier P (1911) Hydrogénations et déshydrogénations par catalyse. Ber Dtsch Chem Ges 44:1984–2001
Yu H, Huang H, Xu K, Hao W, Guo Y, Wang S, Shen X, Pan S, Zhang Y (2017) Liquid-phase exfoliation into monolayered BiOBr nanosheets for photocatalytic oxidation and reduction. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5:10499–10508
Tang C, Sun A, Xu Y, Wu Z, Wang D (2015) High specific surface area Mo2C nanoparticles as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J Power Sources 296:18–22
Huang Y, Zhu C, Zhang S, Hu X, Zhang K, Zhou W, Guo S, Xu F, Zeng H (2019) Ultrathin bismuth nanosheets for stable Na-ion batteries: clarification of structure and phase transition by in situ observation. Nano Lett 19:1118–1123
Gusmão R, Sofer Z, Bouša D, Pumera M (2017) Pnictogen (As, Sb, Bi) nanosheets for electrochemical applications are produced by shear exfoliation using kitchen blenders. Angew Chem 129:14609–14614
Yin L, Hai X, Chang K, Ichihara F, Ye J (2018) Synergetic exfoliation and lateral size engineering of MoS2 for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen generation. Small 14:1704153
Acknowledgements
The research was partially supported by the Provincial Natural Science Foundation of Hunan (No. 2019JJ50612), Open Fund based on innovation platform of Hunan colleges and universities (No. 18K032), and Scientific Research Fund of Hunan Provincial Education Department (No. 18A059), as well as the Program for Changjiang Scholars and Innovative Research Team in University (Grant No. IRT_17R91). The authors thank Zongyu Huang, Yang Zhou, and Gengcheng Liao for proof reading the paper. The authors thank Huanting Liu, Hui Qiao, and Xiang Qi for all helpful advices. The authors also thank Yundan Liu for the technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Duan, C., Liu, H., Huang, Z. et al. Two-dimensional Bi nanosheets as an enhanced electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 99, 132–139 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05562-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-021-05562-6