Abstract
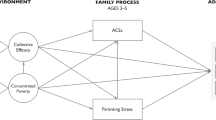
Youth who grow up in disadvantaged neighborhoods experience poorer health later in life, but little is known about the biological mechanisms underlying these effects and socioenvironmental factors that may protect youth from the biological embedding of neighborhood adversity. This study tests whether supportive and consistent parenting buffers associations between neighborhood disadvantage in early adolescence and epigenetic aging in adulthood. A community sample from Birmingham, Alabama, USA (N = 343; 57% female; 81% Black, 19% White) was assessed in early adolescence (T1; ages 11 and 13) and adulthood (T2; age 27). At T1, neighborhood poverty was derived from census data and neighborhood disorder was reported by caregivers. Both youth and parents reported on parental discipline and nurturance. At T2, methylation of salivary DNA was used to derive a mortality risk index and Hannum, Horvath, PhenoAge, and GrimAge epigenetic age estimators. Regression analyses revealed that neighborhood disadvantage was associated with accelerated epigenetic aging and/or mortality risk only when combined with high levels of harsh and inconsistent discipline and low child-reported parental nurturance. These findings identify epigenetic aging and mortality risk as relevant mechanisms through which neighborhood adversity experienced in adolescence may affect later health; they also point to the importance of supportive and consistent parenting for reducing the biological embedding of neighborhood adversity in early adolescence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abar, C. C., Jackson, K. M., Colby, S. M., & Barnett, N. P. (2015). Parent–child discrepancies in reports of parental monitoring and their relationship to adolescent alcohol-related behaviors. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 44, 1688–1701.
Aryee, M. J., Jaffe, A. E., Corrada-Bravo, H., Ladd-Acosta, C., Feinberg, A. P., Hansen, K. D., & Irizarry, R. A. (2014). Minfi: a flexible and comprehensive Bioconductor package for the analysis of Infinium DNA methylation microarrays. Bioinformatics, 30(10), 1363–1369.
Ashokan, A., Sivasubramanian, M., & Mitra, R. (2016). Seeding stress resilience through inoculation. Neural Plasticity, 2016, 4928081.
Barker, D. (2004). Developmental origins of adult health and disease. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 58(2), 114.
Barnes, G. M., & Windle, M. (1987). Family factors in adolescent alcohol and drug abuse. Pediatrician, 14(1-2), 13–18.
Beach, S. R., Lei, M. K., Brody, G. H., Dogan, M. V., & Philibert, R. A. (2015). Higher levels of protective parenting are associated with better young adult health: exploration of mediation through epigenetic influences on pro-inflammatory processes. Frontiers in Psychology, 6, 676.
Bibikova, M., Lin, Z., Zhou, L., Chudin, E., Garcia, E. W., Wu, B., Doucet, D., Thomas, N. J., Wang, Y., & Vollmer, E. (2006). High-throughput DNA methylation profiling using universal bead arrays. Genome Research, 16(3), 383–393.
Brody, G. H., Yu, T., Chen, E., & Miller, G. E. (2017). Family-centered prevention ameliorates the association between adverse childhood experiences and prediabetes status in young black adults. Preventive Medicine, 100, 117–122.
Brody, G. H., Yu, T., Chen, E., Beach, S. R., & Miller, G. E. (2016). Family‐centered prevention ameliorates the longitudinal association between risky family processes and epigenetic aging. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry and Allied Disciplines, 57(5), 566–574.
Carroll, J. E., Gruenewald, T. L., Taylor, S. E., Janicki-Deverts, D., Matthews, K. A., & Seeman, T. E. (2013). Childhood abuse, parental warmth, and adult multisystem biological risk in the Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults study. Proceedings of the National Academy Science, 110(42), 17149–17153.
Carver, A., Timperio, A., & Crawford, D. (2008). Playing it safe: the influence of neighbourhood safety on children’s physical activity—A review. Health & place, 14(2), 217–227.
Cohen, S., Chiang, J. J., Janicki-Deverts, D., & Miller, G. E. (2020). Good relationships with parents during childhood as buffers of the association between childhood disadvantage and adult susceptibility to the common cold. Psychosomatic Medicine, 82(6), 538–547.
