Abstract
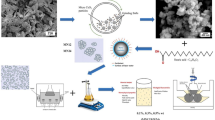
The oleogel acts as a middle phase to improve the dispersion stability of magnesium silicate hydroxide (MSH) nanoparticles in PAO base oils and simultaneously enhance the tribological properties of oil samples. The oleogel is comprised of Sorbitan monostearate (Span60), MSH nanoparticles, and PAO oil which is used as the gelator, anti-wear phase, and the base stock, respectively. The prepared oleogel and PAO oil are mixed by stirring to achieve the dispersion of MSH nanoparticles in oil. Centrifugal experiments showed that dispersion stability of MSH nanoparticles can be greatly improved through the oleogel middle phase. Tribological tests also show that the oleogel can further enhance the anti-wear and friction reduction performance of the lubricating oil.

Using the oleogel as a middle phase, the dispersion stability and tribological properties of magnesium silicate hydroxide (MSH) nanoparticles in PAO base oils was greatly improved.
Highlights
-
The dispersity stability of MSH nanoparticles is improved through the oleogel form.
-
The MSH nanoparticles and Span60 oleogel both improve the anti-wear effect of the base oil.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadauskas SJ, Kreivaitis R, Bikulčius G, Grigucevičiene A, Padgurskas J (2016) Tribological effects of Cu, Fe and Zn nano-particles, suspended in mineral and bio-based oils. Lubr Sci 28:157–76. https://doi.org/10.1002/ls.1307
Charoo MS, Wani MF (2017) Tribological properties of h-BN nanoparticles as lubricant additive on cylinder liner and piston ring. Lubr Sci 29:241–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/ls.1366
Jiao D, Zheng S, Wang Y, Guan R, Cao B (2011) The tribology properties of alumina/silica composite nanoparticles as lubricant additives. Appl Surf Sci 257:5720–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.01.084
Gao K, Chang Q, Wang B, Zhou N, Qing T (2018) The tribological performances of modified magnesium silicate hydroxide as lubricant additive. Tribol Int 121:64–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2018.01.022
Gao K, Chang Q, Wang B, Zhou N, Qing T (2018) Synthetic magnesium silicate hydroxide nanoparticles coated with carbonaceous shell in subcritical water condition. Appl Surf Sci 450:312–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.04.139
Wang B, Chang QY, Gao K, Fang HR, Qing T, Zhou NN (2018) The synthesis of magnesium silicate hydroxide with different morphologies and the comparison of their tribological properties. Tribol Int 119:672–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.11.020
Chang Q, Rudenko P, Miller DJ, Wen J, Berman D, Zhang Y et al. (2017) Operando formation of an ultra-low friction boundary film from synthetic magnesium silicon hydroxide additive. Tribol Int 110:35–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2017.02.003
Chen Q, Zheng S, Yang S, Li W, Song X, Cao B (2012) Enhanced tribology properties of ZnO/Al2O3 composite nanoparticles as liquid lubricating additives. J Sol–Gel Sci Technol 61:501–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-011-2651-0
Guibert C, Dupuis V, Fresnais J, Peyre V (2015) Controlling nanoparticles dispersion in ionic liquids by tuning the pH. J Colloid Interface Sci 454:105–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.04.059
Horst AM, Ji Z, Holden PA. Nanoparticle dispersion in environmentally relevant culture media: a TiO2 case study and considerations for a general approach. J Nanopart Res 2012;14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-012-1014-2.
Wu L, Zhang Y, Yang G, Zhang S, Yu L, Zhang P (2016) Tribological properties of oleic acid-modified zinc oxide nanoparticles as the lubricant additive in poly-alpha olefin and diisooctyl sebacate base oils. RSC Adv 6:69836–44. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA10042B
Ali MKA, Xianjun H, Mai L, Qingping C, Turkson RF, Bicheng C (2016) Improving the tribological characteristics of piston ring assembly in automotive engines using Al2O3 and TiO2 nanomaterials as nano-lubricant additives. Tribol Int 103:540–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.triboint.2016.08.011
Lee CS, Lee JS, Oh ST (2003) Dispersion control of Fe2O3 nanoparticles using a mixed type of mechanical and ultrasonic milling. Mater Lett 57:2643–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0167-577X(02)01343-5
Bittmann B, Haupert F, Schlarb AK (2009) Ultrasonic dispersion of inorganic nanoparticles in epoxy resin. Ultrason Sonochem 16:622–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2009.01.006
Stuyven B, Chen Q, Van de Moortel W, Lipkens H, Caerts B, Aerts A et al. Magnetic field assisted nanoparticle dispersion. Chem Commun 2008:47–9. https://doi.org/10.1039/B816171B.
Uvanesh K, Sagiri SS, Senthilguru K, Pramanik K, Banerjee I, Anis A et al. (2016) Effect of span 60 on the microstructure, crystallization kinetics, and mechanical properties of stearic acid oleogels: an in-depth analysis. J Food Sci 81:E380–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/1750-3841.13170
Dassanayake LSK, Kodali DR, Ueno S (2011) Formation of oleogels based on edible lipid materials. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 16:432–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2011.05.005
Savrik SA, Balköse D, Lku S (2011) Synthesis of zinc borate by inverse emulsion technique for lubrication. J Therm Anal Calorim 104:605–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-010-1159-0
Baek S, Min J, Lee JW (2016) Equilibria of cyclopentane hydrates with varying HLB numbers of sorbitan monoesters in water-in-oil emulsions. Fluid Phase Equilib 413:41–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.FLUID.2015.10.018
Murdan S, Gregoriadis G, Florence AT (1999) Novel sorbitan monostearate organogels. J Pharm Sci 88:608–14. https://doi.org/10.1021/JS980342R
Murdan S, Gregoriadis G, Florence AT (1999) Inverse toroidal vesicles: precursors of tubules in sorbitan monostearate organogels. Int J Pharm 183:47–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0378-5173(99)00042-3
Dhal S, Mohanty A, Yadav I, Uvanesh K, Kulanthaivel S, Banerjee I et al. (2017) Magnetic nanoparticle incorporated oleogel as iontophoretic drug delivery system. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 157:118–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.05.061
Qiu Y, Park K (2001) Environment-sensitive hydrogels for drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 53:321–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0169-409X(01)00203-4
Hashmi SAR, Dwivedi UK, Chand N (2009) Concentration profile of glass fiber bundles in epoxy-based gradient composites during centrifugation. J Appl Polym Sci 113:3840–6. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.30399
Hashmi SAR, Dwivedi UK (2007) Estimation of concentration of particles in polymerizing fluid during centrifugal casting of functionally graded polymer composites. J Polym Res 14:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-006-9083-5
Wen S, Huang P (2011) Principles of Tribology. John Wiley & Sons (Asia) Pte Ltd, Singapore, https://doi.org/10.1002/9781118062913
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (Grant No. 2017YJS160), the National Defense Pre-Research Foundation of China (Grant No. 30103020301) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51075026).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, K., Chang, Q. & Wang, B. The dispersion and tribological performances of magnesium silicate hydroxide nanoparticles enhanced by Span60 oleogel. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 94, 165–173 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05167-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05167-0