Abstract
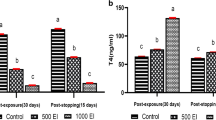
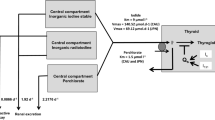
With the use of 125I and 131I radionuclides, we followed the effects of exogenous bromide and perchlorate ions on the metabolism of iodine and of thyroid hormone in the rat. The presumed thyrotoxic effects of bromide and perchlorate have been confirmed and quantified. Correct assay conditions for the radiometric determination of the enzyme activity of thyroid peroxidase (TPO) have been established. The use of the adapted radiometric assay revealed a divergent influence of bromide and perchlorate ions on the TPO activity in the rat thyroids. Excessive bromide exerted a biphasic effect, depending on the extent of bromide intake in the animals. In contrast, in all the rats that were administered with high amounts of perchlorate were found elevated TPO activities.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pavelka S (2009) Bromide interference with iodine metabolism: goitrogenic and whole-body effects of excessive inorganic bromide in the rat. (Chapter 61). In: Preedy VR, Burrow GN, Watson RR (eds) Comprehensive handbook of iodine. Nutritional, biochemical, pathological and therapeutic aspects. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 587–595
Pavelka S (2009) Iodine transfer through mother’s milk: the influence of bromide. (Chapter 20). In: Preedy VR, Burrow GN, Watson RR (eds) Comprehensive handbook of iodine. Nutritional, biochemical, pathological and therapeutic aspects. Academic Press, Oxford, pp 199–206
Pavelka S, Vobecký M, Babický A (2008) Halogen speciation in the rat thyroid: simultaneous determination of bromine and iodine by short-term INAA. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 278:575–579
Pavelka S (2004) Metabolism of bromide and its interference with the metabolism of iodine. Physiol Res 53(Suppl 1):S81–S90
Braverman LE, Utiger RD (eds) (1996) Werner and Ingbar’s the thyroid. A fundamental and clinical text, 7th edn. Lippincott-Raven Publishers, New York
Van Leeuwen FXR, Hanemaaijer R, Loeber JG (1988) The effect of sodium bromide on thyroid function. Arch Toxicol 12(Suppl):93–97
Taurog A, Dorris ML (1991) Peroxidase-catalyzed bromination of tyrosine. Arch Biochem Biophys 287:288–296
Nakashima T, Taurog A (1978) Improved assay procedures for thyroid peroxidase: application to normal and adenomatous human thyroid tissue. Clin Chim Acta 83:129
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Education of the Czech Republic (Research Project No. MSM0021622413), by the Academy of Sciences of the Czech Republic (Research Project No. AV0Z50110509), and by the Czech Science Foundation (GA CR Grant No. 304/08/0256).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pavelka, S. Radioiodine tracers as useful tools in studies of thyrotoxic effects of exogenous bromide and perchlorate ions. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 291, 405–408 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1191-y
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10967-011-1191-y