Crimmins, E. M., Thyagarajan, B., Levine, M. E., Weir, D. R., & Faul, J. (2021). Associations of age, sex, race/ethnicity, and education with 13 epigenetic clocks in a nationally representative US sample: the Health and Retirement Study. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 76(6), 1117–1123.
Daskalakis, N. P., Bagot, R. C., Parker, K. J., Vinkers, C. H., & de Kloet, E. R. (2013). The three-hit concept of vulnerability and resilience: toward understanding adaptation to early-life adversity outcome. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 38(9), 1858–1873.
Dhingra, R., Kwee, L. C., Diaz-Sanchez, D., Devlin, R. B., Cascio, W., Hauser, E. R., Gregory, S., Shah, S., Kraus, W. E., & Olden, K. (2019). Evaluating DNA methylation age on the illumina MethylationEPIC bead chip. PloS One, 14(4), e0207834.
Duan, R., Fu, Q., Sun, Y., & Li, Q. (2022). Epigenetic clock: a promising biomarker and practical tool in aging. Ageing Research Reviews, 81, 101743.
East, P., Delker, E., Blanco, E., Burrows, R., Lozoff, B., & Gahagan, S. (2019). Home and family environment related to development of obesity: A 21-year longitudinal study. Child Obes, 15(3), 156–166.
Fahy, G. M., Brooke, R. T., Watson, J. P., Good, Z., Vasanawala, S. S., Maecker, H., Leipold, M. D., Lin, D. T., Kobor, M. S., & Horvath, S. (2019). Reversal of epigenetic aging and immunosenescent trends in humans. Aging Cell, 18(6), e13028.
Finkelhor, D., Turner, H., Hamby, S. L., & Ormrod, R. (2011). Polyvictimization: Children’s Exposure to Multiple Types of Violence, Crime, and Abuse. Washington, DC: Office of Juvenile Justice and Delinquency Prevention, US Department of Justice.
Fiorito, G., Polidoro, S., Dugue, P. A., Kivimaki, M., Ponzi, E., Matullo, G., Guarrera, S., Assumma, M. B., Georgiadis, P., Kyrtopoulos, S. A., Krogh, V., Palli, D., Panico, S., Sacerdote, C., Tumino, R., Chadeau-Hyam, M., Stringhini, S., Severi, G., Hodge, A. M., & Vineis, P. (2017). Social adversity and epigenetic aging: a multi-cohort study on socioeconomic differences in peripheral blood DNA methylation. Scientific Reports, 7(1), 16266 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-16391-5.
Garthe, R. C., Gorman‐Smith, D., Gregory, J., & Schoeny, E. M. (2018). Neighborhood concentrated disadvantage and dating violence among urban adolescents: the mediating role of neighborhood social processes. American Journal of Community Psychology, 61(3-4), 310–320.
Ge, X., Conger, R. D., Lorenz, F. O., & Simons, R. L. (1994). Parents’ stressful life events and adolescent depressed mood. Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 35, 28–44.
Godoy, L. C., Frankfurter, C., Cooper, M., Lay, C., Maunder, R., & Farkouh, M. E. (2021). Association of adverse childhood experiences with cardiovascular disease later in life: a review. JAMA Cardiology, 6(2), 228–235.
Goldner, J., Peters, T. L., Richards, M. H., & Pearce, S. (2011). Exposure to community violence and protective and risky contexts among low income urban African American adolescents: a prospective study. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 40(2), 174–186.
Graham, J. W., Cumsille, P. E., & Shevock, A. E. (2013). Methods for handling missing data. In W. F. V. J. A. Schinka, I. B. Weiner (Ed.), Handbook of psychology: research methods in psychology (pp. 109–141). John Wiley & Sons.
Hannum, G., Guinney, J., Zhao, L., Zhang, L., Hughes, G., Sadda, S., Klotzle, B., Bibikova, M., Fan, J. B., Gao, Y., Deconde, R., Chen, M., Rajapakse, I., Friend, S., Ideker, T., & Zhang, K. (2013). Genome-wide methylation profiles reveal quantitative views of human aging rates. Molecular Cell, 49(2), 359–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2012.10.016.
