Abstract
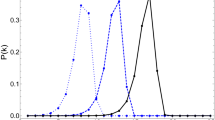
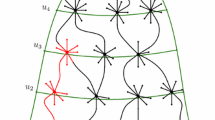
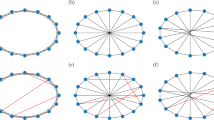
We analyse the so-called small-world network model (originally devised by Strogatz and Watts), treating it, among other things, as a case study of non-linear coupled difference or differential equations. We derive a system of evolution equations containing more of the previously neglected (possibly relevant) non-linear terms. As an exact solution of this entangled system of equations is out of question we develop a (as we think, promising) method of enclosing the “exact” solutions for the expected quantities by upper and lower bounds, which represent solutions of a slightly simpler system of differential equation. Furthermore we discuss the relation between difference and differential equations and scrutinize the limits of the spreading idea for random graphs. We then show that there exists in fact a “broad” (with respect to scaling exponents) crossover zone, smoothly interpolating between linear and logarithmic scaling of the diameter or average distance. We are able to corroborate earlier findings in certain regions of phase or parameter space (as e.g. the finite size scaling ansatz) but find also deviations for other choices of the parameters. Our analysis is supplemented by a variety of numerical calculations, which, among other things, quantify the effect of various approximations being made. With the help of our analytical results we manage to calculate another important network characteristic, the (fractal) dimension, and provide numerical values for the case of the small-world network.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. H. Strogatz, Exploring Complex Networks, Nature 410:268, (2001).
D. J. Watts, Small Worlds, The Dynamics of Networks between Order and Randomness, Princt. Univ. Pr. Princeton 1999.
D. J. Watts and S. H. Strogatz, Collective Dynamics of Small World Networks, Nature 393:440, (1998).
R. Albert and A.-L. Barabasi, Statistical Mechanics of Complex Networks, Rev. Mod. Phys. 74:47, (2002). cond-mat/0106096
A.-L. Barabasi and E. Bonabeau, Scale-Free Networks, Sci. Am. May 2003 p. 50.
M. E. J. Newman, Models of the Small World, J. Stat. Phys. 101:819 (2000).
M. E. J. Newman, The Structure and Function of Complex Networks, SIAM Review 45:167 (2003).
A. Barrat and M. Weigt, On the Properties of Small-World Network Models, Eur. Phys. J. B 13:547 (2000).
M. Requardt, A geometric renormalization group in discrete quantum space-time, J. Math. Phys. 44:5588,(2003).
M. Requardt, Scale Free Small World Networks and the Structure of Quantum Space-Time, gr-qc/0308089.
M. Barthélémy and L. A. Nunes Amaral, Small-world networks: Evidence for a crossover picture, Phys. Rev. Lett. 82:3180 (1999). cond-mat/9903108, and A. Barrat, Comment on ‘Small-World networks: Evidence for a crossover picture,’ cond-mat/9903323.
M. E. J. Newman and D. J. Watts, Renormalization Group Analysis of the Small World Network Model, Phys. Lett. A 263:341 (1999). cond-mat/9903357
M. E. J. Newman, C. Moore and D. J. Watts, Mean-field solution of the small-world network model, PRL 84:3201 (2000). cond-mat/9909165
A. D. Barbour and G. Reinert, Small worlds, Random Structures & Algorithms 19:54 (2001). cond-mat/0006001
B. Bollobas, Random Graphs, Acad. Pr. N. Y. 1985.
B. Bollobas, Modern Graph Theory, Springer, N. Y. 1998.
F. Buckley and F. Harary, Distances in Graphs, Addison-Wesley, N. Y. 1990.
N. E. Noerlund, Vorlesungen ueber Differenzenrechnung, Springer, Berlin 1924.
H. Meschkowski, Differenzengleichungen, Vandenhoeck & Ruprecht, Goettingen 1959.
E. A. Coddington and N. Levinson: Theory of Ordinary Differential Equations, Tata McGraw-Hill Publ., New Dehli 1972.
A. Renyi, Wahrscheinlichkeitsrechnung, Deutscher Verlag Wissenschaften, Berlin 1979.
W. Feller, An Introduction to Probability Theory, Vol. I, Wiley, New York 1968.
C. M. Bender and S. A. Orszag, Advanced Mathematical Methods for Scientists and Engineers, McGraw-Hill, N. Y. 1978.
T. Nowotny and M. Requardt, Dimension Theory of graphs and networks, J. Phys. A. Math. Gen. 31:2447–2463 (1998).
R. J. Baxter, Exactly Solved Models in Statistical Mechanics, Academic. Pr. N.Y. 1982.
D. Dhar, Lattices of Effectively Nonintegral Dimensionality, J. Math. Phys. 18:577 (1977).
Th. Filk, Equivalence of Massive Propagator Distance and Mathematical Distance on Graphs, Mod. Phys. Lett. A 7:2637 (1992).
R. T. Scalettar, Critical Properties of an Ising Model with Dilute Long Range Interactions, Physica A 170:282 (1991).
G. Csányi and B. Szendröi, Fractal–small-world dichotomy in real-world networks, Phys. Rev. E 70:016122 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lochmann, A., Requardt, M. An Analysis of the Transition Zone Between the Various Scaling Regimes in the Small-World Model. J Stat Phys 122, 255–278 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-005-8083-x
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10955-005-8083-x