Abstract
Different aspects related to the sol-gel preparation and structural investigation of silico-phosphate glasses (SiO2–P2O5 system) doped with Fe ions are reported. During the preparation process, tetraethoxysilane was used as a precursor for SiO2 and phosphoric acid (H3PO4-HP) for P2O5. Ferric chloride was used as precursor for Fe ions, water as reagent for hydrolysis reaction and ethylic alcohol as solvent. The pH of the sols was modified by adding hydrochloric acid and ammonia. It was observed that a slight increase of the solution temperature (up to 40 °C) allows a drastic decrease of the gelation time (from days to hours). The structure of the obtained powders dried in air at room temperature and at 100 °C for 10 h and subsequently thermally treated at different temperatures was investigated by Fourier transformed infrared (FTIR) and Raman spectroscopy. Vibration modes specific to Si–O–Et, Si–OH, P–O–P, P–O–Si, hydrogen bonds and H2O, as well as combined modes have been observed. The local structure and electron configurations of the doping Fe ions have been investigated by 57Fe Mössbauer spectroscopy.
Graphical Abstract
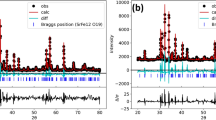
Mössbauer spectra of the sample with molar composition 0.85SiO2 0.08P2O5 0.07Fe2O3 (Fe15) annealed at 300 °C collected at 5.7/6 K, 30 K, 60 K and at room temperature
The magnetic pattern is assigned (by its hyperfine parameters) to α-Fe2O3 (36 % from total Fe, the rest being dispersed in the matrix as paramagnetic Fe with octahedral oxygen configuration).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang C, Nogami M, Abe Y (1999) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 14:273–279
Zaharescu M, Vasilescu A, Badescu V, Radu M (1997) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 8:59–63
Anastasescu M, Gartner M, Ghita A, Predoana L, Todan L, Zaharescu M, Vasiliu C, Grigorescu C, Negrila C (2006) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 40:325–333
Elisa M, Sava BA, Volceanov A, Monteiro RCC, Alves E, Franco N, Costa Oliveira FA, Fernandes H, Ferro MC (2010) J Non Cryst Solids 356 (9–10):495–501
Sava BA, Elisa M, Vasiliu IC, Nastase F, Simon S (2012) J Non Cryst Solids 358:2877-2885
Zaharescu M, Crisan M, Jitianu A, Crisan D, Meghea A, Rau I (2000) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 19:631–635
Ponce-Castaneda S, Martinez E, Martinez JR, Ruiz F, Palomares-Sanchez S, Dominguez O (2002) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 25:29–36
Jitianu A, Raileanu M, Crisan M, Predoi D, Jitianu M, Stanciu L, Zaharescu M (2006) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 40:317–323
Niznansky D, Viart N, Rehspringer JL (1997) J Sol Gel Sci Technol 8:615–618
Tung SP, Hwang BJ (2004) J Membr Sci 241:315–323
Kim YS, Tressler RE (1994) J Mater Sci 29:2531–2535
Guomei W, Jiaheng L (1991) Submolecular glass chemistry and physics. Proc SPIE 1590:229–236
Stefanofanovskii SV, Ivanov IA (1994) Glass Phys Chem 20(2):103
Battisha I, El Nahrawy A (2012) New J Glass Ceram 2:17–22
Todan L, Anghel EM, Osiceanu P, Turcu RVF, Atkinson I, Simon S, Zaharescu M (2015) J Mol Struct 1086:161–171
Sen P, Thorpe MF (1979) Phys Rev B 15:4030
Galeener FL (1979) Phys Rev B 15:4292
Duran A, Serna C, Fornes V, Fernandez-Navarro JM (1984) J Non Cryst Solids 63:45
Chakraborty S, Arora AK (2012) Vib Spectrosc 61:99–104
Elisa M, Iordanescu R, Sava BA, Aldica G, Kuncser V, Valsangiacom C, Schinteie G, Nastase F, Nastase C, Bercu V, Volceanov A, Perez S (2011) J Mater Sci 46:1563–1570
Neel L (1949) Ann Geophys 5:99
Brown WF (1963) Phys Rev 130:1677
Bodker F, Hansen MF, Koch CB, Lefman K and Morup S (2000) Phys Rev B 61:6826
Kuncser V, Schinteie G, Sahoo B, Keune W, Bica D, Vekas L, Filoti G (2007) J Phys Condens Matter 19:016205–016220
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Executive Unity for Financing of Higher Education, Research and Innovation, Romania, for the financial support in the frame of PNII 186/2012 Project from Partnership Program, MNT-ERA.NET SENSGLASS 7-031/2011 project and M-ERA.NET MAGPHOGLAS 7-081/2013. Authors from INCDFM acknowledge the financial support through the Core Program 2016–2017, project 3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sava, B.A.C., Elisa, M., Boroica, L. et al. Sol-gel preparation and structural investigations of silico-phosphate glasses doped with Fe ions. J Sol-Gel Sci Technol 81, 294–302 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4192-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10971-016-4192-z