Hanson, M. A., & Gluckman, P. (2014). Early developmental conditioning of later health and disease: physiology or pathophysiology? Physiological Reviews, 94(4), 1027–1076.
Hao, G., Youssef, N. A., Davis, C. L., & Su, S. (2018). The role of DNA methylation in the association between childhood adversity and cardiometabolic disease. International Journal of Cardiology, 255, 168–174.
Hayes, A. F., & Rockwood, N. J. (2017). Regression-based statistical mediation and moderation analysis in clinical research: observations, recommendations, and implementation. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 98, 39–57.
Horvath, S. (2013). DNA methylation age of human tissues and cell types. Genome Biology, 14(10), R115 https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2013-14-10-r115.
Hu, Z., Kaminga, A. C., Yang, J., Liu, J., & Xu, H. (2021). Adverse childhood experiences and risk of cancer during adulthood: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Child Abuse and Neglect, 117, 105088.
Huan, T., Nguyen, S., Colicino, E., Ochoa‐Rosales, C., Hill, W. D., Brody, J. A., Soerensen, M., Zhang, Y., Baldassari, A., & Elhadad, M. A. (2022). Integrative analysis of clinical and epigenetic biomarkers of mortality. Aging Cell, 21(6), e13608.
Janusek, L. W., Tell, D., Gaylord-Harden, N., & Mathews, H. L. (2017). Relationship of childhood adversity and neighborhood violence to a proinflammatory phenotype in emerging adult African American men: an epigenetic link. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity, 60, 126–135.
Jilani, M. H., Javed, Z., Yahya, T., Valero-Elizondo, J., Khan, S. U., Kash, B., Blankstein, R., Virani, S. S., Blaha, M. J., & Dubey, P. (2021). Social determinants of health and cardiovascular disease: current state and future directions towards healthcare equity. Current atherosclerosis reports, 23, 1–11.
Jocson, R. M., & McLoyd, V. C. (2015). Neighborhood and housing disorder, parenting, and youth adjustment in low-income urban families. American Journal of Community Psychology, 55(3-4), 304–313.
Jose, R., Hipp, J. R., Butts, C. T., Wang, C., & Lakon, C. M. (2021). A multi-contextual examination of non-school friendships and their impact on adolescent deviance and alcohol use. PloS One, 16(2), e0245837.
Kivimäki, M., Vahtera, J., Tabák, A. G., Halonen, J. I., Vineis, P., Pentti, J., Pahkala, K., Rovio, S., Viikari, J., & Kähönen, M. (2018). Neighbourhood socioeconomic disadvantage, risk factors, and diabetes from childhood to middle age in the Young Finns Study: a cohort study. The Lancet Public Health, 3(8), e365–e373.
Lawrence, K. G., Kresovich, J. K., O’Brien, K. M., Hoang, T. T., Xu, Z., Taylor, J. A., & Sandler, D. P. (2020). Association of neighborhood deprivation with epigenetic aging using 4 clock metrics. JAMA network open, 3(11), e2024329.
Lei, M. K., & Beach, S. R. (2020). Can we uncouple neighborhood disadvantage and delinquent behaviors? An experimental test of family resilience guided by the social disorganization theory of delinquent behaviors. Family Process, 59(4), 1801–1817.
Lei, M.-K., Simons, R. L., Beach, S. R., & Philibert, R. A. (2019). Neighborhood disadvantage and biological aging: using marginal structural models to assess the link between neighborhood census variables and epigenetic aging. The Journals of Gerontology: Series B, 74(7), e50–e59.
Lei, M.-K., Berg, M. T., Simons, R. L., & Beach, S. R. (2022). Neighborhood structural disadvantage and biological aging in a sample of Black middle age and young adults. Social Science and Medicine, 293, 114654.
Levine, M. E., Lu, A. T., Quach, A., Chen, B. H., Assimes, T. L., Bandinelli, S., Hou, L., Baccarelli, A. A., Stewart, J. D., & Li, Y. (2018). An epigenetic biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging, 10(4), 573.
