Abstract
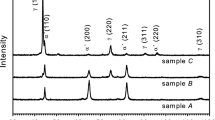
The defects due to cold-rolling deformation in the advanced reduced-activation alloy (ARAA) have been analyzed using positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS). Four different cold-rolled conditions up to 35% reduction from 0% have been used in this study. The mean lifetime of the positron at the cold-worked ARAA samples increased over that of the as-normalized sample, which was comparative to the increase in the amount of grain boundaries in the electron backscatter diffraction images. PALS could determine microstructural change in defects of the cold-rolled ARAA.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kumar R, Singh P, Gupta SK, Gupta R, Jaiswal MK, Prasad M, Roychowdhury A, Chauhan RP, Das D (2017) Radiation induced nano-scale free volume modifications in amorphous polymeric material: a study using positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 314(3):1659–1666
Ono R, Togimitsu T, Sato W (2015) Evaluation of vacancy-type defects in ZnO by the positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 303(2):1223–1226
Tuomisto F, Makkonen I (2013) Defect identification in semiconductors with positron annihilation: experiment and theory. Rev Mod Phys 85(4):1583
Dlubek G, Saarinen K (1996) A positron lifetime and Doppler-broadening study of positron states and free volume in polyethylene. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 210(2):495–503
Ohkubo H, Tang Z, Nagai Y, Hasegawa M, Tawara T, Kiritani M (2003) Positron annihilation study of vacancy-type defects in high-speed deformed Ni, Cu and Fe. Mater Sci Eng A 350(1–2):95–101
Rubel M (2019) Fusion neutrons: tritium breeding and impact on wall materials and components of diagnostic systems. J Fusion Energy 38(3):315–329
Philipps V, Wienhold P, Kirschner A, Rubel M (2002) Erosion and redeposition of wall material in controlled fusion devices. Vacuum 67(3–4):399–408
Fernandez P, Lancha AM, Lapena J, Serrano M, Hernández-Mayoral M (2002) Metallurgical properties of reduced activation martensitic steel Eurofer’97 in the as-received condition and after thermal ageing. J Nucl Mater 307:495–499
Bartošová I, Čížek J, Lukáč F, Slugeň V (2014) Vickers hardness and positron annihilation study of Eurofer97 and ODS Eurofer. Acta Phys Pol A 125(3):702–705
Babu SH, Amarendra G, Rajaraman R, Sundar CS (2013) Microstructural characterization of ferritic/martensitic steels by positron annihilation spectroscopy. J Phys Conf Ser 443(1):012010
Kwon J, Toyama T, Kim YM, Kim W, Hong JH (2009) Effects of radiation-induced defects on microstructural evolution of Fe–Cr model alloys. J Nucl Mater 386:165–168
Lambrecht M, Malerba L (2011) Positron annihilation spectroscopy on binary Fe–Cr alloys and ferritic/martensitic steels after neutron irradiation. Acta Mater 59(17):6547–6555
Huang SS, Sato K, Xu Q, Yoshiie T, Tsuchida H, Itoh A (2014) Positron annihilation and TEM studies on ion irradiated Fe and Fe–Cr model alloys of ferritic/martensitic steel. J Nucl Mater 455(1–3):122–125
Sato K, Ikemura K, Krsjak V, Vieh C, Brun R, Xu Q, Yoshiie T, Dai Y (2016) Defect structures of F82H irradiated at SINQ using positron annihilation spectroscopy. J Nucl Mater 468:281–284
Huang SS, Yoshiie T, Xu Q, Sato K, Troev TD (2013) Positron annihilation studies of electron-irradiated F82H model alloys. J Nucl Mater 440(1–3):617–621
Chun YB, Kang SH, Lee DW, Cho S, Jeong YH, Żywczak A, Rhee CK (2016) Development of Zr-containing advanced reduced-activation alloy (ARAA) as structural material for fusion reactors. Fusion Eng Des 109:629–633
Babu SH, Rajaraman R, Amarendra G, Govindaraj R, Lalla NP, Dasgupta A, Bhalerao G, Sundar CS (2012) Dislocation driven chromium precipitation in Fe–9Cr binary alloy: a positron lifetime study. Philos Mag 92(23):2848–2859
Ragunanthan V, Babu SH, Chirayath VA, Rajaraman R, Amarendra G, Saroja S, Sundar CS, Alamo A, Raj B (2009) Positron annihilation studies on 9Cr reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steels. Phys Status Solidi C 6(11):2307–2309
Lian X, Cao X, Zhao Y, Jin S, Luo J, Zhu T, Gong Y, Wang B, Yu R (2018) Evolution of Thermally-Induced Microstructural Defects in the Fe–9Cr Alloy. Phys Status Solidi A 215(1):1700349
Bertolaccini M, Zappa L (1967) Source-supporting foil effect on the shape of positron time annihilation spectra. Il Nuovo Cimento B 52(2):487–494
Kirkegaard P, Olsen JV, Eldrup MM (2017) PALSfit3: a software package for analyzing positron lifetime spectra. Technical University of Denmark, Kongens Lyngby
Čížek J (2018) Characterization of lattice defects in metallic materials by positron annihilation spectroscopy: a review. J Mater Sci 34(4):577–598
Robles JC, Ogando E, Plazaola F (2007) Positron lifetime calculation for the elements of the periodic table. J Phys Condens Matter 19(17):176222
Mohamed HF, Kwon J, Kim YM, Kim W (2007) Vacancy-type defects in cold-worked iron studied using positron annihilation techniques. Nucl Instrum Methods Phys Res B 258(2):429–434
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Radiation Technology R&D program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (RF-2017M2A2A6A05018529) and the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (1711078081).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, Y.S., Lee, J., Chun, YB. et al. Positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy of advanced reduced-activation alloy (ARAA) in cold‐worked conditions. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 330, 513–519 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07758-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-021-07758-0