Abstract
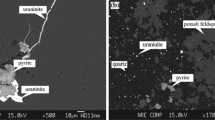
In this study the bioleaching of a low-grade uranium ore containing 480 ppm uranium has been reported. The studies involved extraction of uranium using Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans derived from the uranium mine samples. The maximum specific growth rate (µ max) and doubling time (t d) were obtained 0.08 h−1 and 8.66 h, respectively. Parameters such as Fe2+ concentration, particle size, temperature and pH were optimized. The effect of pulp density (PD) was also studied. Maximum uranium bio-dissolution of 100 ± 5 % was achieved under the conditions of pH 2.0, 5 % PD and 35 °C in 48 h with the particles of d 80 = 100 μm. The optimum concentration of supplementary Fe2+ was dependent to the PD. This value was 0 and 10 g of FeSO4·7H2O/l at the PD of 5 and 15 %, respectively. The effects of time, pH and PD on the bioleaching process were studied using central composite design. New rate equation was improved for the uranium leaching rate. The rate of leaching is controlled with the concentrations of ferric and ferrous ions in solution. This study shows that uranium bioleaching may be an important process for the Saghand U mine at Yazd (Iran).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mishra A, Pradhan N, Kar RN, Sukla LB, Mishra BK (2009) Microbial recovery of uranium using native fungal strains. Hydrometallurgy 95(1–2):175–177
Dwivedy KK, Mathur AK (1995) Bioleaching—our experience. Hydrometallurgy 38:99–109
Chien DCH, Douglas PL, Herman DH, Marchbank A (1990) Modelling a uranium ore bioleaching process. Can J Chem Eng 68:427–434
Hefnawy MA, El-Said M, Hussein M, Amin A (2002) Fungal leaching of uranium from its geological ores in Alloga area, west central Sinai, Egypt. Online J Biol Sci 2(5):346–350
Mathur AK, Viswamohan K, Mohanty KB, Murthy VK, Seshadrinath ST (2000) Technical note: uranium extraction using biogenic ferric sulfate (a case study on quartz chlorite ore from Jaduguda, Singhbhum thrust belt (STB), Bihar, India). Miner Eng 13(5):575–579
Abhilash, Pandey BD (2013) Microbially assisted leaching of uranium—a review. Miner Process Extr Metall Rev 34:81–113
Abhilash, Singh S, Mehta KD, Kumar V, Pandey BD, Pandey VM (2009) Dissolution of uranium from silicate–apatite ore by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Hydrometallurgy 95(2):70–75
Lee JU, Kim SM, Kim KW, Kim IS (2005) Microbial removal of uranium in uranium-bearing black shale. Chemosphere 59:147–154
Bhatti TM, Vuorinen A, Lehtinen M, Tuovinen OH (1998) Dissolution of uraninite in acid solutions. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 73:259–263
Garcia Junior O (1993) Bacterial leaching of uranium ore from Figueira-PR, Brazil, at laboratory and pilot scale. FEMS Microbiol Rev 11:237–242
Guay R, Silver M (1977) Ferrous iron oxidation and uranium extraction by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. Biotechnol Bioeng XIX:727–740
Abhilash, Pandey BD, Ray L (2012) Bioleaching of apatite rich low grade Indian uranium ore. Can Metall Q 51(4):390–402
Choi MS, Cho KS, Kim DS, Ryu HW (2005) Bioleaching of uranium from low grade black schists by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:377–380
Munoz JA, Blazquez ML, Ballester A, Gonzalez F (1995) A study of the bioleaching of a Spanish uranium ore, Part III: column experiments. Hydrometallurgy 38:79–97
Abhilash, Pandey BD (2013) Microbial processing of apatite rich low grade Indian uranium ore in bioreactor. Bioresour Technol 128:619–623
Abhilash, Pandey BD (2013) Bioreactor leaching of uranium from a low grade Indian silicate ore. Biochem Eng J 71:111–117
Donati ER, Sand W (eds) (2007) Microbial processing of metal sulfides. Springer, Dordrecht
Lazic ZR (2004) Design of experiments in chemical engineering. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Sugio T, Wakabayashi M, Kanao T, Takeuchi F (2008) Isolation and characterization of Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans strain D3-2 active in copper bioleaching from a copper mine in Chile. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 72(4):998–1004
Atlas RM (2005) Media for environmental microbiology, 2nd edn. Taylor and Francis, Boca Raton
Herrera L, Ruiz P, Aguillon JC, Fehrmann A (1989) A new spectrophotometric method for the determination of ferrous iron in the presence of ferric iron. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 44:171–181
Karamanev DG, Nikolov LN, Mamatarkova V (2002) Rapid simultaneous quantitative determination of ferric and ferrous ions in drainage waters and similar solutions. Miner Eng 15(5):341–346
Katoh S, Yoshida F (2009) Biochemical engineering. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim
Rawlings DE, Johnson BD (eds) (2007) Biomining. Springer, Berlin
Andrews GF, Darroch M, Hansson T (1988) Bacterial removal of pyrite from concentrated coal slurries. Biotechnol Bioeng 32:813–820
Ryu HW, Cho KS, Chang YK, Kim SD, Mori T (1995) Refinement of low-grade clay by microbial removal of sulfur and iron compounds using Thiobacillus ferrooxidans. J Ferment Bioeng 80:46–52
Mills DB, Bar R, Kirwan DJ (1987) Effect of solids on oxygen transfer in agitated three-phase systems. AIChE J 33:1542–1549
Munoz JA, Gonzalez F, Ballester A, Blazquez ML (1993) Bioleaching of a Spanish uranium ore. FEMS Microbiol Rev 11:109–120
Olivera-Nappa A, Picioreanu C, Asenjo JA (2010) Non-homogeneous biofilm modeling applied to bioleaching processes. Biotechnol Bioeng 106(4):660–676
Rashidi A, Safdari J, Roosta-Azad R, Zokaei-Kadijani S (2012) Modeling of uranium bioleaching by Acidithiobacillus ferrooxidans. Ann Nucl Energy 43:13–18
Vilcaez J, Inoue C (2009) Mathematical modeling of thermophilic bioleaching of chalcopyrite. Miner Eng 22(11):951–960
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashidi, A., Roosta-Azad, R. & Safdari, S.J. Optimization of operating parameters and rate of uranium bioleaching from a low-grade ore. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 301, 341–350 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3164-4
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-014-3164-4