Levine, M. E., Lu, A. T., Quach, A., Chen, B. H., Assimes, T. L., Bandinelli, S., Hou, L., Baccarelli, A. A., Stewart, J. D., Li, Y., Whitsel, E. A., Wilson, J. G., Reiner, A. P., Aviv, A., Lohman, K., Liu, Y., Ferrucci, L., & Horvath, S. (2018). An epigenetic biomarker of aging for lifespan and healthspan. Aging, 10(4), 573–591. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101414.
Liang, A., & Gomaa, N. (2023). Social capital associates with cognitive health, oral health and epigenetic age deceleration: a cross-sectional analysis of the Canadian longitudinal study on aging (CLSA). medRxiv, 2023, 2006.23292314 2007.
De Los Reyes, A., & Kazdin, A. E. (2005). Informant discrepancies in the assessment of childhood psychopathology: a critical review, theoretical framework, and recommendations for further study. Psychological Bulletin, 131(4), 483.
Lu, A. T., Quach, A., Wilson, J. G., Reiner, A. P., Aviv, A., Raj, K., Hou, L., Baccarelli, A. A., Li, Y., & Stewart, J. D. (2019). DNA methylation GrimAge strongly predicts lifespan and healthspan. Aging, 11(2), 303.
Marini, S., Davis, K. A., Soare, T. W., Zhu, Y., Suderman, M. J., Simpkin, A. J., Smith, A. D., Wolf, E. J., Relton, C. L., & Dunn, E. C. (2020). Adversity exposure during sensitive periods predicts accelerated epigenetic aging in children. Psychoneuroendocrinology, 113, 104484.
Martin, C. L., Ward-Caviness, C. K., Dhingra, R., Zikry, T. M., Galea, S., Wildman, D. E., Koenen, K. C., Uddin, M., & Aiello, A. E. (2021). Neighborhood environment, social cohesion, and epigenetic aging. Aging, 13(6), 7883.
Matjasko, J. L., Vivolo-Kantor, A. M., Henry, D. B., Gorman-Smith, D., Schoeny, M. E., & Project, T. M. V. P. (2013). The relationship between a family-focused preventive intervention, parenting practices, and exposure to violence during the transition to adolescence: testing a mediational model. Journal of Aggression, Maltreatment & Trauma, 22(1), 45–66.
Mikeska, T., & Craig, J. M. (2014). DNA methylation biomarkers: cancer and beyond. Genes, 5(3), 821–864.
Miller, G. E., Brody, G. H., Yu, T., & Chen, E. (2014). A family-oriented psychosocial intervention reduces inflammation in low-SES African American youth. Proceedings of the National Academy Science, 111(31), 11287–11292.
Mrug, S., & Windle, M. (2009). Mediators of neighborhood influences on externalizing behavior in preadolescent children. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 265–280.
Mrug, S., Loosier, P. S., & Windle, M. (2008). Violence exposure across multiple contexts: individual and joint effects on adjustment. Am J Orthopsychiatry, 78(1), 70–84. https://doi.org/10.1037/0002-9432.78.1.70.
Mrug, S., Barker-Kamps, M., Orihuela, C. A., Patki, A., & Tiwari, H. K. (2022). Childhood neighborhood disadvantage, parenting, and adult health. American Journal of Preventive Medicine, 63(1), S28–S36.
Muka, T., Koromani, F., Portilla, E., O’Connor, A., Bramer, W. M., Troup, J., Chowdhury, R., Dehghan, A., & Franco, O. H. (2016). The role of epigenetic modifications in cardiovascular disease: a systematic review. International Journal of Cardiology, 212, 174–183.
Oblak, L., van der Zaag, J., Higgins-Chen, A. T., Levine, M. E., & Boks, M. P. (2021). A systematic review of biological, social and environmental factors associated with epigenetic clock acceleration. Ageing research reviews, 69, 101348.
Ogden, C. L., Carroll, M. D., Kit, B. K., & Flegal, K. M. (2012). Prevalence of obesity among adults: United States. NCHS Data Brief, 2013, 1–8.
Pager, D., & Shepherd, H. (2008). The sociology of discrimination: Racial discrimination in employment, housing, credit, and consumer markets. Annual Review of Sociology, 34, 181–209.
