Abstract
Porous composites of water-soluble polymers (polyvinylpyrrolidone, polyethylene oxide, and polyvinyl alcohol) with cellulose nanocrystals (CNC) have been made by mixing the CNC sol with the polymer solution followed by freeze-drying. The composites morphology has been studied by scanning electron microscopy. The porous structure of the composites has been analyzed by the method of low-temperature nitrogen adsorption. Dispersibility of the polymer/CNC aerogels in water has been evaluated. It has been shown that the formation of a CNC hydrogel with a water-soluble polymer is a necessary condition for the formation of the porous structure of the composites.

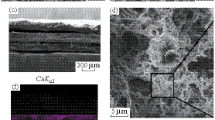
An SEM image of the vertical cross section of a PEO/CNC composite aerogel. The porous structure of the composite is clearly visible. Freeze-drying of PEO/CNC hydrogel produces a porous foam with high alignment of the rod-like CNC nanoparticles in the freezing direction. The arrow shows the direction from the bottom to the top of the sample.
Highlights
-
Porous composites of CNC with water-soluble polymers (PVA, PEO, and PVP) have been made.
-
The composites morphology and porous structure have been studied.
-
Adding CNC increases the porosity and specific surface area of the composites.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
De France KJ, Hoare T, Cranston ED (2017) Review of Hydrogels and Aerogels Containing Nanocellulose. Chem Mater 29:4609–4631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b00531
Silverstein MS, Cameron NR, Hillmyer MA (2011) Porous Polymers. John Wiley & Sons, Inc, Hoboken
Wu D, Xu F, Sun B, Fu R, He H, Matyjaszewski K (2012) Design and Preparation of Porous Polymers. Chem Rev 112:3959–4015. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr200440z
Xiong R, Grant AM, Ma R, Zhang S, Tsukruk VV (2018) Naturally-derived biopolymer nanocomposites: interfacial design, properties and emerging applications. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 125:1–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2018.01.002
Halake K, Birajdar M, Kim BS, Bae H, Lee CC, Kim YJ, Kim S, Kim HJ, Ahn S, An SY, Lee J (2014) Recent application developments of water-soluble synthetic polymers J Ind Eng Chem 20:3913–3918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2014.01.006
Siró I, Plackett D (2010) Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: a review. Cellulose 17:459–494. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-010-9405-y
Peresin MS, Habibi Y, Zoppe JO, Pawlak JJ, Rojas OJ (2010) Nanofiber composites of polyvinyl alcohol and cellulose nanocrystals: Manufacture andcharacterization. Biomacromolecules 11:674–681. https://doi.org/10.1021/bm901254n
Virtanen S, Vartianen J, Setälä H, Tammelin T, Vuoti S (2014) Modified nanofibrillated cellulose–polyvinyl alcohol films with improved mechanical performance. RSC Adv 4:11343–11350. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3RA46287K
Moon RJ, Martini A, Nairn J, Simonsen J, Youngblood J (2011) Cellulose nanomaterials review: structure, properties and nanocomposites. Chem Soc Rev 40:3941–3994. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00108b
Habibi Y (2014) Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses. Chem Soc Rev 43:1519–1542. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60204d
Habibi Y, Lucia LA, Rojas OJ (2010) Cellulose nanocrystals: chemistry, self-assembly, and applications. Chem Rev 110:3479–3500. https://doi.org/10.1021/cr900339w
Salas C, Nypelö T, Rodriguez-Abreu C, Carrillo C, Rojas OJ (2014) Nanocellulose properties and applications in colloids and interfaces. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 19:383–396. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cocis.2014.10.003
Voronova MI, Surov OV, Guseinov SS, Barannikov VP, Zakharov AG (2015) Thermal stability of polyvinyl alcohol/nanocrystalline cellulose composites. Carbohydr Polym 130:440–447. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.05.032
Voronova MI, Surov OV, Zakharov AG (2017) In: Thompson H (ed) Polymer Nanocomposites: Synthesis, Applications and Research. Nova Science Publishers, Inc., New York
Surov OV, Voronova MI, Afineevskii AV, Zakharov AG (2018) Polyethylene oxide films reinforced by cellulose nanocrystals: microstructure-properties relationship. Carbohydr Polym 181:489–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.10.075
Voronova MI, Rubleva NV, Kochkina NE, Afineevskii AV, Zakharov AG, Surov OV (2018) Preparation and characterization of polyvinylpyrrolidone/cellulose nanocrystals composites. Nanomaterials 8:1011. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8121011