Parker, K. J., & Maestripieri, D. (2011). Identifying key features of early stressful experiences that produce stress vulnerability and resilience in primates. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 35(7), 1466–1483.
Paulhus, D. L., Robins, R. W., Trzesniewski, K. H., & Tracy, J. L. (2004). Two replicable suppressor situations in personality research. Multivariate Behavioral Research, 39(2), 303–328.
Perkins, D. D., Florin, P., Rich, R. C., Wandersman, A., & Chavis, D. M. (1990). Participation and the social and physical environment of residential blocks: crime and community context. American Journal of Community Psychology, 18(1), 83–115.
Peterson, R. D., & Krivo, L. J. (2010). Divergent social worlds: neighborhood crime and the racial-spatial divide. Russell Sage Foundation.
Quiñones, A. R., Botoseneanu, A., Markwardt, S., Nagel, C. L., Newsom, J. T., Dorr, D. A., & Allore, H. G. (2019). Racial/ethnic differences in multimorbidity development and chronic disease accumulation for middle-aged adults. PloS One, 14(6), e0218462.
Quiroga, A., López-Rodríguez, L., & Willis, G. B. (2017). Parental support buffering the effect of violence on adolescents’ depression: gender differences. J Interpers Violence, 32(7), 1068–1086.
Raffington, L., Belsky, D. W., Kothari, M., Malanchini, M., Tucker-Drob, E. M., & Harden, K. P. (2021). Socioeconomic disadvantage and the pace of biological aging in children. Pediatrics, 147(6) e2020024406.
Rakesh, D., Seguin, C., Zalesky, A., Cropley, V., & Whittle, S. (2021). Associations between neighborhood disadvantage, resting-state functional connectivity, and behavior in the adolescent brain cognitive development study: the moderating role of positive family and school environments. Biological Psychiatry: Cognitive Neuroscience and Neuroimaging, 6(9), 877–886.
Reuben, A., Sugden, K., Arseneault, L., Corcoran, D. L., Danese, A., Fisher, H. L., Moffitt, T. E., Newbury, J. B., Odgers, C., & Prinz, J. (2020). Association of neighborhood disadvantage in childhood with DNA methylation in young adulthood. JAMA Network Open, 3(6), e206095.
Romero, C. X., Romero, T. E., Shlay, J. C., Ogden, L. G., & Dabelea, D. (2012). Changing trends in the prevalence and disparities of obesity and other cardiovascular disease risk factors in three racial/ethnic groups of USA adults. Advances in Preventive Medicine, 2012, 172423.
Saini, G., Ogden, A., McCullough, L. E., Torres, M., Rida, P., & Aneja, R. (2019). Disadvantaged neighborhoods and racial disparity in breast cancer outcomes: the biological link. Cancer Causes and Control, 30(7), 677–686.
Salameh, Y., Bejaoui, Y., & El Hajj, N. (2020). DNA methylation biomarkers in aging and age-related diseases. Frontiers Genetics, 11, 171.
Schulz, A. J., Mentz, G., Lachance, L., Zenk, S. N., Johnson, J., Stokes, C., & Mandell, R. (2013). Do observed or perceived characteristics of the neighborhood environment mediate associations between neighborhood poverty and cumulative biological risk? Health Place, 24, 147–156.
Shin, S. H., Wang, X., Yoon, S. H., Cage, J. L., Kobulsky, J. M., & Montemayor, B. N. (2019). Childhood maltreatment and alcohol-related problems in young adulthood: the protective role of parental warmth. Child Abuse and Neglect, 98, 104238.
Simpson, D. J., & Chandra, T. (2021). Epigenetic age prediction. Aging Cell, 20(9), e13452.
Stein, B. D., Jaycox, L. H., Kataoka, S., Rhodes, H. J., & Vestal, K. D. (2003). Prevalence of child and adolescent exposure to community violence. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 6(4), 247–264.
Thompson, T. M., Sharfi, D., Lee, M., Yrigollen, C. M., Naumova, O. Y., & Grigorenko, E. L. (2013). Comparison of whole-genome DNA methylation patterns in whole blood, saliva, and lymphoblastoid cell lines. Behavior Genetics, 43(2), 168–176.