Chakrabarty A, Teramoto Y(2018) Recent Advances in Nanocellulose Composites with polymers: a guide for choosing partners and how to incorporate them. Polymers 10:517. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050517
Roberts AD, Zhang H (2013) Poorly water-soluble drug nanoparticles via solvent evaporation in water-soluble porous polymers. Int J Pharm 447:241–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpharm.2013.03.001
Ioelovich M (2017) In: Kargarzadeh H, Ahmad I, Thomas S, Dufresne A (eds) Handbook of nanocellulose and cellulose nanocomposites, 1st edn. Wiley, New York
Adamson AW (1997) Physical chemistry of surfaces. 6th edn. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Gregg SJ, Sing KSW (1982) Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, 2nd edn. Academic Press, London
Munier P, Gordeyeva K, Bergström L, Fall AB (2016) Directional freezing of nanocellulose dispersions aligns the rodlike particles and produces low-density and robust particle networks. Biomacromolecules 17:1875–1881. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.6b00304
Lavoine N, Bergström L (2017) Nanocellulose-based foams and aerogels: processing, properties, and applications. J Mater Chem A 5:16105–16117. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ta02807e
Pääkkö M, Vapaavuori J, Silvennoinen R, Kosonen H, Ankerfors M, Lindström T, Berglund LA, Ikkala O (2008) Long and entangled native cellulose I nanofibers allow flexible aerogels and hierarchically porous templates for functionalities. Soft Matter 4:2492–2499. https://doi.org/10.1039/B810371B
Lu Y, Armentrout AA, Li J, Tekinalp HL, Nanda J, Ozcan S (2015) A cellulose nanocrystal-based composite electrolyte with superior dimensional stability for alkaline fuel cell membranes. J Mater Chem A 3:13350–13356. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5TA02304A
Niinivaara E, Faustini M, Tammelin T, Kontturi E (2015) Water vapor uptake of ultrathin films of biologically derived nanocrystals: quantitative assessment with quartz crystal microbalance and spectroscopic ellipsometry. Langmuir 31:12170–12176. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.5b01763
Mathew AP, Gong G, Bjorngrim N, Wixe D, Oksman K (2011) Moisture adsorption behavior and its impact on the mechanical properties of cellulose whiskers-based polyvinylacetate nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 51:2136–2142. https://doi.org/10.1002/pen.22063
Hakalahti M, Faustini M, Boissière C, Kontturi E, Tammelin T (2017) Interfacial mechanisms of water vapor sorption into cellulose nanofibril films as revealed by quantitative models. Biomacromolecules 18:2951–2958. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biomac.7b00890
Kontturi E, Tammelin T, Oesterberg M (2006) Cellulose—model films and the fundamental approach. Chem Soc Rev 35:1287–1304. https://doi.org/10.1039/B601872F
Kontturi KS, Kontturi E, Laine J (2013) Specific water uptake of thin films from nanofibrillar cellulose. J Mater Chem A 1:13655–13663. https://doi.org/10.1039/C3TA12998E
Hakalahti M, Mautner A, Johansson L-S, Hänninen T, Setälä H, Kontturi E, Bismarck A, Tammelin T (2016) Direct interfacial modification of nanocellulose films for thermoresponsive membrane templates. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:2923–2927. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b12300
Kontturi E, Laaksonen P, Linder MB, Gröschel AH, Rojas OJ, Ikkala O (2018) Advanced materials through assembly of nanocelluloses. Adv Mater 30:1703779. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201703779
Boluk Y, Danumah C (2014) Analysis of cellulose nanocrystal rod lengths by dynamic light scattering and electron microscopy. J Nanopart Res 16:2174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-2174-4
Fraschini C, Chauve G, Le Berre J-F, Ellis S, Méthot M, O’Connor B, Bouchard J (2014) Critical discussion of light scattering and microscopy techniques for CNC particle sizing. Nord Pulp Pap Res J 29:31–40
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Russian Science Foundation (grant number 17-13-01240). The authors thank The Center for Collective use of Scientific Equipment of Ivanovo State University of Chemistry and Technology and The Upper Volga Region Center of Physicochemical Research (Ivanovo, Russia).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zakharov, A.G., Voronova, M.I., Bazanov, A.V. et al. Porous composites of water-soluble polymers with cellulose nanocrystals. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 92, 484–495 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05007-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-019-05007-1