Thornton, R. L., Glover, C. M., Cené, C. W., Glik, D. C., Henderson, J. A., & Williams, D. R. (2016). Evaluating strategies for reducing health disparities by addressing the social determinants of health. Health Affairs, 35(8), 1416–1423.
Unternaehrer, E., Meier, M., Bouvette-Turcot, A.-A., & Dass, S. A. H. (2021). Long-term epigenetic effects of parental caregiving. In Developmental Human Behavioral Epigenetics (pp. 105–117). Elsevier.
Ward-Caviness, C. K., Pu, S., Martin, C. L., Galea, S., Uddin, M., Wildman, D. E., Koenen, K., & Aiello, A. E. (2020). Epigenetic predictors of all-cause mortality are associated with objective measures of neighborhood disadvantage in an urban population. Clinical Epigenetics, 12(1), 1–10.
Weis, R., & Lovejoy, M. C. (2002). Information processing in everyday life: emotion-congruent bias in mothers’ reports of parent-child interactions. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 83(1), 216.
Whittle, S., Vijayakumar, N., Simmons, J. G., Dennison, M., Schwartz, O., Pantelis, C., Sheeber, L., Byrne, M. L., & Allen, N. B. (2017). Role of positive parenting in the association between neighborhood social disadvantage and brain development across adolescence. JAMA Psychiatry, 74(8), 824–832.
Williams, D. R., Lawrence, J. A., & Davis, B. A. (2019). Racism and health: evidence and needed research. Annual Review of Public Health, 40, 105–125.
Wolff, K. T., Cuevas, C., Intravia, J., Baglivio, M. T., & Epps, N. (2018). The effects of neighborhood context on exposure to adverse childhood experiences (ACE) among adolescents involved in the juvenile justice system: Latent classes and contextual effects. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 47(11), 2279–2300.
Xiao, Y., Romanelli, M., Vélez-Grau, C., & Lindsey, M. A. (2021). Unpacking racial/ethnic differences in the associations between neighborhood disadvantage and academic achievement: Mediation of future orientation and moderation of parental support. Journal of Youth and Adolescence, 50, 103–125.
York Cornwell, E., & Behler, R. L. (2015). Urbanism, neighborhood context, and social networks. City & Community, 14(3), 311–335.
Zannas, A. S., Arloth, J., Carrillo-Roa, T., Iurato, S., Röh, S., Ressler, K. J., Nemeroff, C. B., Smith, A. K., Bradley, B., & Heim, C. (2015). Lifetime stress accelerates epigenetic aging in an urban, African American cohort: relevance of glucocorticoid signaling. Genome Biology, 16(1), 1–12.
Zhang, Y., Wilson, R., Heiss, J., Breitling, L. P., Saum, K.-U., Schöttker, B., Holleczek, B., Waldenberger, M., Peters, A., & Brenner, H. (2017). DNA methylation signatures in peripheral blood strongly predict all-cause mortality. Nature Communications, 8(1), 1–11.
Funding
This project was supported by the National Institute on Minority Health and Health Disparities through a grant U54MD000502 and by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention through a grant R49-CCR418569. The study sponsors had no role in the study design; collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; writing the report; and submission for publication.
Data Sharing DeclarationThe datasets generated and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S.M. conceived and designed the study, analyzed data, and drafted the manuscript; M.B.K. coordinated the study, analyzed data, and drafted manuscript sections; M.G. participated in coordination of the study, data analyses, and manuscript revisions; A.P. participated in data acquisition and data analyses; and H.K.T. participated in study design and data analyses. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and was performed in accordance with the ethical standards described in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Informed Consent
Written informed consent was obtained from adult participants and legal guardians. Assent was obtained from adolescents.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Mrug, S., Barker-Kamps, M., Goering, M. et al. Neighborhood Disadvantage and Parenting in Early Adolescence Predict Epigenetic Aging and Mortality Risk in Adulthood. J. Youth Adolescence 53, 258–272 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01863-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-023-01863-x